Generic Name
Salmeterol
Brand Names
Advair HFA, Salmeterol Diskus, Salmeterol HFA, Wixela Inhub, Advair Diskus, SEREVENT Diskus, AirDuo RespiClick
FDA approval date: November 25, 1997
Classification: Corticosteroid
Form: Aerosol, Powder
What is Advair HFA (Salmeterol)?
Fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder is a combination product containing a corticosteroid and a long-acting beta 2 -adrenergic agonist indicated for: Twice-daily treatment of asthma in patients aged 4 years and older.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
ADVAIR HFA (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol xinafoate)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ADVAIR HFA is indicated for treatment of asthma in adult and adolescent patients aged 12 years and older. ADVAIR HFA should be used for patients not adequately controlled on a long-term asthma control medication such as an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) or whose disease warrants initiation of treatment with both an ICS and long-acting beta
Limitations of Use
ADVAIR HFA is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Inhalation aerosol: purple plastic inhaler with a light purple cap containing a pressurized metered-dose aerosol canister containing 60 or 120 metered inhalations and fitted with a counter.
- 45 mcg fluticasone propionate/21 mcg salmeterol from the mouthpiece per actuation
- 115 mcg fluticasone propionate/21 mcg salmeterol from the mouthpiece per actuation
- 230 mcg fluticasone propionate/21 mcg salmeterol from the mouthpiece per actuation
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVAIR HFA is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Primary treatment of status asthmaticus or other acute episodes of asthma where intensive measures are required
- Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious asthma-related events – hospitalizations, intubations, death
- Oropharyngeal candidiasis
- Pneumonia in patients with COPD
- Immunosuppression and risk of infections
- Hypercorticism and adrenal suppression
- Cardiovascular and central nervous system effects
- Reduction in bone mineral density
- Growth effects
- Glaucoma and cataracts
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult and Adolescent Subjects Aged 12 Years and Older
The incidence of adverse reactions associated with ADVAIR HFA in Table 2 is based upon two 12-week, placebo-controlled, U.S. clinical trials (Trials 1 and 3) and 1 active-controlled 12-week U.S. clinical trial (Trial 2). A total of 1,008 adult and adolescent subjects with asthma (556 females and 452 males) previously treated with albuterol alone, salmeterol, or ICS were treated twice daily with 2 inhalations of ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg or ADVAIR HFA 115 mcg/21 mcg, fluticasone propionate CFC inhalation aerosol (44- or 110-mcg doses), salmeterol CFC inhalation aerosol 21 mcg, or placebo HFA inhalation aerosol. The average duration of exposure was 71 to 81 days in the active treatment groups compared with 51 days in the placebo group.
The incidence of common adverse reactions reported in Trial 4, a 12-week non-U.S. clinical trial in 509 subjects previously treated with ICS who were treated twice daily with 2 inhalations of ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg, fluticasone propionate CFC inhalation aerosol 220 mcg, or 1 inhalation of ADVAIR DISKUS 500 mcg/50 mcg was similar to the incidences reported in Table 2.
Additional Adverse Reactions
Other adverse reactions not previously listed, whether considered drug-related or not by the investigators, that occurred in the groups receiving ADVAIR HFA with an incidence of 1% to 3% and that occurred at a greater incidence than with placebo include the following: tachycardia, arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, postoperative complications, wounds and lacerations, soft tissue injuries, ear signs and symptoms, rhinorrhea/postnasal drip, epistaxis, nasal congestion/blockage, laryngitis, unspecified oropharyngeal plaques, dryness of nose, weight gain, allergic eye disorders, eye edema and swelling, gastrointestinal discomfort and pain, dental discomfort and pain, candidiasis mouth/throat, hyposalivation, gastrointestinal infections, disorders of hard tissue of teeth, abdominal discomfort and pain, oral abnormalities, arthralgia and articular rheumatism, muscle cramps and spasms, musculoskeletal inflammation, bone and skeletal pain, muscle injuries, sleep disorders, migraines, allergies and allergic reactions, viral infections, bacterial infections, candidiasis unspecified site, congestion, inflammation, bacterial reproductive infections, lower respiratory signs and symptoms, lower respiratory infections, lower respiratory hemorrhage, eczema, dermatitis and dermatosis, urinary infections.
