Generic Name
Betamethasone Acetate
Brand Names
Betaloan SUIK, Celestone Soluspan, Betalido, BL-C
FDA approval date: April 28, 2010
Classification: Corticosteroid
Form: Injection, Kit
What is Betaloan SUIK (Betamethasone Acetate)?
For use as an first aid antiseptic pre-operative skin preperation. When oral therapy is not feasible, the intramuscular use of Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension is indicated as follows: Allergic States Control of severe or incapacitating allergic conditions intractable to adequate trials of conventional treatment in asthma, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, drug hypersensitivity reactions, perennial or seasonal allergic rhinitis, serum sickness, transfusion reactions. Dermatologic Diseases Bullous dermatitis herpetiformis, exfoliative erythroderma, mycosis fungoides, pemphigus, severe erythema multiforme . Endocrine Disorders Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, hypercalcemia associated with cancer, nonsuppurative thyroiditis. Hydrocortisone or cortisone is the drug of choice in primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency. Synthetic analogs may be used in conjunction with mineralocorticoids where applicable; in infancy mineralocorticoid supplementation is of particular importance. Gastrointestinal Diseases To tide the patient over a critical period of the disease in regional enteritis and ulcerative colitis. Hematologic Disorders Acquired hemolytic anemia, Diamond-Blackfan anemia, pure red cell aplasia, selected cases of secondary thrombocytopenia. Miscellaneous Trichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement, tuberculous meningitis with subarachnoid block or impending block when used with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy. Neoplastic Diseases For palliative management of leukemias and lymphomas. Nervous System Acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis; cerebral edema associated with primary or metastatic brain tumor or craniotomy. Ophthalmic Diseases Sympathetic ophthalmia, temporal arteritis, uveitis and ocular inflammatory conditions unresponsive to topical corticosteroids. Renal Diseases To induce diuresis or remission of proteinuria in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome or that due to lupus erythematosus. Respiratory Diseases Berylliosis, fulminating or disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy, idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonias, symptomatic sarcoidosis. Rheumatic Disorders As adjunctive therapy for short-term administration in acute gouty arthritis; acute rheumatic carditis; ankylosing spondylitis; psoriatic arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis . For the treatment of dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The intra-articular or soft tissue administration of Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension is indicated as adjunctive therapy for short-term administration in acute gouty arthritis, acute and subacute bursitis, acute nonspecific tenosynovitis, epicondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, synovitis of osteoarthritis. The intralesional administration of Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension is indicated for alopecia areata; discoid lupus erythematosus; keloids; localized hypertrophic, infiltrated, inflammatory lesions of granuloma annulare, lichen planus, lichen simplex chronicus , and psoriatic plaques; necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum. Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension may also be useful in cystic tumors of an aponeurosis or tendon . Iodixanol injection is indicated in for: Iodixanol injection is a radiographic contrast agent indicated for the following: Intra-arterial Procedures. Lidocaine hydrochloride injection is indicated for production of local or regional anesthesia by infiltration techniques such as percutaneous injection and intravenous regional anesthesia by peripheral nerve block techniques such as brachial plexus and intercostal and by central neural techniques such as lumbar and caudal epidural blocks, when the accepted procedures for these techniques as described in standard textbooks are observed. For first aid to decrease germs in minor cuts scrapes burns For preparation of the skin prior to injection.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Betaloan SUIK (Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate)
1DESCRIPTION
Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension, USP is a sterile aqueous suspension containing betamethasone 3 mg per milliliter as betamethasone sodium phosphate, and betamethasone acetate 3 mg per milliliter. Inactive ingredients per mL: dibasic sodium phosphate 7.1 mg; monobasic sodium phosphate 3.4 mg; edetate disodium 0.1 mg; and benzalkonium chloride 0.2 mg as a preservative. The pH is adjusted to between 6.8 and 7.2.
