Dronabinol
What is Marinol (Dronabinol)?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The purpose of this research is to assess the impact of CBD on the effects of THC.
Summary: This phase II trials evaluates how well different types of phytocannabinoids (cannabidiol \[CBD\] versus tetrahydrocannabinol \[THC\] and CBD formulation \[THC:CBD\]) work to reduce chronic chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among breast and colon cancer survivors. Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy is a set of symptoms that includes pain, tingling, numbness and motor weakness caus...
Summary: The goal of this clinical trial is to determine whether cannabidiol (CBD, 28%) combined with terpenes and a small amount of THC (1%) can help reduce symptoms of autism, and to evaluate the safety of this treatment. The main questions are: 1. Does this treatment improve behavioral challenges in children with autism? 2. Does this treatment improve social difficulties in children with autism? What wi...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Starting Dosage
The recommended adult starting dosage of MARINOL is 2.5 mg orally twice daily, one hour before lunch and dinner.
In elderly patients or patients unable to tolerate 2.5 mg twice daily, consider initiating MARINOL at 2.5 mg once daily one hour before dinner or at bedtime to reduce the risk of central nervous system (CNS) symptoms [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Dosing later in the day may reduce the frequency of CNS adverse reactions. CNS adverse reactions are dose-related [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]; therefore monitor patients and reduce the dosage as needed. If CNS adverse reactions of feeling high, dizziness, confusion, and somnolence occur, they usually resolve in 1 to 3 days and usually do not require dosage reduction. If CNS adverse reactions are severe or persistent, reduce the dosage to 2.5 mg in the evening or at bedtime.
Dosage Titration
If tolerated and further therapeutic effect is desired, the dosage may be increased gradually to 2.5 mg one hour before lunch and 5 mg one hour before dinner. Increase the dose of MARINOL gradually in order to reduce the frequency of dose-related adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Most patients respond to 2.5 mg twice daily, but the dose may be further increased to 5 mg one hour before lunch and 5 mg one hour before dinner, as tolerated to achieve a therapeutic effect.
Maximum Dosage: 10 mg twice daily.
2.2 Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Cancer Chemotherapy in Adult Patients Who Failed Conventional Antiemetics
Starting Dosage
The recommended starting dosage of MARINOL is 5 mg/m2, orally administered 1 to 3 hours prior to the administration of chemotherapy and then every 2 to 4 hours after chemotherapy, for a total of 4 to 6 doses per day.
In elderly patients, consider initiating MARINOL at 2.5 mg/m2 once daily 1 to 3 hours prior to chemotherapy to reduce the risk of CNS symptoms [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Administer the first dose on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before eating. Subsequent doses can be taken without regard to meals [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The timing of dosing in relation to meal times should be kept consistent for each chemotherapy cycle, once the dosage has been determined from the titration process.
Dosage Titration
The dosage can be titrated to clinical response during a chemotherapy cycle or subsequent cycles, based upon initial response, as tolerated to achieve a clinical effect, in increments of 2.5 mg/m2.
The maximum dosage is 15 mg/m2 per dose for 4 to 6 doses per day.
Adverse reactions are dose-related and psychiatric symptoms increase significantly at the maximum dosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Monitor patients for adverse reactions and consider decreasing the dose to 2.5 mg once daily 1 to 3 hours prior to chemotherapy to reduce the risk of CNS adverse reactions.
Psychiatric Adverse Reactions
Dronabinol has been reported to exacerbate mania, depression, or schizophrenia. Significant CNS symptoms followed oral doses of 0.4 mg/kg (28 mg per 70 kg patient) of MARINOL in antiemetic studies.
Prior to initiating treatment with MARINOL, screen patients for a history of these illnesses. Avoid use in patients with a psychiatric history or, if the drug cannot be avoided, monitor patients for new or worsening psychiatric symptoms during treatment. Also, avoid concomitant use with other drugs that are associated with similar psychiatric effects.
Cognitive Adverse Reactions
Use of MARINOL has been associated with cognitive impairment and altered mental state. Reduce the dose of MARINOL or discontinue use of MARINOL if signs or symptoms of cognitive impairment develop. Elderly patients may be more sensitive to the neurological and psychoactive effects of MARINOL [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4, 8.5)].
Hazardous Activities
MARINOL can cause and may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks such as driving a motor vehicle or operating machinery. Concomitant use of other drugs that cause dizziness, confusion, sedation, or somnolence such as CNS depressants may increase this effect (e.g., barbiturates, benzodiazepines, ethanol, lithium, opioids, buspirone, scopolamine, antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, other anticholinergic agents, muscle relaxants). Inform patients not to operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery until they are reasonably certain that MARINOL does not affect them adversely.
5.2 Hemodynamic Instability
Patients may experience occasional hypotension, possible hypertension, syncope, or tachycardia while taking MARINOL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Patients with cardiac disorders may be at higher risk. Avoid concomitant use of other drugs that are also associated with similar cardiac effects (e.g., amphetamines, other sympathomimetic agents, atropine, amoxapine, scopolamine, antihistamines, other anticholinergic agents, amitriptyline, desipramine, other tricyclic antidepressants). Monitor patients for changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and syncope after initiating or increasing the dosage of MARINOL.