Laboratory Test Abnormalities
In Trial 3, there were more reports of hyperglycemia among adults and adolescents receiving ADVAIR HFA, but this was not seen in Trials 1 and 2.
4.2Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of any formulation of ADVAIR, fluticasone propionate, and/or salmeterol regardless of indication. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These events have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or causal connection to ADVAIR, fluticasone propionate, and/or salmeterol or a combination of these factors.
Cardiovascular
Arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation, extrasystoles, supraventricular tachycardia), hypertension, ventricular tachycardia.
Ear, Nose, and Throat
Aphonia, earache, facial and oropharyngeal edema, paranasal sinus pain, rhinitis, throat soreness, tonsillitis.
Endocrine and Metabolic
Cushing’s syndrome, Cushingoid features, growth velocity reduction in children/adolescents, hypercorticism, osteoporosis.
Eye
Cataracts, glaucoma.
Gastrointestinal
Dyspepsia, xerostomia.
Hepatobiliary Tract and Pancreas
Abnormal liver function tests.
Immune System
Immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions, including rash and rare events of angioedema, bronchospasm, and anaphylaxis.
Infections and Infestations
Esophageal candidiasis.
Musculoskeletal
Back pain, myositis.
Neurology
Paresthesia, restlessness.
Non-Site Specific
Fever, pallor.
Psychiatry
Agitation, aggression, anxiety, depression. Behavioral changes, including hyperactivity and irritability, have been reported very rarely and primarily in children.
Respiratory
Asthma; asthma exacerbation; chest congestion; chest tightness; cough; dyspnea; immediate bronchospasm; influenza; paradoxical bronchospasm; tracheitis; wheezing; pneumonia; reports of upper respiratory symptoms of laryngeal spasm, irritation, or swelling such as stridor or choking.
Skin
Contact dermatitis, contusions, ecchymoses, photodermatitis, pruritus.
Urogenital
Dysmenorrhea, irregular menstrual cycle, pelvic inflammatory disease, vaginal candidiasis, vaginitis, vulvovaginitis.
5DRUG INTERACTIONS
ADVAIR HFA has been used concomitantly with other drugs, including short-acting beta
5.1Inhibitors of Cytochrome P450 3A4
Fluticasone propionate and salmeterol, the individual components of ADVAIR HFA, are substrates of CYP3A4. The use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, saquinavir, ketoconazole, telithromycin) with ADVAIR HFA is not recommended because increased systemic corticosteroid and increased cardiovascular adverse effects may occur.
Ritonavir
Fluticasone Propionate: A drug interaction trial with fluticasone propionate aqueous nasal spray in healthy subjects has shown that ritonavir (a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) can significantly increase plasma fluticasone propionate exposure, resulting in significantly reduced serum cortisol concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. During postmarketing use, there have been reports of clinically significant drug interactions in patients receiving fluticasone propionate and ritonavir, resulting in systemic corticosteroid effects including Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal suppression.
Ketoconazole
Fluticasone Propionate: Coadministration of orally inhaled fluticasone propionate (1,000 mcg) and ketoconazole (200 mg once daily) resulted in a 1.9-fold increase in plasma fluticasone propionate exposure and a 45% decrease in plasma cortisol area under the curve (AUC), but had no effect on urinary excretion of cortisol.
Salmeterol: In a drug interaction trial in 20 healthy subjects, coadministration of inhaled salmeterol (50 mcg twice daily) and oral ketoconazole (400 mg once daily) for 7 days resulted in greater systemic exposure to salmeterol (AUC increased 16-fold and Cmax increased 1.4-fold). Three (3) subjects were withdrawn due to beta2-agonist side effects (2 with prolonged QTc and 1 with palpitations and sinus tachycardia). Although there was no statistical effect on the mean QTc, coadministration of salmeterol and ketoconazole was associated with more frequent increases in QTc duration compared with salmeterol and placebo administration.
5.2Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors and Tricyclic Antidepressants
ADVAIR HFA should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, because the action of salmeterol, a component of ADVAIR HFA, on the vascular system may be potentiated by these agents.
