Brand Name
Roctavian
Generic Name
Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec-Rvox
View Brand Information FDA approval date: June 29, 2023
Form: Injection
What is Roctavian (Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec-Rvox)?
ROCTAVIAN is an adeno-associated virus vector-based gene therapy indicated for the treatment of adults with severe hemophilia A without antibodies to adeno-associated virus serotype 5 detected by an FDA-approved test. ROCTAVIAN is an adeno-associated virus vector-based gene therapy indicated for the treatment of adults with severe hemophilia A without pre-existing antibodies to adeno-associated virus serotype 5 detected by an FDA-approved test.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
ROCTAVIAN (valoctocogene roxaparvovec-rvox)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ROCTAVIAN is an adeno-associated virus vector-based gene therapy indicated for the treatment of adults with severe hemophilia A (congenital factor VIII deficiency with factor VIII activity < 1 IU/dL) without antibodies to adeno-associated virus serotype 5 (AAV5) detected by an FDA-approved test.
2DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For one-time single-dose intravenous use only.
Treatment with ROCTAVIAN should be under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of hemophilia and/or bleeding disorders.
2.1Dose
The recommended dose of ROCTAVIAN is 6 × 10
2.2Administration
- Administer ROCTAVIAN in a setting where personnel and equipment are immediately available to treat infusion-related reactions
- Infuse the suspension through a suitable peripheral vein, using an infusion catheter with in-line filter and a programmable syringe pump.
- Start the infusion at a rate of 1 mL/min. If tolerated, the rate may be increased every 30 minutes by 1 mL/min up to a maximum rate of 4 mL/min. The infusion time depends on infusion volume, rate and patient response and can be, for example, 2 to 5 hours or longer for a patient weighing 100 kg.
- In the event of an infusion-related reaction during administration
- DO NOT administer ROCTAVIAN as an intravenous push or bolus.
- DO NOT infuse ROCTAVIAN in the same intravenous line with any other products.
- DO NOT use a central line or port.
- To ensure the patient receives the complete dose, after the content of the last ROCTAVIAN-containing syringe is infused, flush the infusion line with a sufficient volume of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, through the same tubing and filter, and at the same infusion rate.
- Maintain venous access during the subsequent observation period
3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ROCTAVIAN is a clear, colorless to pale yellow suspension for intravenous infusion containing 2 × 10
ROCTAVIAN is provided in vials containing an extractable volume of not less than 8 mL.
Dose volume is based on body weight, with a recommended dose of 6 × 10
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
Administration of ROCTAVIAN is contraindicated in:
- patients with active infections, either acute (such as acute respiratory infections or acute hepatitis) or uncontrolled chronic (such as chronic active hepatitis B)
- patients with known significant hepatic fibrosis (stage 3 or 4 on the Batts-Ludwig scale or equivalent), or cirrhosis
- patients with known hypersensitivity to mannitol.
5ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are also discussed in other sections of the label:
- Infusion-Related Reactions
- Hepatotoxicity
5.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described in this section reflect the exposure of 134 adult patients with severe hemophilia A (defined as residual factor VIII activity ≤ 1 IU/dL) to a single dose of 6 × 10
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 5%) to ROCTAVIAN were nausea, fatigue, headache, infusion-related reactions, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
The most common laboratory abnormalities (≥ 10%) to ROCTAVIAN were ALT, AST, LDH, CPK, factor VIII activity levels, GGT, and bilirubin > ULN.
Non-laboratory adverse reactions (≥ 5%) to ROCTAVIAN are listed in Table 5. There were 6 serious adverse reactions related to ROCTAVIAN treatment including ALT elevation, presyncope, maculopapular rash, anaphylaxis, and hypersensitivity reaction.
Table 6 lists laboratory abnormalities in patients treated with ROCTAVIAN.
Twelve (9%), 9 (7%) and 1 (1%) of patients experienced > 5-20 × ULN ALT, AST and GGT elevations, respectively. Seven (5%) patients and 5 (4%) patients experienced > 5-10 × ULN and > 10 × ULN CPK increases, respectively.
Infusion-related reactions were observed in 9 patients (7%), including hypersensitivity reactions (4%) and anaphylaxis (1%), and have occurred during and/or following ROCTAVIAN administration.
