Brand Name
Sevenfact
Generic Name
VIIa
View Brand Information FDA approval date: April 01, 2023
Form: Kit
What is Sevenfact (VIIa)?
SEVENFACT [coagulation factor VIIa -jncw] is indicated for the treatment and control of bleeding episodes occurring in adults and adolescents with hemophilia A or B with inhibitors. Limitation of Use: SEVENFACT is not indicated for the treatment of patients with congenital Factor VII deficiency. SEVENFACT [coagulation factor VIIa -jncw] is a coagulation factor VIIa concentrate indicated for the treatment and control of bleeding episodes occurring in adults and adolescents with hemophilia A or B with inhibitors . Limitation of Use: SEVENFACT is not indicated for treatment of congenital factor VII deficiency.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Sevenfact (Coagulation Factor VIIa Recombinant Human)
WARNING: THROMBOSIS
● Serious arterial and venous thrombotic events may occur following administration of SEVENFACT®. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
● Discuss the risks and explain the signs and symptoms of thrombotic and thromboembolic events to patients who will receive SEVENFACT®.
● Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of activation of the coagulation system and for thrombosis.
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SEVENFACT is indicated for the treatment and control of bleeding episodes occurring in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older with hemophilia A or B with inhibitors.
Limitations of Use:
SEVENFACT is not indicated for the treatment of patients with congenital Factor VII deficiency.
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
SEVENFACT is a white to off-white lyophilized powder for reconstitution in a colorless solution for injection. It is supplied in single-dose vial sizes containing 1 mg, 2 mg or 5 mg of coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw.
The diluent for reconstitution of SEVENFACT is supplied in single-dose prefilled glass syringes containing 1.1 mL, 2.2 mL or 5.2 mL sterile Water for Injection. It is a clear colorless solution.
After reconstitution with the appropriate volume of Water for Injection diluent, each mL of SEVENFACT contains 1 mg per mL of coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw (1,000 micrograms per mL).
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
SEVENFACT is contraindicated in patients with:
- known allergy to rabbits or rabbit proteins. Exposure to SEVENFACT in these patients can result in severe hypersensitivity reaction.
- severe hypersensitivity reaction to SEVENFACT or any of its components. Exposure to SEVENFACT in these patients can result in severe hypersensitivity reaction.
4DRUG INTERACTIONS
Clinical experience with pharmacologic use of FVIIa-containing products indicates an elevated risk of serious thrombotic events when used simultaneously with activated prothrombin complex concentrates.
5DESCRIPTION
SEVENFACT [coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw] is a sterile, white to off-white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial containing either 1 mg, 2 mg or 5 mg of coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw as the active ingredient. SEVENFACT is to be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection in a pre-filled syringe supplied with the product. The reconstituted product is a clear to slightly opaque solution of coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw at a concentration of 1 mg of protein per mL with a pH of approximately 6.0. SEVENFACT is formulated with arginine, isoleucine, citrate, glycine, lysine and polysorbate 80. It does not contain any antimicrobial preservatives nor human or bovine plasma-derived proteins.
The active ingredient in SEVENFACT, activated coagulation Factor VII, is a glycoprotein of 406 amino acids with a molecular weight of approximately 50 kilodaltons. The amino acid sequence of activated coagulation Factor VII is identical to that of human plasma-derived Factor VIIa. It is >99% pure with a nominal specific activity of 45,000 IU/mg of protein when tested against the World Health Organization international standard for human Factor VIIa activity.
