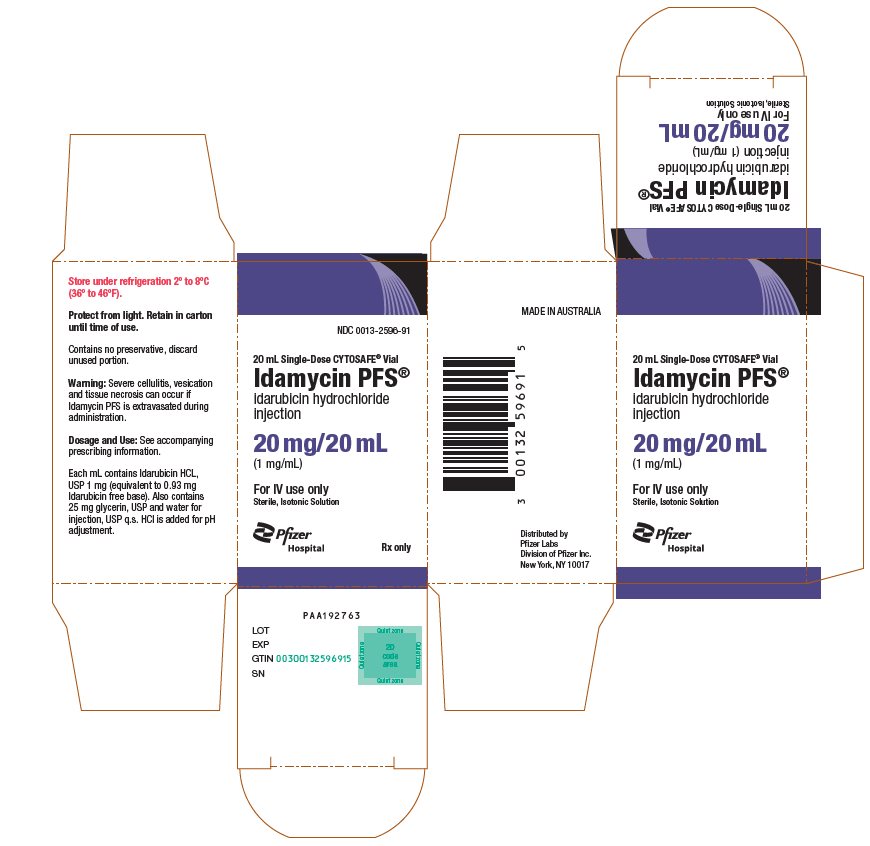
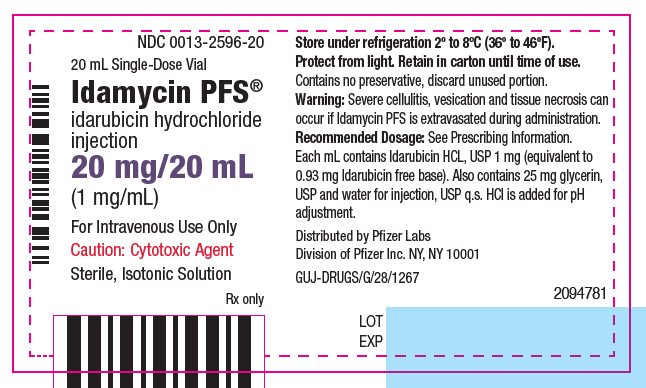
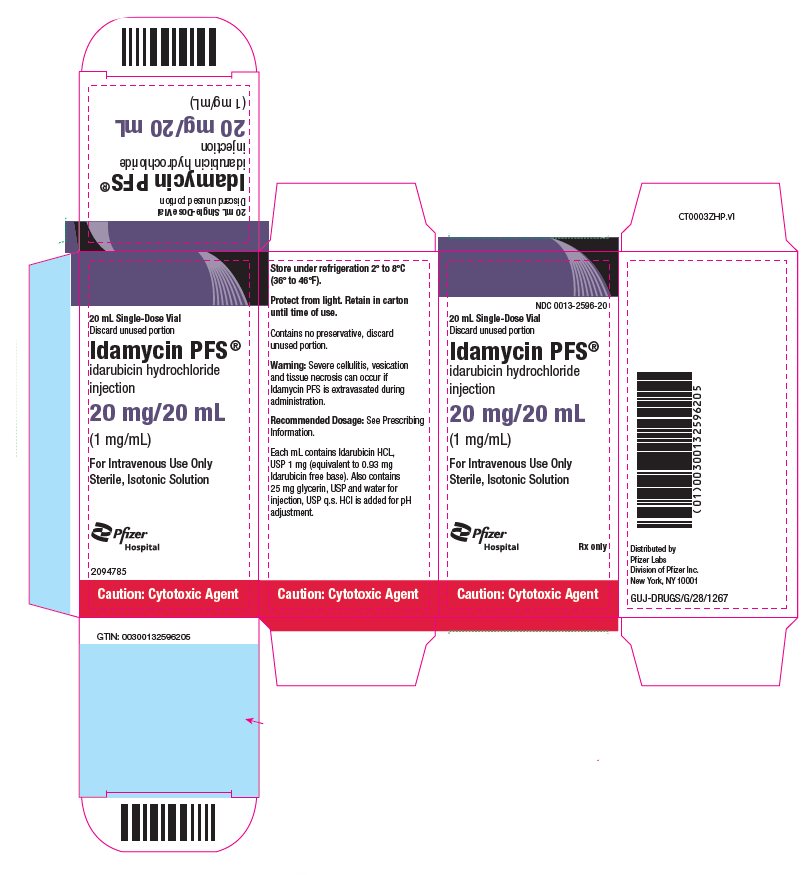
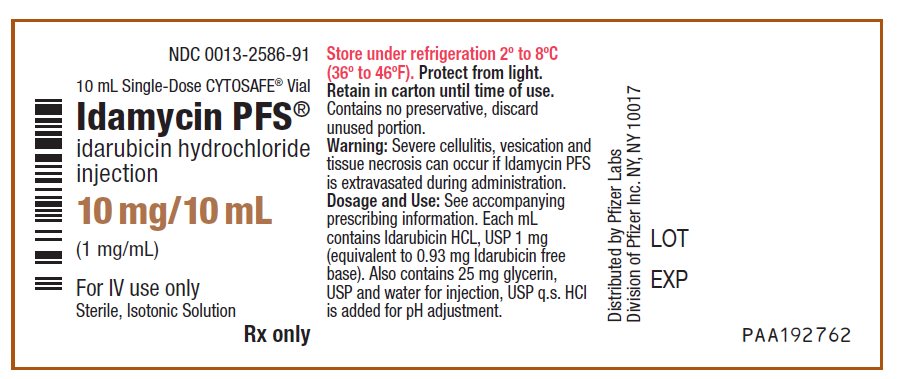
Idamycin PFS
What is Idamycin PFS (Idarubicin)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This phase I/II trial studies the side effects and how well cladribine, idarubicin, cytarabine, and quizartinib work in treating patients with acute myeloid leukemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome that is newly diagnosed, has come back (relapsed), or does not respond to treatment (refractory). Drugs used in chemotherapy, such as cladribine, idarubicin, and cytarabine, work in different ways...
Summary: This phase II trial tests the safety, side effects, and how well combination chemotherapy with fludarabine, high-dose cytarabine, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and idarubicin (FLAG-Ida) followed immediately by reduced-intensity total body radiation therapy, called total body irradiation (TBI), and donor hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) works in treating adults age 60 and older ...
Summary: This study will compare the effects of Quizartinib versus placebo in combination with chemotherapy in participants with newly diagnosed FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3)-internal tandem duplication (ITD) negative acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- IDAMYCIN PFS Injection should be given slowly into a freely flowing intravenous infusion. It must never be given intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Severe local tissue necrosis can occur if there is extravasation during administration.
- As is the case with other anthracyclines the use of IDAMYCIN PFS can cause myocardial toxicity leading to congestive heart failure. Cardiac toxicity is more common in patients who have received prior anthracyclines or who have pre-existing cardiac disease.
- As is usual with antileukemic agents, severe myelosuppression occurs when IDAMYCIN PFS is used at effective therapeutic doses.
- It is recommended that IDAMYCIN PFS be administered only under the supervision of a physician who is experienced in leukemia chemotherapy and in facilities with laboratory and supportive resources adequate to monitor drug tolerance and protect and maintain a patient compromised by drug toxicity. The physician and institution must be capable of responding rapidly and completely to severe hemorrhagic conditions and/or overwhelming infection.
- Dosage should be reduced in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. (See

- ONS Clinical Practice Committee. Cancer Chemotherapy Guidelines and Recommendations for Practice. Pittsburgh, PA: Oncology Nursing Society. 1999: 32–41.
