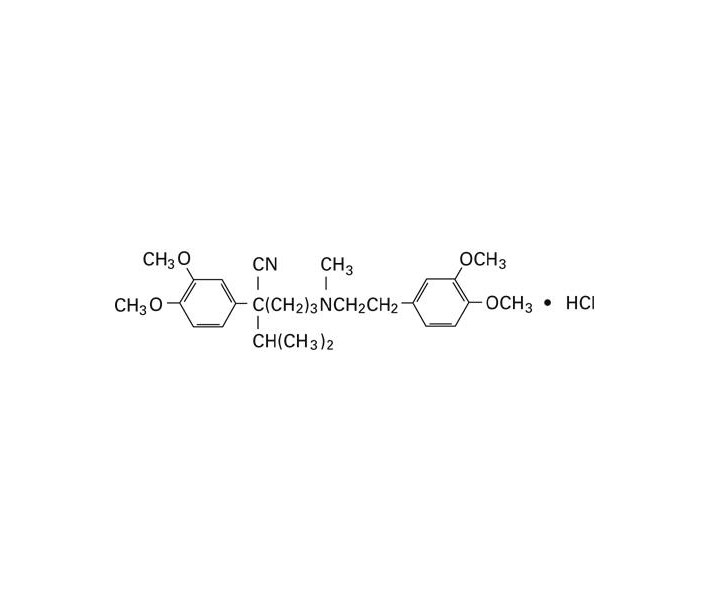
VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE SHOULD BE GIVEN AS A SLOW INTRAVENOUS INJECTION OVER AT LEAST A TWO-MINUTE PERIOD OF TIME (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
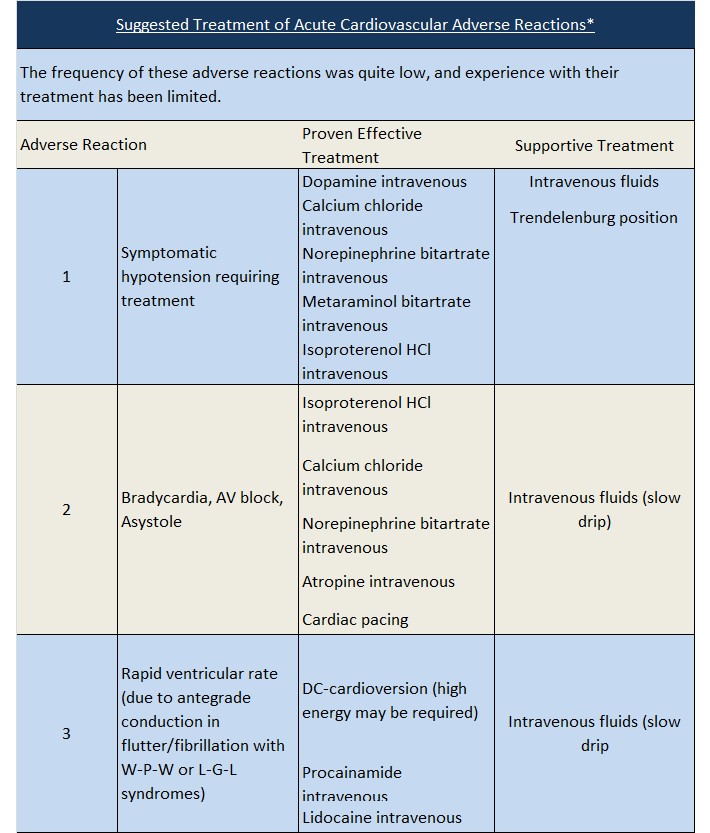
Hypotension: Verapamil hydrochloride injection often produces a decrease in blood pressure below baseline levels that is usually transient and asymptomatic but may result in dizziness. Systolic pressure less than 90 mm Hg and/or diastolic pressure less than 60 mm Hg was seen in 5% to 10% of patients in controlled U.S. trials in supraventricular tachycardia and in about 10% of the patients with atrial flutter/fibrillation. The incidence of symptomatic hypotension observed in studies conducted in the U.S. was approximately 1.5%. Three of the five symptomatic patients required intravenous pharmacologic treatment (norepinephrine bitartrate, metaraminol bitartrate, or 10% calcium gluconate). All recovered without sequelae.