SEVENFACT is produced by recombinant DNA technology using genetically engineered rabbits into which the DNA coding sequence for human Factor VII has been introduced. Human Factor VII is expressed in the rabbit mammary gland and secreted into the milk. During purification and processing, Factor VII is enzymatically converted to activated Factor VII. The manufacturing process of SEVENFACT includes specific steps to reduce impurities. SEVENFACT may contain trace amounts of rabbit proteins. The purification process also includes steps that are validated to inactivate or remove viruses, such as Xenotropic murine leukemia virus (X-MuLV), bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), Pseudorabies virus (PRV), Feline Calicivirus (FCV), and Porcine Parvovirus (PPV).
6CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy and safety of SEVENFACT for treatment of bleeding episodes was evaluated in Study 1, a global, multicenter, randomized, open-label, cross-over study (NCT02020369). The study enrolled 27 patients with hemophilia A or B with inhibitors who were treated for 468 bleeding events, of which 465 were mild or moderate and three were severe bleeding events.
The population characteristics were as follows: Mean age was 31 years (range 12 to 54 years) including five patients 12 to < 18 years of age who experienced 79 bleeding events. Patients were male, predominantly Caucasian (93%), median of 10 (range 3-50) bleeding episodes in six months prior to study enrollment. Overall, target joint(s)/bleeding site(s) were reported in 63% of patients at study entry.
Of the 468 bleeding events in diverse anatomic locations that were treated, 82% were spontaneous and the remaining (18%) were traumatic bleeding episodes; 465 were mild or moderate bleeding events and three were severe (refer to Table 5). The majority (98%) of bleeding events were treated at home, with 88% treated within one hour of recognition of bleeding.
Treatment Regimens for Mild or Moderate Bleeding Episodes
For mild to moderate bleeding episodes, patients were randomized to one of two initial dose regimens of SEVENFACT:
- 75 mcg/kg followed by subsequent doses of 75 mcg/kg every 3 hours as necessary to achieve hemostatic efficacy. A total of eight administrations were allowed in this dose regimen.
- 225 mcg/kg dose followed nine hours later with 75 mcg/kg doses every 3 hours as necessary to achieve hemostatic efficacy. A total of six administrations were allowed in this dose regimen.
Treatment with SEVENFACT was discontinued when bleeding persisted 24 hours after the first administration of SEVENFACT.
In Study 1, patients were randomized to one of two initial dosing regimens and continued on the dose regimen for three months, after which the patients were crossed over to the other dose regimen for three months.
Treatment Regimens for Severe Bleeding Episodes
Patients in the randomized study who experienced a severe bleed were administered the initial dose of 225 mcg/kg SEVENFACT at home, and were required to receive subsequent treatments at 75 mcg/kg every two hours in a hospital or hemophilia treatment center (HTC), if additional doses were considered necessary for treatment of ongoing bleeding. If response to treatment after the first or any subsequent administrations of study drug were satisfactory (i.e., efficacy assessment was rated as “good” or “excellent”), the dosing interval was changed from two hours to three hours for 1 to 2 days, after which the interval could be increased to 4 to 12 hours, depending on the severity of the bleeding episode, for as long as needed.
Bleeding Assessment
The primary endpoint of the study was successful treatment of mild or moderate bleeding episode at 12 hours after initial SEVENFACT dose administration. Success was defined by a combination of the following: patient’s response of “good” or “excellent” using a 4-point hemostatic efficacy scale (presented in Table 4), no further treatment with SEVENFACT beyond the 12-hour time point, no other hemostatic treatment needed for the bleeding episode, no administration of blood products, and no increase in pain beyond 12 hours.
The primary efficacy analysis compared hemostatic efficacy of each dosing regimen with a prespecified objective performance criterion (OPC) of 55%. This OPC was based on historical data for hemostatic efficacy of bypassing agents. The study was powered to detect a 15% improvement over OPC for each dosing regimen. Results of the primary efficacy analysis are shown in Table 5.
Of the 465 mild or moderate bleeding episodes, 17 bleeding events were not evaluable due to missing a hemostatic efficacy assessment at 12 hours.
The proportion of mild or moderate bleeding events with hemostatic efficacy at 12 hours was 82% in the 75 mcg/kg dose regimen group and was 91% in the 225 mcg/kg dose regimen group.
Hemostatic efficacy was evaluated in 79 bleeding events in the five adolescent patients: for the 75 mcg/kg dose regimen, hemostatic efficacy was 93% (95% CI; 81%- 99%) and for the 225 mcg/kg dose regimen, it was 91% (95% CI; 77%-98%), with the confidence intervals given by the Clopper-Pearson exact method.
The median and mean (SD) numbers of administrations per mild or moderate bleeding episode were 2.0 and 2.5 (1.75) for the 75 mcg/kg dose regimen and 1.0 and 1.4 (0.96) for the 225 mcg/kg dose regimen.
The median time to attain good or excellent assessment by the patient was six hours for the 75 mcg/kg dose regimen and three hours for the 225 mcg/kg dose regimen.
There were three severe bleeding episodes, of which one was a traumatic intramuscular bleeding episode and two were spontaneous bleeding episodes in the right hip and kidney. Hemostasis was achieved at 12 hours in the three severe bleeding events. One severe bleed was treated with three 225 mcg/kg doses administered every six hours, which was a deviation from the study protocol-specified dosing. The remaining two patients were treated with 1 and 5 doses of SEVENFACT respectively.
No patient received any alternative therapy prior to 24 hours. In addition, 97.6% of bleeding episodes treated with the 75 mcg/kg dose regimen, and 99.5% of bleeding episodes treated with the 225 mcg/kg dose regimen, did not require treatment with alternative bypassing agents.
7HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
- SEVENFACT [coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw], is supplied as a room temperature stable, white to off-white, lyophilized powder in single-dose vials, one vial per carton. The diluent for reconstitution of SEVENFACT is Water for Injection supplied as a clear colorless solution in a pre-filled syringe.
- Single 1 mg, 2 mg or 5 mg vials of SEVENFACT are available in packages as indicated in Table 6.
- The SEVENFACT vials are made of glass, closed with a bromobutyl rubber stopper (not made with natural rubber latex), and sealed with an aluminum cap.
- The pre-filled diluent syringes are made of glass, with a siliconized bromobutyl rubber plunger (not made with natural rubber latex).
Storage and Handling
- Prior to reconstitution, the SEVENFACT kit should be stored at room temperature but can be stored between 36°F to 86°F (2°C to 30°C), protected from light in the product package. Do not freeze.
- After reconstitution, SEVENFACT should be stored at room temperature but can be stored between 36°F to 86°F (2°C to 30°C), for up to 4 hours. Do not freeze or store in syringes.
8PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients:
- to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Product Information and Instructions for Use).
- about the early signs of hypersensitivity reactions and to seek medical help if the following occur:
- about the signs of thrombosis and to seek medical help if the following occur:
Revised: November 13, 2025
For Information Contact:
Call: 855.718.HEMA (4362)
Email: medinfo@hemabio.com
Call: 855.718.HEMA (4362)
Email: medinfo@hemabio.com
Manufactured by:
Laboratoire Français du Fractionnement et des Biotechnologies S.A. (LFB S.A.)
Puteaux, 92800
France
Laboratoire Français du Fractionnement et des Biotechnologies S.A. (LFB S.A.)
Puteaux, 92800
France
U.S. License Number: 2061
Distributed by:
HEMA Biologics
Louisville, KY 40241
HEMA Biologics
Louisville, KY 40241
U.S. License Number: 2061
9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-1000-1
SEVENFACT
For intravenous use only
Dosage and Administration: Read Package Insert
CONTENTS:
Not made with natural rubber latex
Rx only
LFB
HEMA Biologics
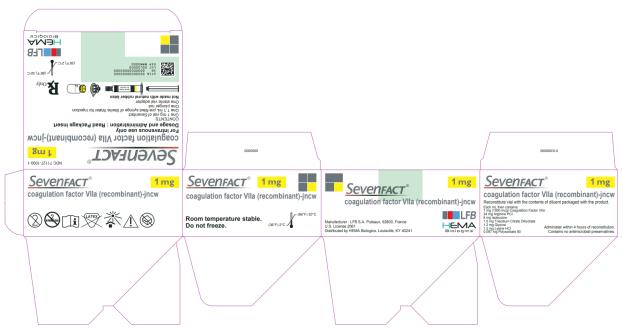
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-2000-1
SEVENFACT
For intravenous use only
Dosage and Administration: Read Package Insert
CONTENTS:
Rx only
LFB
HEMA Biologics
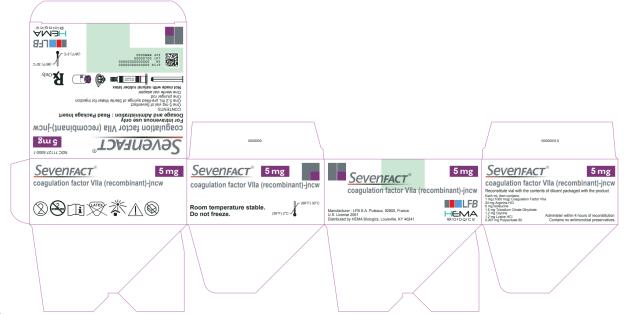
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-5000-1
SEVENFACT
For intravenous use only
Dosage and Administration: Read Package Insert
CONTENTS:
Rx only
LFB
HEMA Biologics

12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-1100-1

13PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-2100-1

14PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-5100-1
15PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-1200-1
LOT 000000000A
EXP MMM0000
Manufactured by LFB S.A.

16PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-2200-1
LOT 000000000AB
EXP MMM0000
Manufactured by LFB S.A. Puteaux, 92800, France

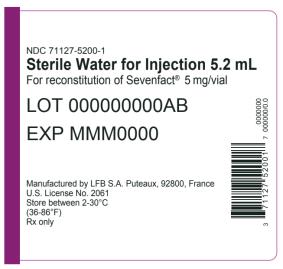
17PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71127-5200-1
LOT 000000000AB
EXP MMM0000
Manufactured by LFB S.A. Puteaux, 92800, France