- Recommendations for the Safe Handling of Parenteral Antineoplastic Drugs. Washington, DC; Division of Safety, Clinical Center Pharmacy Department and Cancer Nursing Services, National Institutes of Health; 1992. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service Publication NIH 92–2621.
- AMA Council on Scientific Affairs. Guidelines for Handling Parenteral Antineoplastics. JAMA. 1985; 253:1590–1591.
- National Study Commission on Cytotoxic Exposure - Recommendations for Handling Cytotoxic Agents. 1987. Available from Louis P. Jeffrey, Sc.D., Chairman, National Study Commission on Cytotoxic Exposure, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Allied Health Sciences, 179 Longwood Avenue, Boston, MA 02115.
- Clinical Oncological Society of Australia: Guidelines and Recommendations for Safe Handling of Antineoplastic Agents. Med J Australia. 1983; 1:426–428.
- Jones RB, Frank R, Mass T. Safe Handling of Chemotherapeutic Agents: A Report from the Mount Sinai Medical Center. CA Cancer J Clin.1983; 33: 258–263.
- American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. ASHP Technical Assistance Bulletin on Handling Cytotoxic and Hazardous Drugs. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1990; 47:1033–1049.
- Controlling Occupational Exposure to Hazardous Drugs (OSHA Work-Practice Guidelines). Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 1996; 53: 1669–1685.
idarubicin hydrochloride
injection
(1 mg/mL)

idarubicin hydrochloride
injection
(1 mg/mL)

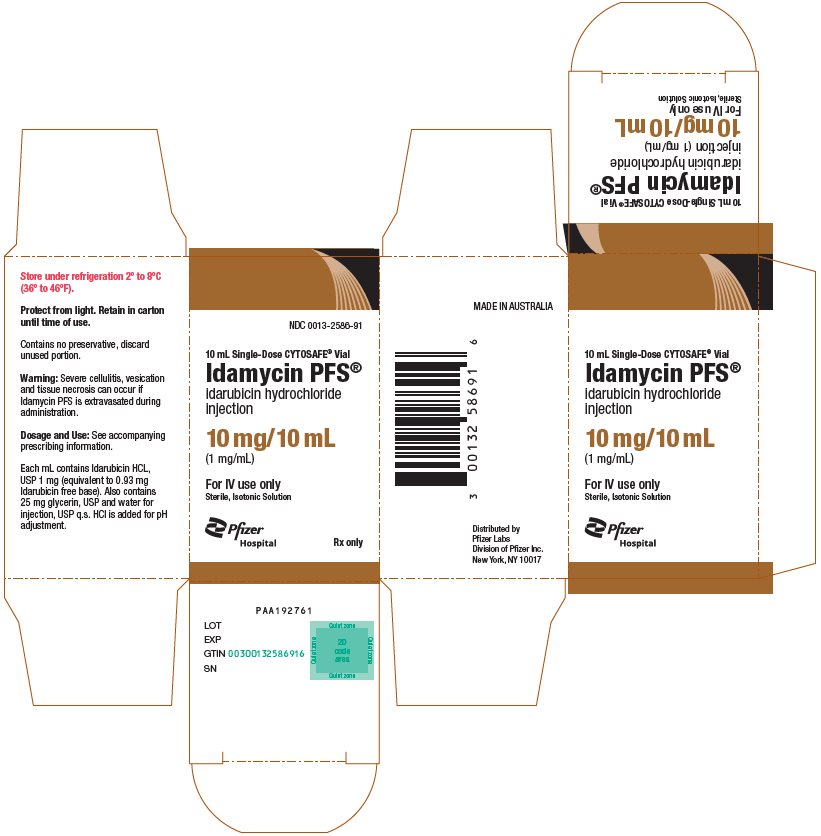
idarubicin hydrochloride
injection
(1 mg/mL)
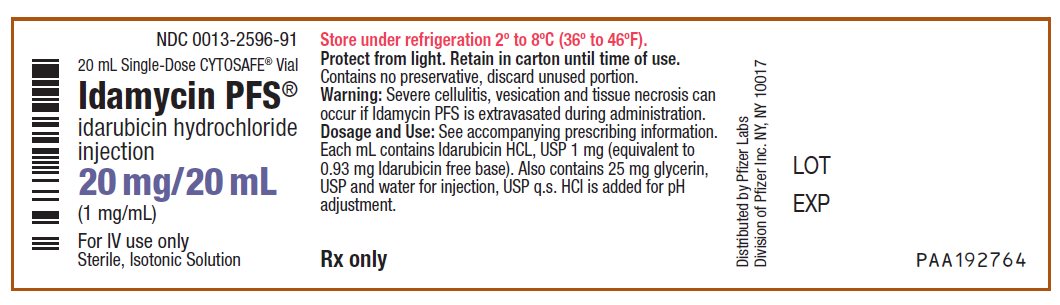
idarubicin hydrochloride
injection
(1 mg/mL)
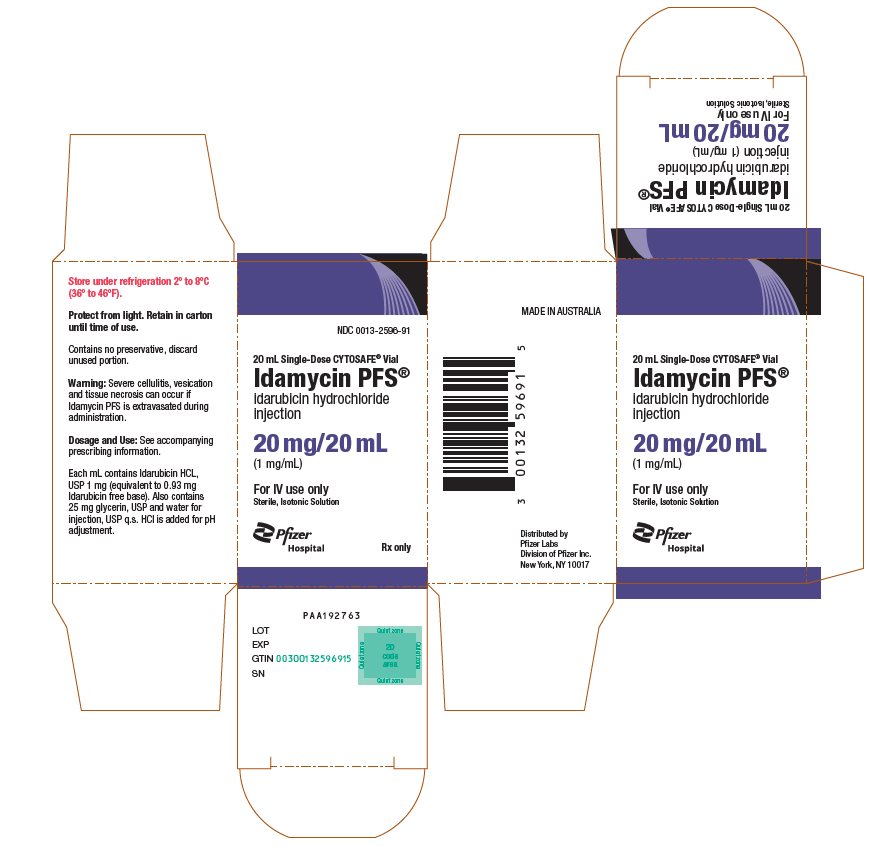

idarubicin hydrochloride
injection
(1 mg/mL)

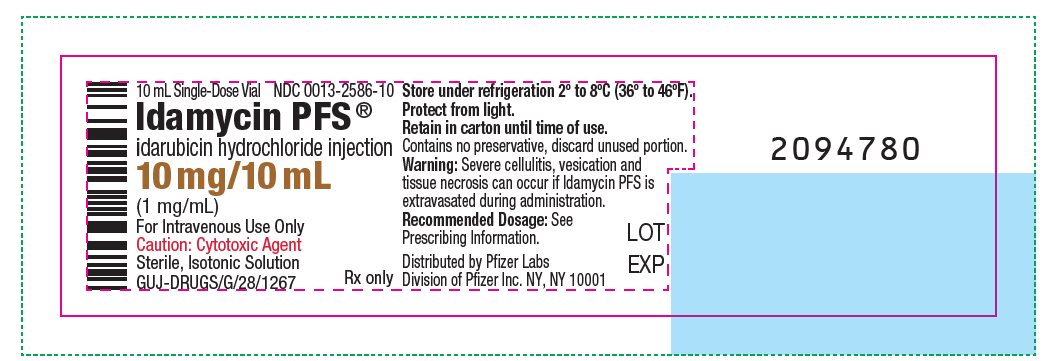
idarubicin hydrochloride
injection
(1 mg/mL)