5.3Beta-adrenergic Receptor Blocking Agents
Beta-blockers not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists, such as salmeterol, a component of ADVAIR HFA, but may also produce severe bronchospasm in patients with asthma. Therefore, patients with asthma should not normally be treated with beta-blockers. However, under certain circumstances, there may be no acceptable alternatives to the use of beta-adrenergic blocking agents for these patients; cardioselective beta-blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution.
5.4Non–Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
The ECG changes and/or hypokalemia that may result from the administration of non–potassium-sparing diuretics (such as loop or thiazide diuretics) can be acutely worsened by beta-agonists, such as salmeterol, a component of ADVAIR HFA, especially when the recommended dose of the beta-agonist is exceeded. Although the clinical significance of these effects is not known, caution is advised in the coadministration of ADVAIR HFA with non–potassium-sparing diuretics.
6OVERDOSAGE
No human overdosage data has been reported for ADVAIR HFA.
ADVAIR HFA contains both fluticasone propionate and salmeterol; therefore, the risks associated with overdosage for the individual components described below apply to ADVAIR HFA. Treatment of overdosage consists of discontinuation of ADVAIR HFA together with institution of appropriate symptomatic and/or supportive therapy. The judicious use of a cardioselective beta-receptor blocker may be considered, bearing in mind that such medication can produce bronchospasm. Cardiac monitoring is recommended in cases of overdosage.
Fluticasone Propionate
Chronic overdosage of fluticasone propionate may result in signs/symptoms of hypercorticism
Salmeterol
The expected signs and symptoms with overdosage of salmeterol are those of excessive beta‑adrenergic stimulation and/or occurrence or exaggeration of any of the signs and symptoms of beta-adrenergic stimulation (e.g., seizures, angina, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia with rates up to 200 beats/min, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, muscle cramps, dry mouth, palpitation, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, insomnia, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis). Overdosage with salmeterol can lead to clinically significant prolongation of the QTc interval, which can produce ventricular arrhythmias.
As with all inhaled sympathomimetic medicines, cardiac arrest and even death may be associated with an overdose of salmeterol.
7DESCRIPTION
ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg, ADVAIR HFA 115 mcg/21 mcg, and ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg are combinations of fluticasone propionate and salmeterol xinafoate.
One active component of ADVAIR HFA is fluticasone propionate, a corticosteroid having the chemical name
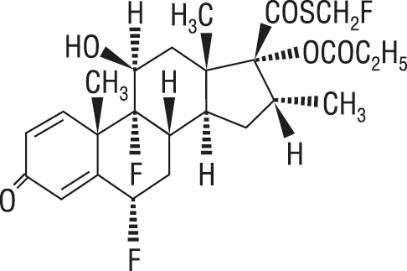
Fluticasone propionate is a white powder with a molecular weight of 500.6, and the empirical formula is C
The other active component of ADVAIR HFA is salmeterol xinafoate, a beta
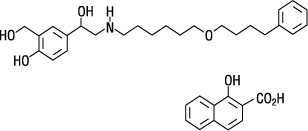
Salmeterol xinafoate is a white powder with a molecular weight of 603.8, and the empirical formula is C
ADVAIR HFA is a purple plastic inhaler with a light purple cap containing a pressurized metered-dose aerosol canister fitted with a counter. Each canister contains a microcrystalline suspension of micronized fluticasone propionate and micronized salmeterol xinafoate in propellant HFA-134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane). It contains no other excipients.
After priming, each actuation of the inhaler delivers 50, 125, or 250 mcg of fluticasone propionate and 25 mcg of salmeterol in 75 mg of suspension from the valve. Each actuation delivers 45, 115, or 230 mcg of fluticasone propionate and 21 mcg of salmeterol from the actuator. Twenty-one micrograms (21 mcg) of salmeterol base is equivalent to 30.45 mcg of salmeterol xinafoate. The actual amount of drug delivered to the lung will depend on patient factors, such as the coordination between the actuation of the inhaler and inspiration through the delivery system.
