Verquvo
What is Verquvo (Vericiguat)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This study aims to compare the efficacy of vericiguat versus placebo on change in n-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP) from baseline to Week 16 of the Base Period. The primary hypothesis is that vericiguat is superior to placebo in reducing NT-proBNP at Week 16 of the Base Period.
Summary: This is a randomised controlled trial to determine the effectiveness of Vericiguat to improve stress myocardial blood flow (MBF) and myocardial perfusion reserve as measured by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging.
Summary: This is an observational study in which only data are collected from participants receiving their usual treatment. The study is done in people with chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). HFrEF is a long-term condition in which the heart does not pump blood as well as it should. Blood and fluid may collect in the lungs, blood vessels, and tissues causing shortness of breath o...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
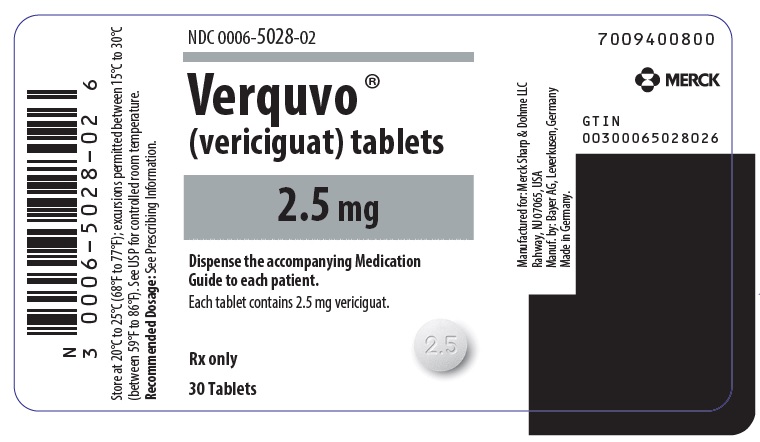
- VERQUVO 2.5 mg (vericiguat 2.5 mg) are round, biconvex, white film-coated tablets debossed with “2.5” on one side and “VC” on the other side.
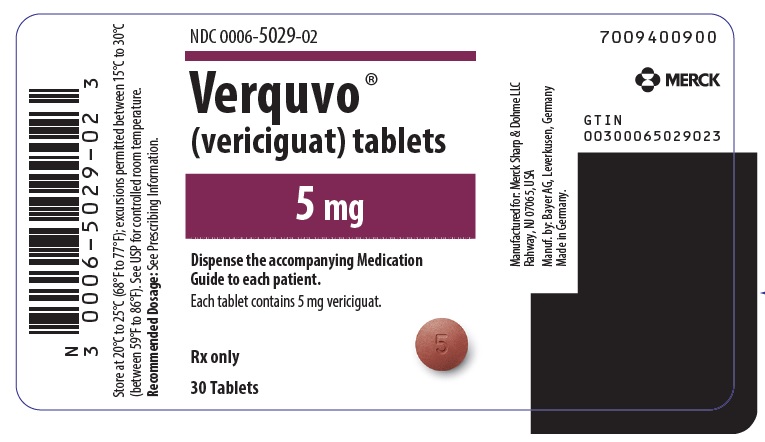
- VERQUVO 5 mg (vericiguat 5 mg) are round, biconvex, brown-red film-coated tablets debossed with “5” on one side and “VC” on the other side.
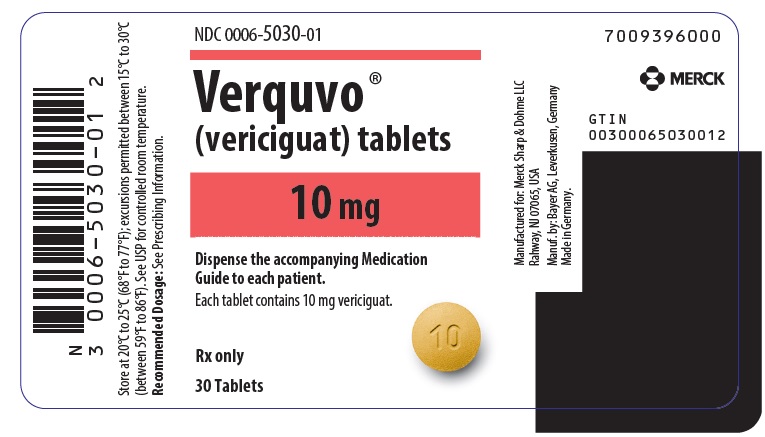
- VERQUVO 10 mg (vericiguat 10 mg) are round, biconvex, yellow-orange film-coated tablets debossed with “10” on one side and “VC” on the other side.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with VERQUVO and for one month after the final dose [see
Advise women who are exposed to VERQUVO during pregnancy to report their pregnancy to their healthcare provider. Health care providers should report any prenatal exposure to VERQUVO by calling 1-877-888-4231 or at https://pregnancyreporting.verquvo-us.com. [See
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with VERQUVO [see .