Brand Name
Tolectin
Generic Name
Tolmetin
View Brand Information FDA approval date: April 11, 2023
Classification: Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug
Form: Tablet, Capsule
What is Tolectin (Tolmetin)?
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of TOLECTIN tablets, USP and other treatment options before deciding to use TOLECTIN tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. TOLECTIN tablets are indicated for the relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. TOLECTIN tablets are indicated in the treatment of acute flares and the long-term management of the chronic disease. TOLECTIN tablets are also indicated for treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. The safety and effectiveness of TOLECTIN tablets have not been established in pediatric patients under 2 years of age.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Tolectin (tolmetin sodium)
BOXED WARNING
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use (see WARNINGSand PRECAUTIONS).
• TOLECTIN tablets are contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see CONTRAINDICATIONSand WARNINGS).
Gastrointestinal Risk
• NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events (see WARNINGS).
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use (see WARNINGSand PRECAUTIONS).
• TOLECTIN tablets are contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see CONTRAINDICATIONSand WARNINGS).
Gastrointestinal Risk
• NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events (see WARNINGS).
1DESCRIPTION
Each tablet for oral administration contains 738 mg of tolmetin sodium, USP as the dihydrate in an amount equivalent to 600 mg of tolmetin. Each tablet contains 54 mg (2.35 mEq) of sodium and the following inactive ingredients: black iron oxide, crospovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, pregelatinized starch (maize), sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, triacetin and yellow iron oxide.
The pKa of tolmetin is 3.5 and tolmetin sodium is freely soluble in water, soluble in methanol and slightly soluble in alcohol. Tolmetin sodium is a nonselective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent. The structural formula is:
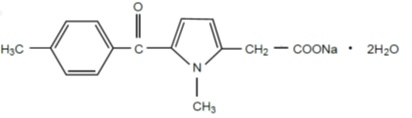
(C
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Studies in animals have shown TOLECTIN (tolmetin sodium) to possess anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activity. In the rat, TOLECTIN prevents the development of experimentally induced polyarthritis and also decreases established inflammation.
The mode of action of TOLECTIN is not known. However, studies in laboratory animals and man have demonstrated that the anti-inflammatory action of TOLECTIN is not due to pituitary- adrenal stimulation. TOLECTIN inhibits prostaglandin synthetase in vitro and lowers the plasma level of prostaglandin E in man. This reduction in prostaglandin synthesis may be responsible for the anti-inflammatory action. TOLECTIN does not appear to alter the course of the underlying disease in man.
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in normal volunteers, TOLECTIN is rapidly and almost completely absorbed with peak plasma levels being reached within 30 to 60 minutes after an oral therapeutic dose. In controlled studies, the time to reach peak tolmetin plasma concentration is approximately 20 minutes longer following administration of a 600 mg tablet, compared to an equivalent dose given as 200 mg tablets. The clinical meaningfulness of this finding, if any, is unknown. Tolmetin displays a biphasic elimination from the plasma consisting of a rapid phase with a half-life of 1 to 2 hours followed by a slower phase with a half-life of about 5 hours. Peak plasma levels of approximately 40 mcg/mL are obtained with a 400 mg oral dose. Essentially all of the administered dose isrecovered in the urine in 24 hours either as an inactive oxidative metabolite or as conjugates of tolmetin. An 18-day multiple- dose study demonstrated no accumulation of tolmetin when compared with a single dose.
In two fecal blood loss studies of 4 to 6 days duration involving 15 subjects each, TOLECTIN did not induce an increase in blood loss over that observed during a 4-day drug free control period. In the same studies, aspirin produced a greater blood loss than occurred during the drug free control period, and a greater blood loss than occurred during the TOLECTIN treatment period. In one of the two studies, indomethacin produced a greater fecal blood loss than occurred during the drug free control period; in the second study, indomethacin did not induce a significant increase in blood loss.
TOLECTIN is effective in treating both the acute flares and in the long-term management of the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
In patients with either rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, TOLECTIN is as effective as aspirin and indomethacin in controlling disease activity, but the frequency of the milder gastrointestinal adverse effects and tinnitus was less than in aspirin-treated patients, and the incidence of central nervous system adverse effects was less than in indomethacin-treated patients.
In patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, TOLECTIN is as effective as aspirin in controlling disease activity, with a similar incidence of adverse reactions. Mean SGOT values, initially elevated in patients on previous aspirin therapy, remained elevated in the aspirin group and decreased in the TOLECTIN group.
TOLECTIN has produced additional therapeutic benefit when added to a regimen of gold salts and, to a lesser extent, with corticosteroids. TOLECTIN should not be used in conjunction with salicylates since greater benefit from the combination is not likely, but the potential for adverse reactions is increased.