Prime ADVAIR HFA before using for the first time by releasing 4 sprays into the air away from the face, shaking well for 5 seconds before each spray. In cases where the inhaler has not been used for more than 4 weeks or when it has been dropped, prime the inhaler again by releasing 2 sprays into the air away from the face, shaking well for 5 seconds before each spray. Avoid spraying in eyes.
8CLINICAL STUDIES
ADVAIR HFA has been studied in subjects with asthma aged 12 years and older. ADVAIR HFA has not been studied in subjects younger than 12 years or in subjects with COPD. In clinical trials comparing ADVAIR HFA with its individual components, improvements in most efficacy endpoints were greater with ADVAIR HFA than with the use of either fluticasone propionate or salmeterol alone. In addition, clinical trials showed comparable results between ADVAIR HFA and ADVAIR DISKUS.
8.1Trials Comparing ADVAIR HFA with Fluticasone Propionate Alone or Salmeterol Alone
Four (4) double-blind, parallel-group clinical trials were conducted with ADVAIR HFA in 1,517 adult and adolescent subjects (aged 12 years and older, mean baseline FEV
Trial 1: Clinical Trial with ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg
This placebo-controlled, 12-week, U.S. trial compared ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg with fluticasone propionate CFC inhalation aerosol 44 mcg or salmeterol CFC inhalation aerosol 21 mcg, each given as 2 inhalations twice daily. The primary efficacy endpoints were predose FEV
Predefined withdrawal criteria for lack of efficacy, an indicator of worsening asthma, were utilized for this placebo-controlled trial. Worsening asthma was defined as a clinically important decrease in FEV
The FEV
Figure 1. Mean Percent Change from Baseline in FEV1 in Subjects Previously Treated with Either Beta
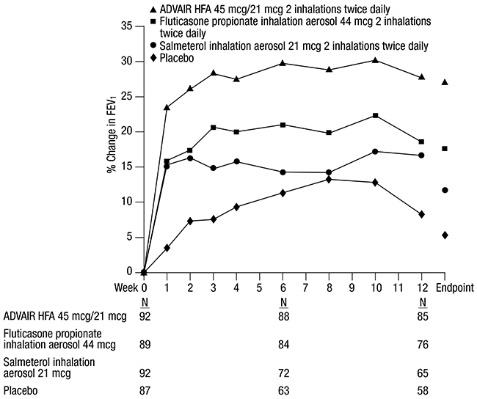
The effect of ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg on the secondary efficacy parameters, including morning and evening PEF, usage of VENTOLIN Inhalation Aerosol, and asthma symptoms over 24 hours on a scale of 0 to 5 is shown in Table 4.
The subjective impact of asthma on subjects’ perception of health was evaluated through use of an instrument called the Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ) (based on a 7-point scale where 1 = maximum impairment and 7 = none). Subjects receiving ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg had clinically meaningful improvements in overall asthma-specific quality of life as defined by a difference between groups of ≥0.5 points in change from baseline AQLQ scores (difference in AQLQ score of 1.14 [95% CI: 0.85, 1.44] compared with placebo).
Trial 2: Clinical Trial with ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg
This active-controlled, 12-week, U.S. trial compared ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg with fluticasone propionate CFC inhalation aerosol 44 mcg and salmeterol CFC inhalation aerosol 21 mcg, each given as 2 inhalations twice daily, in 283 subjects using as-needed albuterol alone. The primary efficacy endpoint was predose FEV
Efficacy results in this trial were similar to those observed in Trial 1. Subjects receiving ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg had significantly greater improvements in FEV
Trial 3: Clinical Trial with ADVAIR HFA 115 mcg/21 mcg
This placebo-controlled, 12-week, U.S. trial compared ADVAIR HFA 115 mcg/21 mcg with fluticasone propionate CFC inhalation aerosol 110 mcg or salmeterol CFC inhalation aerosol 21 mcg, each given as 2 inhalations twice daily, in 365 subjects using ICS (daily doses of beclomethasone dipropionate 378 to 840 mcg; budesonide 800 to 1,200 mcg; flunisolide 1,250 to 2,000 mcg; fluticasone propionate inhalation aerosol 440 to 660 mcg; fluticasone propionate inhalation powder 400 to 600 mcg; or triamcinolone acetonide 900 to 1,600 mcg). The primary efficacy endpoints were predose FEV
Efficacy results in this trial were similar to those observed in Trials 1 and 2. Subjects receiving ADVAIR HFA 115 mcg/21 mcg had significantly greater improvements in FEV
Trial 4: Clinical Trial with ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg
This active-controlled, 12-week, non-U.S. trial compared ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg with fluticasone propionate CFC inhalation aerosol 220 mcg, each given as 2 inhalations twice daily, and with ADVAIR DISKUS 500 mcg /50 mcg given as 1 inhalation twice daily in 509 subjects using ICS (daily doses of beclomethasone dipropionate CFC inhalation aerosol 1,500 to 2,000 mcg; budesonide 1,500 to 2,000 mcg; flunisolide 1,500 to 2,000 mcg; fluticasone propionate inhalation aerosol 660 to 880 mcg; or fluticasone propionate inhalation powder 750 to 1,000 mcg). The primary efficacy endpoint was morning PEF.