Hepatotoxicity as defined by ALT ≥ 1.5 × baseline or ALT > ULN occurred in 107 of 112 (96%) patients. Nine (8%) patients had ALT between > 5-20 × ULN. One hundred (89%) patients had ALT elevations that occurred within the first 26 weeks, 74 (66%) patients had ALT elevations that occurred between weeks 27 to 52, and 72 (64%) patients had ALT elevations that occurred beyond 52 weeks after administration. Thirty-four of 112 (30%) patients had ALT elevations that were associated with a decline in factor VIII activity of ≥ 30%.
The majority of patients (82%, 92/112) required corticosteroids for one or more episodes of ALT elevation while 35% (39/112) required alternate immunosuppression. Seventy-six percent, 5%, and 1% of patients used corticosteroids within the first 26 weeks, weeks 27 to 52, and beyond 52 weeks respectively following ROCTAVIAN administration.
The most common (≥ 10%) adverse reactions from corticosteroid use (N = 92) included acne (34%), insomnia (27%), mood disorders (20%), cushingoid (20%), rash (18%), weight gain (16%), hypertension (12%), folliculitis (11%), abdominal pain (10%), and vision disorders (10%). Other clinically meaningful adverse events while on corticosteroid therapy included bone fracture (5%), impaired glucose tolerance (5%), herpes zoster (3%), oral candidiasis (3%), and adrenal insufficiency (1%). The most common adverse reactions from alternate immunosuppressant use (N = 39) included hypomagnesemia (15%) and diarrhea (10%). Infections requiring intravenous antimicrobial therapy occurred in 3 (3%) patients while on corticosteroid or other immunosuppressant therapy (N = 97).
One case of autoimmune hepatitis was reported during third year follow-up in a patient with history of hepatitis C and steatohepatitis.
6DRUG INTERACTIONS
Prior to ROCTAVIAN administration, the patient's existing medications should be reviewed to determine if they should be modified to prevent anticipated interactions described in this section.
Concomitant medications should be monitored after ROCTAVIAN administration, and the need to change concomitant medications based on patient's hepatic status and risk should be evaluated. When a new medication is started, close monitoring of ALT and factor VIII activity levels (e.g., weekly to every 2 weeks for the first month) is recommended to assess potential effects on both levels.
No
6.1Isotretinoin
In one patient, decreased factor VIII activity without ALT elevation was detected after starting treatment with systemic isotretinoin following ROCTAVIAN infusion. Factor VIII activity was 75 IU/dL at Week 60 and transiently decreased to < 3 IU/dL at Week 64, after initiating isotretinoin. After discontinuing isotretinoin at Week 72, factor VIII activity recovered to 46 IU/dL at Week 122. An
6.2Efavirenz
One HIV positive patient treated with ROCTAVIAN at a dose of 4 × 10
6.3Interactions with Agents that May Reduce or Increase Plasma Concentrations of Corticosteroids
Agents that may reduce or increase the plasma concentration of corticosteroids (e.g., agents that induce or inhibit cytochrome P450 3A4) can decrease the efficacy of the corticosteroid regimen or increase their side effects
6.4Vaccinations
Prior to ROCTAVIAN infusion, ensure up to date vaccinations. Individual vaccination schedules may need to be adjusted to accommodate concomitant immunosuppressive therapy
7DESCRIPTION
ROCTAVIAN (valoctocogene roxaparvovec-rvox) is an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector-based gene therapy product. ROCTAVIAN is replication-incompetent and consists of an AAV serotype 5 capsid containing a DNA sequence encoding the B-domain deleted SQ form of the human coagulation factor VIII (hFVIII-SQ). ROCTAVIAN is derived from naturally occurring adeno-associated virus and is produced using Sf9 insect cells and recombinant baculovirus technology.
ROCTAVIAN is a sterile suspension for intravenous infusion. When thawed, the suspension is clear and colorless to pale yellow.
Each vial of ROCTAVIAN contains an extractable volume of 8 mL of valoctocogene roxaparvovec-rvox at a concentration of 2 × 10
The product contains no preservative.
8CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of ROCTAVIAN was evaluated in a prospective, phase 3, open-label, single-dose, single-arm, multinational study in 134 adult males (18 years of age and older) with severe hemophilia A, who received a single intravenous dose of 6 × 10
Only patients without detectable, pre-existing antibodies to AAV5 capsid were eligible for therapy. Presence of pre-existing antibodies to AAV5 capsid was identified during screening using the ARUP Laboratories AAV5 DetectCDx
Of the 134 patients who received ROCTAVIAN in the clinical trial, 112 patients had baseline annualized bleeding rate (ABR) data prospectively collected during a period of at least six months on factor VIII prophylaxis prior to receiving ROCTAVIAN (rollover population). The remaining 22 patients had baseline ABR collected retrospectively (directly enrolled population). All patients were followed for at least 3 years.