The formula for betamethasone sodium phosphate is C
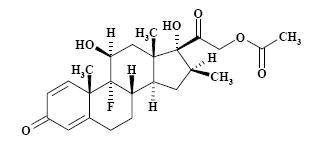
The formula for betamethasone acetate is C
The chemical structures for betamethasone sodium phosphate and betamethasone acetate are as follows:
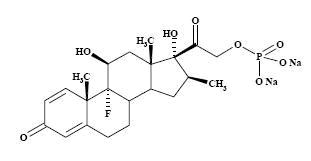
Betamethasone sodium phosphate is a white to practically white, odorless powder, and is hygroscopic. It is freely soluble in water and in methanol, but is practically insoluble in acetone and in chloroform.
Betamethasone acetate is a white to creamy white, odorless powder that sinters and resolidifies at about 165ºC, and remelts at about 200ºC to 220ºC with decomposition. It is practically insoluble in water, but freely soluble in acetone, and is soluble in alcohol and in chloroform.
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Glucocorticoids, naturally occurring and synthetic, are adrenocortical steroids that are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Naturally occurring glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone and cortisone), which also have salt-retaining properties, are used as replacement therapy in adrenocortical deficiency states. Their synthetic analogs are primarily used for their anti-inflammatory effects in disorders of many organ systems. A derivative of prednisolone, betamethasone has a 16β-methyl group that enhances the anti-inflammatory action of the molecule and reduces the sodium- and water-retaining properties of the fluorine atom bound at carbon 9.
Betamethasone sodium phosphate, a soluble ester, provides prompt activity, while betamethasone acetate is only slightly soluble and affords sustained activity.
3INDICATIONS AND USAGE
When oral therapy is not feasible, the
Allergic StatesControl of severe or incapacitating allergic conditions intractable to adequate trials of conventional treatment in asthma, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, drug hypersensitivity reactions, perennial or seasonal allergic rhinitis, serum sickness, transfusion reactions.
Dermatologic DiseasesBullous dermatitis herpetiformis, exfoliative erythroderma, mycosis fungoides, pemphigus, severe erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
Endocrine DisordersCongenital adrenal hyperplasia, hypercalcemia associated with cancer, nonsuppurative thyroiditis.
Hydrocortisone or cortisone is the drug of choice in primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency. Synthetic analogs may be used in conjunction with mineralocorticoids where applicable; in infancy mineralocorticoid supplementation is of particular importance.
Gastrointestinal DiseasesTo tide the patient over a critical period of the disease in regional enteritis and ulcerative colitis.
Hematologic DisordersAcquired (autoimmune) hemolytic anemia, Diamond-Blackfan anemia, pure red cell aplasia, selected cases of secondary thrombocytopenia.
MiscellaneousTrichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement, tuberculous meningitis with subarachnoid block or impending block when used with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy.
Neoplastic DiseasesFor palliative management of leukemias and lymphomas.
Nervous SystemAcute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis; cerebral edema associated with primary or metastatic brain tumor or craniotomy.
Ophthalmic DiseasesSympathetic ophthalmia, temporal arteritis, uveitis and ocular inflammatory conditions unresponsive to topical corticosteroids.
Renal DiseasesTo induce diuresis or remission of proteinuria in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome or that due to lupus erythematosus.
Respiratory DiseasesBerylliosis, fulminating or disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy, idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonias, symptomatic sarcoidosis.
Rheumatic DisordersAs adjunctive therapy for short-term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in acute gouty arthritis; acute rheumatic carditis; ankylosing spondylitis; psoriatic arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low-dose maintenance therapy). For the treatment of dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
The
The
Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension may also be useful in cystic tumors of an aponeurosis or tendon (ganglia).
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any components of this product.
5ADVERSE REACTIONS
(listed alphabetically, under each subsection)
Allergic Reactions
Anaphylactoid reaction, anaphylaxis, angioedema.