5.3 Seizures
Seizure and seizure-like activity have been reported in patients receiving dronabinol.
Weigh this potential risk against the benefits before prescribing MARINOL to patients with a history of seizures, including those receiving anti-epileptic medication or with other factors that can lower the seizure threshold. Monitor patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control during MARINOL therapy.
If a seizure occurs, advise patients to discontinue MARINOL and contact a healthcare provider immediately.
5.4 Multiple Substance Abuse
Patients with a history of substance abuse or dependence, including marijuana or alcohol, may be more likely to abuse MARINOL as well.
Assess each patient’s risk for abuse or misuse prior to prescribing MARINOL and monitor patients with a history of substance abuse during treatment with MARINOL for the development of these behaviors or conditions.
5.5 Paradoxical Nausea, Vomiting, or Abdominal Pain
Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain can occur during treatment with synthetic delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta-9-THC), the active ingredient in MARINOL®(dronabinol capsules, USP). In some cases, these adverse reactions were severe (e.g., dehydration, electrolyte abnormalities) and required dose reduction or drug discontinuation. Symptoms are similar to cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS), which is described as cyclical events of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting in chronic, long-term users of delta-9-THC products.
Because patients may not recognize these symptoms as abnormal, it is important to specifically ask patients or their caregivers about the development of worsening of nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain while being treated with MARINOL. Consider dose reduction or discontinuing MARINOL if a patient develops worsening nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain while on treatment.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling.
• Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
• Hemodynamic Instability [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
• Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
• Paradoxical Nausea, Vomiting, and Abdominal Pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Studies of AIDS-related weight loss included 157 patients receiving MARINOL at a dose of 2.5 mg twice daily and 67 receiving placebo. Studies of nausea and vomiting related to cancer chemotherapy included 317 patients receiving MARINOL and 68 receiving placebo. In the tables below is a summary of the adverse reactions in 474 patients exposed to MARINOL in studies.
Studies of different durations were combined by considering the first occurrence of events during the first 28 days.
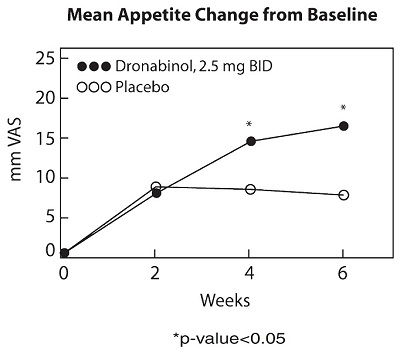
A cannabinoid dose-related "high" (easy laughing, elation and heightened awareness) has been reported by patients receiving MARINOL in both the antiemetic (24%) and the lower dose appetite stimulant clinical trials (8%). The most frequently reported adverse experiences in patients with AIDS during placebo-controlled clinical trials involved the CNS and were reported by 33% of patients receiving MARINOL. About 25% of patients reported a CNS adverse reaction during the first 2 weeks and about 4% reported such a reaction each week for the next 6 weeks thereafter.
Common Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions were reported in clinical trials at an incidence greater than 1%.
The following adverse reactions were reported in clinical trials at an incidence less than or equal to 1%.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of dronabinol capsules. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
General disorders and administration site conditions: Fatigue
Hypersensitivity reactions: Lip swelling, hives, disseminated rash, oral lesions, skin burning, flushing, throat tightness [see Contraindications (4)]
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: Fall [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]
Nervous system disorders: Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)], disorientation, movement disorder, loss of consciousness
Psychiatric disorders: Delirium, insomnia, panic attack
Vascular disorders: Syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Additive CNS effects (e.g., dizziness, confusion, sedation, somnolence) may occur when MARINOL is taken concomitantly with drugs that have similar effects on the central nervous system such as CNS depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.2 Additive Cardiac Effects
Additive cardiac effects (e.g., hypotension, hypertension, syncope, tachycardia) may occur when MARINOL is taken concomitantly with drugs that have similar effects on the cardiovascular system [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.3 Effect of Other Drugs on Dronabinol
Dronabinol is primarily metabolized by CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 enzymes based on published in vitro studies. Inhibitors of these enzymes may increase, while inducers may decrease, the systemic exposure of dronabinol and/or its active metabolite resulting in an increase in dronabinol-related adverse reactions or loss of efficacy of MARINOL.
Monitor for potentially increased dronabinol-related adverse reactions when MARINOL is co-administered with inhibitors of CYP2C9 (e.g., amiodarone, fluconazole) and inhibitors of CYP3A4 enzymes (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, ritonavir, erythromycin, grapefruit juice).
7.4 Highly Protein-Bound Drugs
Dronabinol is highly bound to plasma proteins, and therefore, might displace and increase the free fraction of other concomitantly administered protein-bound drugs.
Although this displacement has not been confirmed in vivo, monitor patients for increased adverse reactions to narrow therapeutic index drugs that are highly protein bound (e.g., warfarin, cyclosporine, amphotericin B) when initiating treatment or increasing the dosage of MARINOL.