The primary efficacy outcome was a non-inferiority (NI) test of the difference in ABR in the efficacy evaluation period (EEP) following ROCTAVIAN administration compared with ABR during the baseline period in the rollover population. The NI margin was 3.5 bleeds per year. All bleeding episodes, regardless of treatment, were counted towards ABR. The EEP started from Study Day 33 (Week 5) or the end of factor VIII prophylaxis including a washout period after ROCTAVIAN treatment, whichever was later, and ended when a patient completed the study, had the last visit, or withdrew or was lost to follow-up from the study, whichever was the earliest.
Table 9 summarizes the NI comparison between the mean ABR after ROCTAVIAN treatment and the mean baseline ABR while patients were on factor VIII prophylaxis in the rollover population (N = 112). The mean EEP ABR was 2.6 bleeds/year, compared to a mean baseline ABR of 5.4 bleeds/year. The mean difference in ABR was -2.8 (95% confidence interval: -4.3, -1.2) bleeds/year. The NI analysis met the pre-specified NI margin, indicating the effectiveness of ROCTAVIAN.
A majority of patients treated with ROCTAVIAN received immunosuppressive medications, including steroids, to control elevations in transaminases and to prevent loss of transgene expression
In the rollover population, a total of 5 patients (4%) did not respond and 17 patients (15%) lost response to ROCTAVIAN treatment over a median time of 2.3 (range: 1.0 to 3.3) years. In the directly enrolled population with a longer follow-up, a total of 1 patient (5%) did not respond and 6 patients (27%) lost response to ROCTAVIAN treatment over a median time of 3.6 (range: 1.2 to 4.3) years.
9PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform patients of the following risks and required precautions prior to ROCTAVIAN infusion:
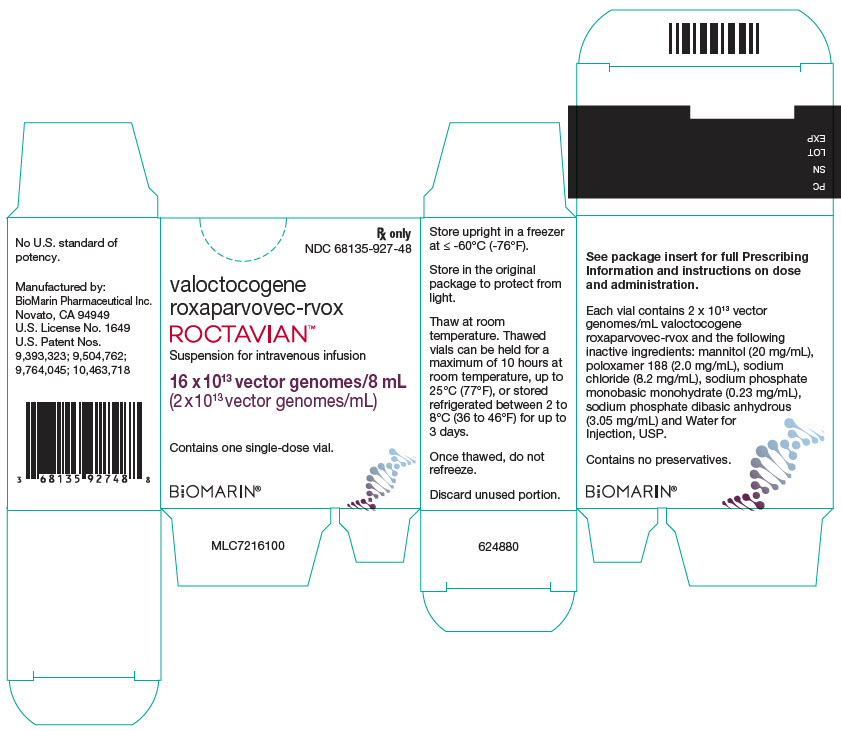
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 8 mL Vial Label
NDC 68135-927-01
valoctocogene roxaparvovec-rvox
ROCTAVIAN™
Suspension for intravenous infusion
16 x 10
BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
Single-dose
Discard unused portion
BiOMARIN

11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 8 mL Vial Carton
Rx only
valoctocogene
ROCTAVIAN™
Suspension for intravenous infusion
16 x 10
Contains one single-dose vial.
BiOMARIN