Cardiovascular
Bradycardia, cardiac arrest, cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac enlargement, circulatory collapse, congestive heart failure, fat embolism, hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in premature infants, myocardial rupture following recent myocardial infarction (see
Dermatologic
Acne, allergic dermatitis, cutaneous and subcutaneous atrophy, dry scaly skin, ecchymoses and petechiae, edema, erythema, hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation, impaired wound healing, increased sweating, rash, sterile abscess, striae, suppressed reactions to skin tests, thin fragile skin, thinning scalp hair, urticaria.
Endocrine
Decreased carbohydrate and glucose tolerance, development of cushingoid state, glucosuria, hirsutism, hypertrichosis, increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness (particularly in times of stress, as in trauma, surgery, or illness), suppression of growth in pediatric patients.
Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances
Congestive heart failure in susceptible patients, fluid retention, hypokalemic alkalosis, potassium loss, sodium retention.
Gastrointestinal
Abdominal distention, bowel/bladder dysfunction (after intrathecal administration), elevation in serum liver enzyme levels (usually reversible upon discontinuation), hepatomegaly, increased appetite, nausea, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer with possible perforation and hemorrhage, perforation of the small and large intestine (particularly in patients with inflammatory bowel disease), ulcerative esophagitis.
Metabolic
Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism.
Musculoskeletal
Aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads, calcinosis (following intra-articular or intralesional use), Charcot-like arthropathy, loss of muscle mass, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, pathologic fracture of long bones, postinjection flare (following intra-articular use), steroid myopathy, tendon rupture, vertebral compression fractures.
Neurologic/Psychiatric
Convulsions, depression, emotional instability, euphoria, headache, increased intracranial pressure with papilledema (pseudotumor cerebri) usually following discontinuation of treatment, insomnia, mood swings, neuritis, neuropathy, paresthesia, personality changes, psychic disorders, vertigo. Arachnoiditis, meningitis, paraparesis/paraplegia, and sensory disturbances have occurred after intrathecal administration (see
Ophthalmic
Exophthalmos, glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure, posterior subcapsular cataracts, rare instances of blindness associated with periocular injections.
Other
Abnormal fat deposits, decreased resistance to infection, hiccups, increased or decreased motility and number of spermatozoa, malaise, moon face, weight gain.
6OVERDOSAGE
Treatment of acute overdose is by supportive and symptomatic therapy. For chronic overdosage in the face of severe disease requiring continuous steroid therapy, the dosage of the corticosteroid may be reduced only temporarily, or alternate day treatment may be introduced.
7DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Benzyl alcohol as a preservative has been associated with a fatal “Gasping Syndrome” in premature infants and infants of low birth weight. Solutions used for further dilution of this product should be preservative-free when used in the neonate, especially the premature infant. The initial dosage of parenterally administered Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension may vary from 0.25 to 9 mg per day depending on the specific disease entity being treated. However, in certain overwhelming, acute, life-threatening situations, administrations in dosages exceeding the usual dosages may be justified and may be in multiples of the oral dosages.
It Should Be Emphasized That Dosage Requirements Are Variable and Must Be Individualized on the Basis of the Disease Under Treatment and the Response of the Patient.After a favorable response is noted, the proper maintenance dosage should be determined by decreasing the initial drug dosage in small decrements at appropriate time intervals until the lowest dosage which will maintain an adequate clinical response is reached. Situations which may make dosage adjustments necessary are changes in clinical status secondary to remissions or exacerbations in the disease process, the patient’s individual drug responsiveness, and the effect of patient exposure to stressful situations not directly related to the disease entity under treatment. In this latter situation it may be necessary to increase the dosage of the corticosteroid for a period of time consistent with the patient’s condition. If after long-term therapy the drug is to be stopped, it is recommended that it be withdrawn gradually rather than abruptly.
In the treatment of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis, daily doses of 30 mg of betamethasone for a week followed by 12 mg every other day for 1 month are recommended (see
In pediatric patients, the initial dose of betamethasone may vary depending on the specific disease entity being treated. The range of initial doses is 0.02 to 0.3 mg/kg/day in three or four divided doses (0.6 to 9 mg/m
These dose relationships apply only to oral or intravenous administration of these compounds. When these substances or their derivatives are injected intramuscularly or into joint spaces, their relative properties may be greatly altered.