What is the most important information I should know about MARINOL?
• Worsening mental (psychiatric) symptoms. Psychiatric symptoms can worsen in people who have mania, depression, or schizophrenia and who take MARINOL® (dronabinol capsules, USP). MARINOL taken with medicines that cause psychiatric symptoms can worsen psychiatric symptoms. Elderly people who take MARINOL may have a greater risk of having psychiatric symptoms. Tell your doctor if you have new or worsening mood symptoms, including symptoms of mania, depression, or schizophrenia.
• Problems thinking clearly. Tell your doctor if you have trouble remembering things, concentrating, have increased sleepiness, or confusion. Elderly people may have a greater risk of having problems thinking clearly.
• Changes in your blood pressure. MARINOL may increase or decrease your blood pressure, especially when you start taking MARINOL or when your dose is changed. Tell your doctor if you have signs or symptoms of changes in your blood pressure including: headaches, vision problems, dizziness, feeling lightheaded, fainting, or a fast heartbeat. Elderly people, especially those with dementia, and people with heart problems may have an increased risk of changes in blood pressure and an increased risk of falls.
What is MARINOL?
• MARINOL is a prescription medicine used in adults to treat:
◦ loss of appetite (anorexia) in people with AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) who have lost weight.
◦ nausea and vomiting caused by anti-cancer medicine (chemotherapy) in people whose nausea and vomiting have not improved with usual anti-nausea medicines.
MARINOL is a controlled substance (CIII) because it contains dronabinol, which can be a target for people who abuse prescription medicines or street drugs. Keep your MARINOL in a safe place to protect it from theft. Never give your MARINOL to anyone else because it may cause death or harm them. Selling or giving away this medicine is against the law.
It is not known if MARINOL is safe and effective in children.
Do not take MARINOL if you:
• had an allergic reaction to dronabinol. Signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction to dronabinol include: swelling of the lips, hives, a rash over your whole body, mouth sores, skin burning, flushing, and throat tightness.
• had an allergic reaction to sesame oil.
Before taking MARINOL, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
• have or had heart problems.
• have or had problems with drug abuse or dependence.
• have or had problems with alcohol abuse or dependence.
• have or had mental health problems including mania, depression, or schizophrenia.
• have had a seizure or have a medical condition that may increase your risk of having a seizure.
• are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. MARINOL may harm your unborn baby. Avoid the use of MARINOL if you are pregnant.
• are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that mothers with HIV not breastfeed because they can pass the HIV through their breast milk to the baby. It is not known if MARINOL passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take MARINOL. Do not breastfeed while taking MARINOL and for 9 days after your last dose of MARINOL if you are being treated for nausea and vomiting caused by anti-cancer medicine.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take or have taken in the last 14 days, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. MARINOL and certain other medicines can affect each other, causing serious side effects.
How should I take MARINOL?
• Take MARINOL exactly as your doctor tells you to. Your doctor may change your dose after seeing how it affects you. Do not change your dose unless your doctor tells you to change it.
• If you are an adult with AIDS with loss of appetite and weight loss:
◦ MARINOL is usually taken 2 times each day, 1 hour before lunch and 1 hour before dinner. If you are elderly or unable to tolerate this dose of MARINOL, your doctor may prescribe MARINOL to be taken 1 time each day, 1 hour before dinner or bedtime to reduce your chance of having nervous system problems.
• If you are an adult with nausea and vomiting caused by anti-cancer medicine:
◦ MARINOL® (dronabinol capsules, USP) is usually taken 1 to 3 hours before your chemotherapy treatment and then every 2 to 4 hours after chemotherapy for up to 4 to 6 doses each day. If you are elderly, your doctor may prescribe MARINOL to be taken 1 to 3 hours before your chemotherapy, 1 time each day to reduce your chance of having nervous system problems.
◦ Take your first dose of MARINOL on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before eating. After your first dose of MARINOL, you can take MARINOL with or without food. Always take your dose at the same time with regard to meals.
• If you take too much MARINOL, call your Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 right away.Do not drive, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how MARINOL affects you. MARINOL taken with other medicines that cause dizziness, confusion, and sleepiness may make these symptoms worse.
What are the possible side effects of MARINOL?
MARINOL may cause serious side effects, including:
• See "What is the most important information I should know about MARINOL?"
• Seizures. MARINOL may increase your risk of seizures. Stop taking MARINOL and call your doctor and get medical care right away if you have a seizure during treatment with MARINOL.
• Drug and alcohol abuse. You may have an increased risk of abusing MARINOL if you have a history of drug or alcohol abuse or dependence, including marijuana. Tell your doctor if you develop abuse behaviors such as increased irritability, nervousness, restlessness or want more or higher doses of MARINOL during your treatment.
• Nausea, vomiting, or stomach-area (abdominal) pain. Tell your doctor if you have nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain or if your nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain gets worse during treatment with MARINOL.
The most common side effects of MARINOL include:





