Effexor
What is Effexor (Venlafaxine)?
Effexor (venlafaxine) is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) antidepressant that works by affecting the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain. The medication has received FDA approval for several mental health conditions and is one of the more widely prescribed antidepressants in its class.
Primary FDA-approved uses include:
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
- Panic Disorder with or without agoraphobia
Healthcare providers may also prescribe Effexor “off-label” for other conditions, including:
- Hot flashes associated with menopause
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
The medication works by increasing the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, which helps improve mood, reduce anxiety, and restore interest in daily activities. Unlike some other antidepressants, Effexor’s dual action on both neurotransmitters can make it particularly effective for patients who haven’t responded well to other antidepressant medications.
What are the side effects of Effexor?
Effexor can cause a range of side effects, from mild to severe, and it’s important for patients to be aware of these potential effects. Common side effects typically appear within the first few weeks of treatment and may diminish over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
Common side effects include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Sleep problems (insomnia or unusual dreams)
- Dry mouth
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Sexual dysfunction
- Loss of appetite
- Constipation
- Fatigue
More serious side effects that require immediate medical attention:
- Increased blood pressure
- Serotonin syndrome
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma
- Unusual bleeding or bruising
- Seizures
- Hyponatremia (low sodium levels)
- Increased suicidal thoughts, particularly in young adults
Effexor carries a black box warning (the FDA’s strongest warning) regarding an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children, adolescents, and young adults. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential, especially during the first few months of treatment or after dose adjustments.
One particularly important consideration with Effexor is its discontinuation syndrome. Stopping the medication abruptly can lead to severe withdrawal symptoms, including:
- Brain zaps (electric shock sensations)
- Dizziness and vertigo
- Nausea and vomiting
- Irritability
- Anxiety and agitation
- Sensory disturbances
Is there a generic drug version of Effexor?
Yes, generic versions of Effexor (venlafaxine) are widely available and have been FDA-approved since 2006. The generic is available in both immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (XR) formulations, making it a more cost-effective option for many patients. Generic venlafaxine is considered therapeutically equivalent to brand-name Effexor and contains the same active ingredient.
The availability of generic versions has significantly reduced treatment costs, as generic medications typically cost substantially less than their brand-name counterparts. While the active ingredient remains the same, generic versions may contain different inactive ingredients, which rarely can affect how individual patients respond to the medication. Most patients transition seamlessly between brand-name and generic versions, though some may notice slight differences in side effects or effectiveness.
Effexor Dosage Information
Effexor dosing varies depending on the condition being treated, the formulation being used (IR or XR), and individual patient factors. The medication is available in multiple strengths, and dosing typically starts low and increases gradually to minimize side effects.
For Major Depressive Disorder:
- Starting dose: 37.5-75 mg/day
- Usual target dose: 150-225 mg/day
- Maximum dose: 375 mg/day
For Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
- Starting dose: 37.5-75 mg/day
- Usual target dose: 75-225 mg/day
- Maximum dose: 225 mg/day
For Social Anxiety Disorder:
- Starting dose: 75 mg/day
- Usual maintenance dose: 75 mg/day
- Maximum dose: 75 mg/day
Important dosing considerations include:
Administration Guidelines:
- Take at the same time each day
- Extended-release capsules should be taken with food
- Capsules should be swallowed whole, not crushed or chewed
- If using extended-release capsules, they can be carefully opened and sprinkled on applesauce if needed
Special Populations:
- Elderly patients may require lower doses
- Patients with liver or kidney problems may need dose adjustments
- Gradual dose reduction is essential when discontinuing
Healthcare providers will determine the most appropriate starting dose and adjust based on response and tolerability. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is important, as Effexor can cause hypertension in some patients. Any dose changes should be made under medical supervision to minimize the risk of discontinuation symptoms or other adverse effects.
The medication should be stored at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. Patients should never adjust their dose or stop taking Effexor without consulting their healthcare provider, as this can lead to severe withdrawal symptoms. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress and address any concerns that may arise during treatment.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
- Panic Disorder (PD)
- 37.5 mg extended-release capsule: grey cap and peach body with "W" and "Effexor XR" on the cap and "37.5" on the body
- 75 mg extended-release capsule: peach cap and body with "W" and "Effexor XR" on the cap and "75" on the body
- 150 mg extended-release capsule: dark orange cap and body with "W" and "Effexor XR" on the cap and "150" on the body
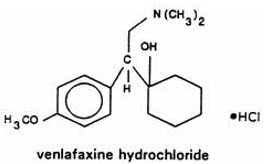
- with known hypersensitivity to venlafaxine hydrochloride, desvenlafaxine succinate or to any excipients in the formulation
- taking, or within 14 days of stopping, MAOIs (including the MAOIs linezolid and intravenous methylene blue) because of the risk of serotonin syndrome
- Hypersensitivity
- Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Adolescents and Young Adults
- Serotonin Syndrome
- Elevated Blood Pressure
- Increased Risk of Bleeding
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma
- Activation of Mania/Hypomania
- Discontinuation Syndrome
- Seizure
- Hyponatremia
- Weight and Height changes in Pediatric Patients
- Appetite Changes in Pediatric Patients
- Interstitial Lung Disease and Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- Sexual Dysfunction
- 37.5 mg, grey cap/peach body with "W" and "Effexor XR" on the cap and "37.5" on the body.
- 75 mg, peach cap and body with "W" and "Effexor XR" on the cap and "75" on the body.
- 150 mg, dark orange cap and body with "W" and "Effexor XR" on the cap and "150" on the body.

(venlafaxine HCl)
Extended-Release Capsules
37.5 mg

NDC 0008-0837-03
(venlafaxine HCl)
Extended-Release Capsules

(venlafaxine HCl)
Extended-Release Capsules
75 mg
NDC 0008-0833-03
(venlafaxine HCl)
Extended-Release Capsules


(venlafaxine HCl)
Extended-Release Capsules
150 mg

NDC 0008-0836-03
(venlafaxine HCl)
Extended-Release Capsules