Extreme Bradycardia/Asystole: Verapamil hydrochloride affects the AV and SA nodes and rarely may produce second- or third-degree AV block, bradycardia, and, in extreme cases, asystole. This is more likely to occur in patients with a sick sinus syndrome (SA nodal disease), which is more common in older patients. Bradycardia associated with sick sinus syndrome was reported in 0.3% of the patients treated in controlled double-blind trials in the U.S. The total incidence of bradycardia (ventricular rate less than 60 beats/min) was 1.2% in these studies. Asystole in patients other than those with sick sinus syndrome is usually of short duration (few seconds or less), with spontaneous return to AV nodal or normal sinus rhythm. If this does not occur promptly, appropriate treatment should be initiated immediately. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS and Suggested Treatment of Acute Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions.)
Heart Failure: When heart failure is not severe or rate related, it should be controlled with digitalis glycosides and diuretics, as appropriate, before verapamil is used. In patients with moderately severe to severe cardiac dysfunction (pulmonary wedge pressure above 20 mm Hg, ejection fraction less than 30%), acute worsening of heart failure may be seen.
Concomitant Antiarrhythmic Therapy:
Digitalis: Verapamil hydrochloride injection has been used concomitantly with digitalis preparations without the occurrence of serious adverse effects. However, since both drugs slow AV conduction, patients should be monitored for AV block or excessive bradycardia.
Procainamide: Verapamil hydrochloride injection has been administered to a small number of patients receiving oral procainamide without the occurrence of serious adverse effects.
Quinidine: Verapamil hydrochloride injection has been administered to a small number of patients receiving oral quinidine without the occurrence of serious adverse effects. However, three patients have been described in whom the combination resulted in an exaggerated hypotensive response presumably from the combined ability of both drugs to antagonize the effects of catecholamines on α-adrenergic receptors. Caution should therefore be used when employing this combination of drugs.
Beta-Adrenergic Blocking Drugs: Verapamil hydrochloride injection has been administered to patients receiving oral beta-blockers without the development of serious adverse effects. However, since both drugs may depress myocardial contractility and AV conduction, the possibility of detrimental interactions should be considered. The concomitant administration of intravenous beta-blockers and intravenous verapamil has resulted in serious adverse reactions (see CONTRAINDICATIONS), especially in patients with severe cardiomyopathy, congestive heart failure, or recent myocardial infarction.
Disopyramide: Until data on possible interactions between verapamil and all forms of disopyramide phosphate are obtained, disopyramide should not be administered within 48 hours before or 24 hours after verapamil administration.
Flecainide: A study in healthy volunteers showed that the concomitant administration of flecainide and verapamil may have additive effects reducing myocardial contractility, prolonging AV conduction, and prolonging repolarization.
Heart Block: Verapamil prolongs AV conduction time. While high-degree AV block has not been observed in controlled clinical trials in the United States, a low percentage (less than 0.5%) has been reported in the world literature. Development of second- or third-degree AV block or unifascicular, bifascicular, or trifascicular bundle branch block requires reduction in subsequent doses or discontinuation of verapamil and institution of appropriate therapy, if needed. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS, Suggested Treatment of Acute Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions.)
Hepatic and Renal Failure: Significant hepatic and renal failure should not increase the effects of a single intravenous dose of verapamil hydrochloride but may prolong its duration. Repeated injections of verapamil hydrochloride injection in such patients may lead to accumulation and an excessive pharmacologic effect of the drug. There is no experience to guide use of multiple doses in such patients, and this generally should be avoided. If repeated injections are essential, blood pressure and PR interval should be closely monitored and smaller repeat doses should be utilized.
Verapamil cannot be removed by hemodialysis.
Premature Ventricular Contractions: During conversion to normal sinus rhythm, or marked reduction in ventricular rate, a few benign complexes of unusual appearance (sometimes resembling premature ventricular contractions) may be seen after treatment with verapamil hydrochloride. Similar complexes are seen during spontaneous conversion of supraventricular tachycardias, after D.C.-cardioversion and other pharmacologic therapy. These complexes appear to have no clinical significance.
Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy: Verapamil hydrochloride injection can precipitate respiratory muscle failure in these patients and should, therefore, be used with caution.
Increased Intracranial Pressure: Verapamil hydrochloride injection has been seen to increase intracranial pressure in patients with supratentorial tumors at the time of anesthesia induction. Caution should be taken and appropriate monitoring performed.