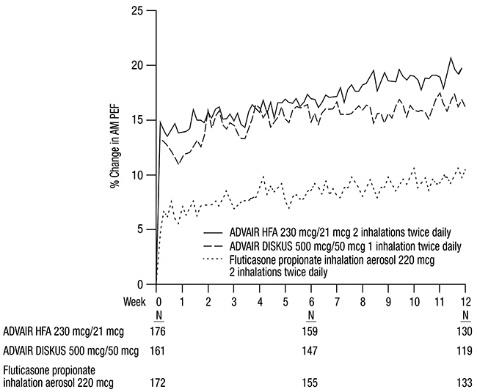
Baseline morning PEF measurements were similar across treatments: ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg, 327 L/min; ADVAIR DISKUS 500 mcg/50 mcg, 341 L/min; and fluticasone propionate 220 mcg, 345 L/min. As shown in Figure 2, morning PEF improved significantly with ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg compared with fluticasone propionate 220 mcg over the 12-week treatment period. Improvements in morning PEF observed with ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg were similar to improvements observed with ADVAIR DISKUS 500 mcg/50 mcg.
Figure 2. Mean Percent Change from Baseline in Morning Peak Expiratory Flow in Subjects Previously Treated with Inhaled Corticosteroids (Trial 4)
8.2One-Year Safety Trial
Clinical Trial with ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg, ADVAIR HFA 115 mcg/21 mcg, and ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg
This 1-year, open-label, non-U.S. trial evaluated the safety of ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg, ADVAIR HFA 115 mcg/21 mcg, and ADVAIR HFA 230 mcg/21 mcg given as 2 inhalations twice daily in 325 subjects. This trial was stratified into 3 groups according to baseline asthma therapy: subjects using short-acting beta
Improvements in FEV
8.3Onset of Action and Progression of Improvement in Control
The onset of action and progression of improvement in asthma control were evaluated in 2 placebo-controlled U.S. trials and 1 active-controlled U.S. trial. Following the first dose, the median time to onset of clinically significant bronchodilatation (≥15% improvement in FEV
Following the initial dose, predose FEV
No diminution in the 12-hour bronchodilator effect was observed with either ADVAIR HFA 45 mcg/21 mcg (Figures 3 and 4) or ADVAIR HFA 230/21 as assessed by FEV
Figure 3. Percent Change in Serial 12-Hour FEV1 in Subjects Previously Using Either Beta
First Treatment Day
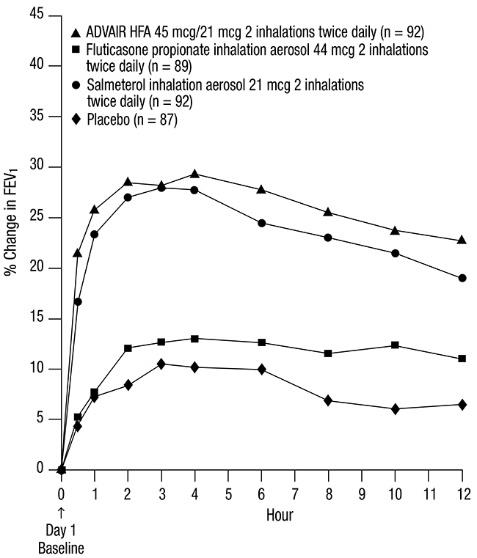
Last Treatment Day (Week 12)
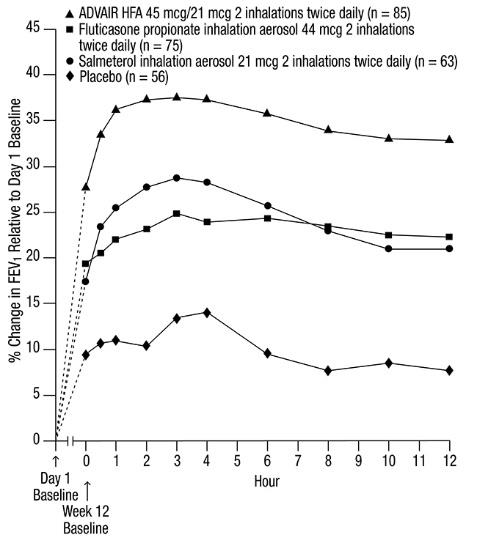
Reduction in asthma symptoms and use of rescue VENTOLIN Inhalation Aerosol and improvement in morning and evening PEF also occurred within the first day of treatment with ADVAIR HFA and continued to improve over the 12 weeks of therapy in all 3 trials.
9HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Product: 50090-4504
NDC: 50090-4504-0 120 AEROSOL, METERED in a INHALER / 1 in a CARTON
10PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Serious Asthma-Related Events
Inform patients with asthma that LABA when used alone increases the risk of asthma-related hospitalization or asthma-related death. Available data show that when ICS and LABA are used together, such as with ADVAIR HFA, there is not a significant increase in the risk of these events.
Not for Acute Symptoms
