Brand Name
Moexipril
View Brand InformationFDA approval date: May 08, 2003
Classification: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor
Form: Tablet
What is Moexipril?
Moexipril hydrochloride tablets are indicated for treatment of patients with hypertension. They may be used alone or in combination with thiazide diuretics. In using moexipril hydrochloride tablets, consideration should be given to the fact that another ACE inhibitor, captopril, has caused agranulocytosis, particularly in patients with renal impairment or collagen-vascular disease. Available data are insufficient to show that moexipril hydrochloride tablets do not have a similar risk. In considering use of moexipril hydrochloride tablets, it should be noted that in controlled trials ACE inhibitors have an effect on blood pressure that is less in black patients than in non-blacks. In addition, ACE inhibitors cause a higher rate of angioedema in black than in non-black patients.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
Effect of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Cardiac Function Assessed by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) in Hypertensive Patients Stratified by Body Mass Index (BMI): A Real World Study
Summary: The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of sacubitril/valsartan on cardiac function assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) in hypertensive patients stratified by BMI.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Moexipril Hydrochloride (Moexipril Hydrochloride)
1DESCRIPTION
Moexipril hydrochloride USP, the hydrochloride salt of moexipril, has the empirical formula C
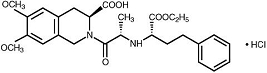
Moexipril hydrochloride USP is a fine white to off-white powder. It is soluble (about 10% weight-to-volume) in distilled water at room temperature.
Moexipril hydrochloride tablets USP are supplied as scored, coated tablets containing 7.5 mg and 15 mg of moexipril hydrochloride USP for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient, moexipril hydrochloride USP, the tablet core contains the following inactive ingredients: crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, magnesium oxide, magnesium stearate and povidone. The film coating contains: hypromellose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol 6000, magnesium stearate, ferric oxide red, ferric oxide black and ferric oxide yellow (15 mg tablet only).
2INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Moexipril hydrochloride tablets are indicated for treatment of patients with hypertension. They may be used alone or in combination with thiazide diuretics.
In using moexipril hydrochloride tablets, consideration should be given to the fact that another ACE inhibitor, captopril, has caused agranulocytosis, particularly in patients with renal impairment or collagen-vascular disease. Available data are insufficient to show that moexipril hydrochloride tablets do not have a similar risk (see
In considering use of moexipril hydrochloride tablets, it should be noted that in controlled trials ACE inhibitors have an effect on blood pressure that is less in black patients than in non-blacks. In addition, ACE inhibitors (for which adequate data are available) cause a higher rate of angioedema in black than in non-black patients (see
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
Moexipril hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to this product and in patients with a history of angioedema related to previous treatment with an ACE inhibitor.
Do not co-administer aliskiren with moexipril hydrochloride in patients with diabetes (see
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
Moexipril hydrochloride has been evaluated for safety in more than 2500 patients with hypertension; more than 250 of these patients were treated for approximately one year. The overall incidence of reported adverse events was only slightly greater in patients treated with moexipril hydrochloride than patients treated with placebo.
Reported adverse experiences were usually mild and transient, and there were no differences in adverse reaction rates related to gender, race, age, duration of therapy, or total daily dosage within the range of 3.75 mg to 60 mg. Discontinuation of therapy because of adverse experiences was required in 3.4% of patients treated with moexipril hydrochloride and in 1.8% of patients treated with placebo. The most common reasons for discontinuation in patients treated with moexipril hydrochloride were cough (0.7%) and dizziness (0.4%).
All adverse experiences considered at least possibly related to treatment that occurred at any dose in placebo-controlled trials of once-daily dosing in more than 1% of patients treated with moexipril hydrochloride alone and that were at least as frequent in the moexipril hydrochloride group as in the placebo group are shown in the following table:
Other adverse events occurring in more than 1% of patients on moexipril that were at least as frequent on placebo include: headache, upper respiratory infection, pain, rhinitis, dyspepsia, nausea, peripheral edema, sinusitis, chest pain, and urinary frequency. See
Other potentially important adverse experiences reported in controlled or uncontrolled clinical trials in less than 1% of moexipril patients or that have been attributed to other ACE inhibitors include the following:
4.1Cardiovascular:
Symptomatic hypotension, postural hypotension, or syncope were seen in 9/1750 (0.51%) patients; these reactions led to discontinuation of therapy in controlled trials in 3/1254 (0.24%) patients who had received moexipril hydrochloride monotherapy and in 1/344 (0.3%) patients who had received moexipril hydrochloride with hydrochlorothiazide (see
4.1.1Renal:
Of hypertensive patients with no apparent preexisting renal disease, 1% of patients receiving moexipril hydrochloride alone and 2% of patients receiving moexipril hydrochloride with hydrochlorothiazide experienced increases in serum creatinine to at least 140% of their baseline values (see
4.1.2Gastrointestinal:
Abdominal pain, constipation, vomiting, appetite/weight change, dry mouth, pancreatitis, hepatitis.
4.1.3Respiratory:
Bronchospasm, dyspnea, eosinophilic pneumonitis.
4.1.4Urogenital:
Renal insufficiency, oliguria.
4.1.5Dermatologic:
Apparent hypersensitivity reactions manifested by urticaria, rash, pemphigus, pruritus, photosensitivity, alopecia.
4.1.6Neurological and Psychiatric:
Drowsiness, sleep disturbances, nervousness, mood changes, anxiety.
4.1.7Other:
Angioedema (see
5OVERDOSAGE
Human overdoses of moexipril have not been reported. In case reports of overdoses with other ACE inhibitors, hypotension has been the principal adverse effect noted. Single oral doses of 2 g/kg moexipril were associated with significant lethality in mice. Rats, however, tolerated single oral doses of up to 3 g/kg.
No data are available to suggest that physiological maneuvers (e.g., maneuvers to change the pH of the urine) would accelerate elimination of moexipril and its metabolites. The dialyzability of moexipril is not known.
Angiotensin II could presumably serve as a specific antagonist-antidote in the setting of moexipril overdose, but angiotensin II is essentially unavailable outside of research facilities. Because the hypotensive effect of moexipril is achieved through vasodilation and effective hypovolemia, it is reasonable to treat moexipril overdose by infusion of normal saline solution. In addition, renal function and serum potassium should be monitored.
6HOW SUPPLIED
Moexipril hydrochloride tablets USP 7.5 mg are peach, round, biconvex, film coated tablets with ‘G' and breakline engraved on one side and ‘209’ on the other side.
Bottles of 90 NDC 68462-209-90
Moexipril hydrochloride tablets USP 15 mg are brown, round, biconvex, film coated tablets with ‘G' and breakline engraved on one side and ‘208’ on the other side.
Bottles of 90 NDC 68462-208-90
7Principal Display Panel - 7.5 mg Bottle
NDC 68462-209-01
MOEXIPRILHYDROCHLORIDETABLETS
7.5 mg

MOEXIPRILHYDROCHLORIDETABLETS
7.5 mg

8Principal Display Panel - 15 mg Bottle
NDC 68462-208-01
MOEXIPRILHYDROCHLORIDETABLETS
15 mg

MOEXIPRILHYDROCHLORIDETABLETS
15 mg
