Brand Name
Zunveyl
Generic Name
Benzgalantamine
View Brand Information FDA approval date: August 09, 2024
Form: Tablet
What is Zunveyl (Benzgalantamine)?
ZUNVEYL is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type in adults. ZUNVEYL is a cholinesterase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type in adults
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
ZUNVEYL (benzgalantamine)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZUNVEYL is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type in adults.
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ZUNVEYL delayed-release tablets are enteric coated and available in the following strengths of benzgalantamine:
- 5 mg white, round, and convex, debossed with "B05" in grey
- 10 mg purple, round, and convex, debossed with "B10" in grey
- 15 mg grey, round, and convex, debossed with "B15" in dark grey
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZUNVEYL is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to benzgalantamine, galantamine, or to any inactive ingredient in ZUNVEYL. Serious skin reactions have occurred
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in more detail elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Skin Reactions
- Cardiovascular Conditions
- Gastrointestinal Conditions
- Genitourinary Conditions
- Neurological Conditions
- Pulmonary Conditions
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ZUNVEYL has been established in studies of galantamine immediate-release tablets and galantamine extended-release capsules
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of galantamine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity [see
Psychiatric Disorders: Hallucinations
Nervous System Disorders: Seizures, extrapyramidal disorder [see
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: Tinnitus
Cardiac Disorders: Complete atrioventricular block
Vascular Disorders: Hypertension
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatitis, increased hepatic enzyme
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis [see erythema multiforme
5OVERDOSAGE
Because strategies for the management of overdose are continually evolving, it is advisable to contact a poison control center to determine the latest recommendations for the management of an overdose of any drug.
As in any case of overdose, general supportive measures should be utilized. Signs and symptoms of significant overdosing of galantamine are predicted to be similar to those of overdosing of other cholinomimetics. These effects generally involve the central nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system, and the neuromuscular junction. In addition to muscle weakness or fasciculations, some or all of the following signs of cholinergic crisis may develop: severe nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal cramping, salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, respiratory depression, collapse and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved.
Tertiary anticholinergics such as atropine may be used as an antidote for ZUNVEYL overdosage. Intravenous (IV) atropine sulfate titrated to effect is recommended at an initial dose of 0.5 to 1.0 mg IV with subsequent doses based upon clinical response. Atypical responses in blood pressure and heart rate have been reported with other cholinomimetics when co-administered with quaternary anticholinergics. It is not known whether galantamine and/or its metabolites can be removed by dialysis (hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or hemofiltration). Dose-related signs of toxicity in animals included hypoactivity, tremors, clonic convulsions, salivation, lacrimation, chromodacryorrhea, mucoid feces, and dyspnea.
In one postmarketing report, one patient who had been taking 4 mg of galantamine daily for a week inadvertently ingested eight 4 mg tablets (32 mg total) on a single day. Subsequently, she developed bradycardia, QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia and torsades de pointes accompanied by a brief loss of consciousness for which she required hospital treatment. Two additional cases of accidental ingestion of 32 mg (nausea, vomiting, and dry mouth; nausea, vomiting, and substernal chest pain) and one of 40 mg (vomiting), resulted in brief hospitalizations for observation with full recovery. One patient, who was prescribed 24 mg/day and had a history of hallucinations over the previous two years, mistakenly received 24 mg twice daily for 34 days and developed hallucinations requiring hospitalization. Another patient, who was prescribed 16 mg/day of oral solution, inadvertently ingested 160 mg (40 mL) and experienced sweating, vomiting, bradycardia, and near-syncope one hour later, which necessitated hospital treatment. His symptoms resolved within 24 hours.
6DESCRIPTION
ZUNVEYL (benzgalantamine) is a prodrug of galantamine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor . Benzgalantamine gluconate is known chemically as (4aS,6R,8aS)-4a,5,9,10,11,12-hexahydro-3-methoxy-11-methyl-6H-benzofuro[3a,3,2-ef][2]benzazepin-6- benzoate gluconate salt. It has an empirical formula of C
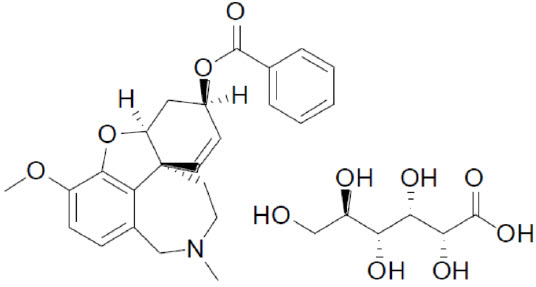
ZUNVEYL contains 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg benzgalantamine equivalent to 7.49 mg, 14.98 mg, and 22.47 mg benzgalantamine gluconate, respectively. ZUNVEYL delayed-release tablets are for oral use. Inactive ingredients include calcium silicate, colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol, methacrylic acid, poloxamer 407, polyethylene glycol/macrogol, sodium bicarbonate, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium stearyl fumarate, talc, and titanium dioxide. The 10 mg tablet also contains Carmine, FD&C Blue #2/Indigo Carmine Aluminum Lake, and FD&C Red #40/Allura Red AC Aluminum Lake. The 15 mg tablet also contains FD&C Blue #2/Indigo Carmine Aluminum Lake, FD&C Red #40/Allura Red AC Aluminum Lake, and FD&C Yellow #6/Sunset Yellow FCF Aluminum Lake.
7CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of ZUNVEYL is based upon 3 bioavailability studies in healthy adults comparing galantamine immediate-release tablets and galantamine extended-release capsules to ZUNVEYL
The effectiveness of galantamine as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease is demonstrated by the results of 5 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical investigations in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease, 4 with the immediate-release tablet and 1 with the extendedrelease capsule [diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA criteria, with Mini-Mental State Examination scores that were ≥10 and ≤24]. Doses studied with the immediate-release tablet were 8-32 mg/day given as twice daily doses. In 3 of the 4 studies with the immediate-release tablet, patients were started on a low dose of 8 mg, then titrated weekly by 8 mg/day to 24 or 32 mg as assigned. In the fourth study (USA 4-week Dose Escalation Fixed-Dose Study) dose escalation of 8 mg/day occurred over 4-week intervals. The mean age of patients participating in these 4 galantamine trials was 75 years with a range of 41 to 100. Approximately 62% of patients were women and 38% were men. The racial distribution was White 94%, Black 3% and other races 3%. Two other studies examined a three times daily dosing regimen; these also showed or suggested benefit but did not suggest an advantage over twice daily dosing.
7.1Study Outcome Measures
In each study, the primary effectiveness of galantamine was evaluated using a dual outcome assessment strategy as measured by the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-cog) and the Clinician's Interview Based Impression of Change that required the use of caregiver information (CIBIC-plus).
The ability of galantamine to improve cognitive performance was assessed with the cognitive sub-scale of the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-cog), a multi-item instrument that has been validated in longitudinal cohorts of Alzheimer's disease patients. The ADAS-cog examines selected aspects of cognitive performance including elements of memory, orientation, attention, reasoning, language and praxis. The ADAS-cog scoring range is from 0 to 70, with higher scores indicating greater cognitive impairment. Elderly normal adults may score as low as 0 or 1, but it is not unusual for non-demented adults to score slightly higher.
The patients recruited as participants in each study using the immediate-release tablet formulation had mean scores on ADAS-cog of approximately 27 units, with a range from 5 to 69. Experience using the ADAS-cog in longitudinal studies of ambulatory patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease suggests that patients typically gain 6 to 12 units a year. Because the ADAS-cog is not uniformly sensitive to change over the course of the disease, a less than typical degree of change may be seen in patients at very early or later stages of disease. The annualized rate of decline in the placebo patients participating in galantamine trials was approximately 4.5 units per year.
The ability of galantamine to produce an overall clinical effect was assessed using a Clinician's Interview Based Impression of Change that required the use of caregiver information, the CIBICplus. The CIBIC-plus is not a single instrument and is not a standardized instrument like the ADAS-cog. Clinical trials for investigational drugs have used a variety of CIBIC formats, each different in terms of depth and structure. As such, results from a CIBIC-plus reflect clinical experience from the trial or trials in which it was used and cannot be compared directly with the results of CIBIC-plus evaluations from other clinical trials. The CIBIC-plus used in the trials was a semi-structured instrument based on a comprehensive evaluation at baseline and subsequent time-points of 4 major areas of patient function: general, cognitive, behavioral and activities of daily living. It represents the assessment of a skilled clinician based on his/her observation at an interview with the patient, in combination with information supplied by a caregiver familiar with the behavior of the patient over the interval rated. The CIBIC-plus is scored as a seven-point categorical rating, ranging from a score of 1, indicating "markedly improved," to a score of 4, indicating "no change" to a score of 7, indicating "marked worsening." The CIBIC-plus has not been systematically compared directly to assessments not using information from caregivers (CIBIC) or other global methods.
7.2Galantamine Extended-Release Capsules
The efficacy of galantamine extended-release capsules was studied in a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial which was 6 months in duration and had an initial 4-week doseescalation phase. In this trial, patients were assigned to one of 3 treatment groups: glantamine extended-release capsules in a flexible dose of 16 to 24 mg once daily; galantamine immediaterelease tablets in a flexible dose of 8 to 12 mg twice daily; and placebo. The primary efficacy measures in this study were the ADAS-cog and CIBIC-plus. On the protocol-specified primary efficacy analysis at Month 6, a statistically significant improvement favoring galantamine extended-release capsules over placebo was seen for the ADAS-cog, but not for the CIBIC-plus. Galantamine extended-release capsules showed a statistically significant improvement when compared with placebo on the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living (ADCS-ADL) scale, a measure of function, and a secondary efficacy measure in this study. The effects of both galantamine extended-release capsules and galantamine immediaterelease tablets on the ADAS-cog, CIBIC-plus, and ADCS-ADL were similar in this study.
8PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 84054 -005-60
ZUNVEYL
DELAYED RELEASE TABLETS
5 mg
60 Tablets

9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 84054 -010-60
ZUNVEYL
DELAYED RELEASE TABLETS
10 mg
60 Tablets

10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 84054 -015-60
ZUNVEYL
DELAYED RELEASE TABLETS
15 mg
60 Tablets