Inform patients that ADVAIR HFA is not meant to relieve acute asthma symptoms and extra doses should not be used for that purpose. Advise patients to treat acute asthma symptoms with an inhaled, short-acting beta
Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of the following:
- Decreasing effectiveness of inhaled, short-acting beta
- Need for more inhalations than usual of inhaled, short-acting beta
- Significant decrease in lung function as outlined by the physician
Tell patients they should not stop therapy with ADVAIR HFA without physician/provider guidance since symptoms may recur after discontinuation.
Do Not Use Additional Long-acting Beta
Instruct patients not to use other LABA for asthma.
Oropharyngeal Candidiasis
Inform patients that localized infections with
Pneumonia
Patients with COPD have a higher risk of pneumonia; instruct them to contact their healthcare providers if they develop symptoms of pneumonia.
Immunosuppression and Risk of Infections
Warn patients who are on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids to avoid exposure to chickenpox or measles and, if exposed, to consult their physicians without delay. Inform patients of potential worsening of existing tuberculosis; fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections; or ocular herpes simplex.
Hypercorticism and Adrenal Suppression
Advise patients that ADVAIR HFA may cause systemic corticosteroid effects of hypercorticism and adrenal suppression. Additionally, inform patients that deaths due to adrenal insufficiency have occurred during and after transfer from systemic corticosteroids. Patients should taper slowly from systemic corticosteroids if transferring to ADVAIR HFA.
Hypersensitivity Reactions, including Anaphylaxis
Advise patients that immediate hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm, hypotension), including anaphylaxis, may occur after administration of ADVAIR HFA. Patients should discontinue ADVAIR HFA if such reactions occur.
Risks Associated with Beta-agonist Therapy
Inform patients of adverse effects associated with beta
Reduction in Bone Mineral Density
Advise patients who are at an increased risk for decreased BMD that the use of corticosteroids may pose an additional risk.
Reduced Growth Velocity
Inform patients that orally inhaled corticosteroids, including fluticasone propionate, may cause a reduction in growth velocity when administered to pediatric patients. Physicians should closely follow the growth of children and adolescents taking corticosteroids by any route.
Glaucoma and Cataracts
Advise patients that long-term use of ICS may increase the risk of some eye problems (cataracts or glaucoma); consider regular eye examinations.
Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies.
GlaxoSmithKline
Durham, NC 27701
©2024 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
ADH:19PI
11fluticasone propionate and salmeterol xinafoate