If coadministration of a local anesthetic is desired, Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension may be mixed with 1% or 2% lidocaine hydrochloride, using the formulations which do not contain parabens. Similar local anesthetics may also be used. Diluents containing methylparaben, propylparaben, phenol, etc., should be avoided, since these compounds may cause flocculation of the steroid. The required dose of Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension is first withdrawn from the vial into the syringe. The local anesthetic is then drawn in, and the syringe shaken briefly.
7.1Bursitis, Tenosynovitis, Peritendinitis
In acute subdeltoid, subacromial, olecranon, and prepatellar bursitis, one intrabursal injection of 1 mL Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension can relieve pain and restore full range of movement. Several intrabursal injections of corticosteroids are usually required in recurrent acute bursitis and in acute exacerbations of chronic bursitis. Partial relief of pain and some increase in mobility can be expected in both conditions after one or two injections. Chronic bursitis may be treated with reduced dosage once the acute condition is controlled. In tenosynovitis and tendinitis, three or four local injections at intervals of 1 to 2 weeks between injections are given in most cases. Injections should be made into the affected tendon sheaths rather than into the tendons themselves. In ganglions of joint capsules and tendon sheaths, injection of 0.5 mL directly into the ganglion cysts has produced marked reduction in the size of the lesions.
7.2Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Following intra-articular administration of 0.5 to 2 mL of Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension, relief of pain, soreness, and stiffness may be experienced. Duration of relief varies widely in both diseases. Intra-articular Injection of Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension is well tolerated in joints and periarticular tissues. There is virtually no pain on injection, and the “secondary flare” that sometimes occurs a few hours after intra-articular injection of corticosteroids has not been reported with Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension. Using sterile technique, a 20- to 24-gauge needle on an empty syringe is inserted into the synovial cavity and a few drops of synovial fluid are withdrawn to confirm that the needle is in the joint. The aspirating syringe is replaced by a syringe containing Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension and injection is then made into the joint.
A portion of the administered dose of Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension is absorbed systemically following intra-articular injection. In patients being treated concomitantly with oral or parenteral corticosteroids, especially those receiving large doses, the systemic absorption of the drug should be considered in determining intra-articular dosage.
7.3Dermatologic Conditions
In intralesional treatment, 0.2 mL/cm
7.4Disorders of the Foot
A tuberculin syringe with a 25-gauge, 3/4-inch needle is suitable for most injections into the foot. The following doses are recommended at intervals of 3 days to a week.
8HOW SUPPLIED
Betaloan Suik Kit supplied as:
1 Kit NDC 80425-0347-01
Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate Injectable Suspension, USP, 5 mL multiple dose vial; box of one: NDC 0517-0720-01
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Rx only
AMERICAN
REGENT, INC.
SHIRLEY, NY 11967
REGENT, INC.
SHIRLEY, NY 11967
Revised September 2015
Distributed by Advanced Rx Pharmacy of Tennessee, LLC
9Principal Display Panel – Carton Label
NDC: 80425-0347-01 Rx Only
Betaloan SUIK
Kit Contains
1 Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Betamethasone Acetate mg/mL (5mL)
1 Gebauer's Pain Ease
1 BD Integra Syringe with Retracting BD PrecisionGlide™ Needle (3mL 23G x 1”)
1 BD Integra Syringe with Retracting BD PrecisionGlide™ Needle (3mL 25G x 1”)
1 Pair Nitrile Powder Free Sterile Gloves (M)
1 Drape
1 Adhesive Bandage
1 Isopropyl Alcohol 70% Prep Pad
5 Non-sterile 4x4 gauze
1 Face Mask
1 Dose
Single Use Only
Distributed by
Advanced Rx Pharmacy of Tennessee, LLC