3INDICATIONS & USAGE
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of TOLECTIN tablets, USP and other treatment options before deciding to use TOLECTIN tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see
TOLECTIN tablets are indicated for the relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. TOLECTIN tablets are indicated in the treatment of acute flares and the long-term management of the chronic disease.
TOLECTIN tablets are also indicated for treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. The safety and effectiveness of TOLECTIN tablets have not been established in pediatric patients under 2 years of age (see PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Useand DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
TOLECTIN tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to tolmetin sodium.
5ADVERSE REACTIONS
The adverse reactions which have been observed in clinical trials encompass observations in about 4,370 patients treated with TOLECTIN, over 800 of whom have undergone at least one year of therapy. These adverse reactions, reported below by body system, are among those typical of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and, as expected, gastrointestinal complaints were most frequent. In clinical trials with tolmetin, about 10% of patients dropped out because of adverse reactions, mostly gastrointestinal in nature.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Poly Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-256-270-7552 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
6MANAGEMENT OF OVERDOSAGE
In the event of overdosage, the stomach should be emptied by inducing vomiting or by gastric lavage followed by the administration of activated charcoal.
7DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of TOLECTIN and other treatment options before deciding to use TOLECTIN. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see
8HOW SUPPLIED
TOLECTIN Tablets, USP are available containing 738 mg of tolmetin sodium, USP as the dihydrate in an amount equivalent to 600 mg of tolmetin. The 600 mg tablets are a beige, film-coated, oval-shaped, biconvex, beveled-edge tablet debossed with “R 25” on one side of the tablet and plain on the other side. They are available as follows:
Bottles of 30 Tablets NDC 50991-988-30
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Manufactured for:
Poly Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Owens Cross Roads, AL 35763
Issued: 02/2024
9SPL MEDGUIDE
Medication Guide for Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase:
° with increasing doses of NSAIDs
° with longer use of NSAIDs
Do not take NSAIDs right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).”
° anytime during use
° without warning symptoms
° that may cause death
The risk of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
° past history of stomach ulcers, or stomach or intestinal bleeding with use of NSAIDs
° taking medicines called “corticosteroids”, “anticoagulants”, “SSRIs”, or “SNRIs”
° increasing doses of NSAIDs
° older age
° poor health
° advanced liver disease
° bleeding problems
° longer use of NSAID
° smoking
° drinking alcohol
NSAIDs should only be used:
° exactly as prescribed
° at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
° for the shortest time needed
What are NSAIDs?
NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain.
Who should not take NSAIDs?
Do not take NSAIDs:
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase:
° with increasing doses of NSAIDs
° with longer use of NSAIDs
Do not take NSAIDs right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).”
° anytime during use
° without warning symptoms
° that may cause death
The risk of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
° past history of stomach ulcers, or stomach or intestinal bleeding with use of NSAIDs
° taking medicines called “corticosteroids”, “anticoagulants”, “SSRIs”, or “SNRIs”
° increasing doses of NSAIDs
° older age
° poor health
° advanced liver disease
° bleeding problems
° longer use of NSAID
° smoking
° drinking alcohol
NSAIDs should only be used:
° exactly as prescribed
° at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
° for the shortest time needed
What are NSAIDs?
NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain.
Who should not take NSAIDs?
Do not take NSAIDs:
- if you have had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAIDs.
- right before or after heart bypass surgery.
Before taking NSAIDs, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver or kidney problems
- have high blood pressure
- have asthma
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Taking NSAIDs at about 20 weeks of pregnancy or later may harm your unborn baby. If you need to take NSAIDs for more than 2 days when you are between 20 and 30 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider may need to monitor the amount of fluid in your womb around your baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breast feed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins or herbal supplements. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Do not start taking any new medicine without talking to your healthcare provider first.
- new or worse high blood pressure
- heart failure
- liver problems including liver failure
- kidney problems including kidney failure
- low red blood cells (anemia)
- life-threatening skin reactions
- life threatening allergic reactions
- Other side effects of NSAIDs include:stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
Get emergency help right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- chest pain
- weakness in one part or side of your body
- slurred speech
- swelling of the face or throat
Stop taking your NSAID and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- nausea
- more tired or weaker than usual
- diarrhea
- itching
- your skin or eyes look yellow
- indigestion or stomach pain
- flu-like symptoms
- vomit blood
- there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
- unusual weight gain
- skin rash or blisters with fever
- swelling of the arms, legs, hands and feet
If you take too much of your NSAID, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away.
These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask
your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask
your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
- Aspirin is an NSAID but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
- Some NSAIDs are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
General information about the safe and effective use of NSAIDs
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which they were not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. They may harm them.
If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
Manufactured for:
Rising Pharma Holdings, Inc.
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
Issued: 04/2023
200607
MGR82501-00
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which they were not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. They may harm them.
If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
Manufactured for:
Rising Pharma Holdings, Inc.
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
Issued: 04/2023
200607
MGR82501-00
10PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
