Brand Name
Pyrazinamide
View Brand InformationFDA approval date: July 27, 2020
Classification: Antimycobacterial
Form: Tablet
What is Pyrazinamide?
Pyrazinamide is indicated for the initial treatment of active tuberculosis in adults and children when combined with other antituberculous agents. It is also indicated after treatment failure with other primary drugs in any form of active tuberculosis. Pyrazinamide should only be used in conjunction with other effective antituberculous agents. *See recommendations of Center for Disease Control and American Thoracic Society for complete regimen and dosage recommendations. 4.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Pyrazinamide (Pyrazinamide)
1DESCRIPTION:
Pyrazinamide, USP the pyrazine analogue of nicotinamide, is an antituberculous agent. It is a white crystalline powder, stable at room temperature, and sparingly soluble in water. Pyrazinamide USP has the following structural formula:
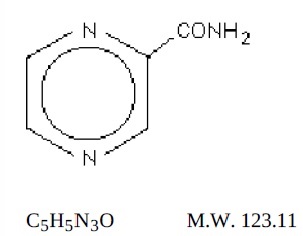
Each pyrazinamide tablet, USP for oral administration contains 500 mg of pyrazinamide and the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, povidone, sodium starch glycolate and talc.
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Pyrazinamide is well absorbed from the GI tract and attains peak plasma concentrations within 2 hours.
The half-life (t
Approximately 70% of an oral dose is excreted in the urine, mainly by glomerular filtration within 24 hours.
Pyrazinamide may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal against
3INDICATIONS & USAGE:
Pyrazinamide is indicated for the initial treatment of active tuberculosis in adults and children when combined with other antituberculous agents. (The current recommendation of the CDC for drug- susceptible disease is to use a six-month regimen for initial treatment of active tuberculosis, consisting of isoniazid, rifampin and pyrazinamide given for 2 months, followed by isoniazid and rifampin for 4 months.*
(Patients with drug-resistant disease should be treated with regimens individualized to their situation. Pyrazinamide frequently will be an important component of such therapy.)
(In patients with concomitant HIV infection, the physician should be aware of current recommendation of CDC. It is possible these patients may require a longer course of treatment).
It is also indicated after treatment failure with other primary drugs in any form of active tuberculosis.
Pyrazinamide should only be used in conjunction with other effective antituberculous agents.
*See recommendations of Center for Disease Control (CDC) and American Thoracic Society for complete regimen and dosage recommendations.
4CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Pyrazinamide is contraindicated in persons:
5WARNINGS:
Patients started on pyrazinamide should have baseline serum uric acid and liver function determinations.
Pyrazinamide should be discontinued and not be resumed if signs of hepatocellular damage or hyperuricemia accompanied by an acute gouty arthritis appear.
6ADVERSE REACTIONS:
General:
Fever, porphyria and dysuria have rarely been reported. Gout (see PRECAUTIONS:).
Fever, porphyria and dysuria have rarely been reported. Gout (see PRECAUTIONS:).
Gastrointestinal:
The principal adverse effect is a hepatic reaction (see WARNINGS:). Hepatotoxicity appears to be dose related, and may appear at any time during therapy. GI disturbances including nausea, vomiting and anorexia have also been reported.
The principal adverse effect is a hepatic reaction (see WARNINGS:). Hepatotoxicity appears to be dose related, and may appear at any time during therapy. GI disturbances including nausea, vomiting and anorexia have also been reported.
Hematologic and Lymphatic:
Thrombocytopenia and sideroblastic anemia with erythroid hyperplasia, vacuolation of erythrocytes and increased serum iron concentration have occurred rarely with this drug. Adverse effects on blood clotting mechanisms have also been rarely reported.
Thrombocytopenia and sideroblastic anemia with erythroid hyperplasia, vacuolation of erythrocytes and increased serum iron concentration have occurred rarely with this drug. Adverse effects on blood clotting mechanisms have also been rarely reported.
Other:
Mild arthralgia and myalgia have been reported frequently. Hypersensitivity reactions including rashes, urticaria, and pruritis have been reported. Fever, acne, photosensitivity, porphyria, dysuria and interstitial nephritis have been reported rarely.
Mild arthralgia and myalgia have been reported frequently. Hypersensitivity reactions including rashes, urticaria, and pruritis have been reported. Fever, acne, photosensitivity, porphyria, dysuria and interstitial nephritis have been reported rarely.
7OVERDOSAGE:
Overdosage experience is limited. In one case report of overdose, abnormal liver function tests developed. These spontaneously reverted to normal when the drug was stopped. Clinical monitoring and supportive therapy should be employed. Pyrazinamide is dialyzable.
8DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION:
Pyrazinamide should always be administered with other effective antituberculous drugs. It is administered for the initial 2 months of a 6-month or longer treatment regimen for drug-susceptible patients. Patients who are known or suspected to have drug-resistant disease should be treated with regimens individualized to their situation. Pyrazinamide frequently will be an important component of such therapy.
Definition of abbreviations: PO = perorally; IM = intramuscularly.
* Doses based on weight should be adjusted as weight changes.
9HOW SUPPLIED
Pyrazinamide Tablets, USP 500 mg are round, white to off white uncoated, scored tablets with notches, debossed "F" above the score and "43" below the score and plain on other side.
Tablets are supplied in the following strengths and package configurations:
Store at 20° to 25° C (68° F to 77° F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30° C (59° F to 86° F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Manufactured for:
Manufactured by:
Revised: December 2022
10REFERENCES
1.Drug Information, American Hospital Formulary Service. American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Bethesda, Md. 1991.
11PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Pyrazinamide Tablets USP 500mg

Pyrazinamide Tablets USP 500mg

Pyrazinamide Tablets USP 500mg
Pyrazinamide Tablets USP 500mg