Brand Name
Lescol
Generic Name
Fluvastatin
View Brand Information FDA approval date: October 06, 2000
Classification: HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor
Form: Tablet, Capsule
What is Lescol (Fluvastatin)?
Therapy with lipid-altering agents should be only one component of multiple risk factor intervention in individuals at significantly increased risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease due to hypercholesterolemia. Drug therapy is indicated as an adjunct to diet when the response to a diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol and other non-pharmacologic measures alone has been inadequate. Fluvastatin capsules are an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor indicated as an adjunctive therapy to diet to: Reduce elevated TC, LDL-C, Apo B, and TG, and to increase HDL-C in adult patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
Evaluation of the Effect of Statins on the Incidence of Side Effects of Platinum Based Chemotherapy in Patients With Solid Tumors
Summary: Platinum based chemotherapy (mainly Cisplatin) is known to cause a variety of adverse effects, including Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Ototoxicity is estimated to affect about 36% of adult patients treated with cisplatin, many therapeutic interventions have been studied to reduce the risk of developing ototoxicity from Cisplatin treatment, Statins have been studied in animals and have shown prom...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Lescol (fluvastatin sodium)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LESCOL XL is indicated:
- To reduce the risk of undergoing coronary revascularization procedures and slow the progression of coronary atherosclerosis in adults with clinically evident coronary heart disease.
- As an adjunct to diet to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in adults with primary hyperlipidemia.
- As an adjunct to diet to reduce LDL-C in adults and pediatric patients 10 years of age and older with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) who require 80 mg of fluvastatin daily.
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Extended-release tablets: 80 mg of fluvastatin: yellow, round, slightly biconvex film-coated tablets with beveled edges debossed with “LESCOL XL” on one side and “80” on the other.
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
LESCOL XL is contraindicated in patients with:
- Acute liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis
- Hypersensitivity to fluvastatin or any of the excipients in LESCOL XL. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome have been reported
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Myopathy and Rhabdomyolysis
- Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy
- Hepatic Dysfunction
- Increases in HbA1c and Fasting Serum Glucose Levels
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In the fluvastatin capsule, clinical trials there were 2326 patients treated with fluvastatin (age range, 18 to 75 years, 44% women, 94% White, 4% Black or African American, 2% other ethnicities) with a median treatment duration of 24 weeks. The most common adverse reactions that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at an incidence greater than placebo were: transaminase increased (0.8%), upper abdominal pain (0.3%), dyspepsia (0.3%), fatigue (0.2%), and diarrhea (0.2%).
In the LESCOL XL clinical trials there were 912 patients treated with LESCOL XL (age range, 21 to 87 years, 52% women, 91% White, 4% Black of African American, 5% other ethnicities) with a median treatment duration of 24 weeks. The most common adverse reactions that led to treatment discontinuation were abdominal pain (0.7%), diarrhea (0.5%), nausea (0.4%), dyspepsia (0.4%) and chest pain (0.3%).
Adverse reactions occurring in the fluvastatin capsules and LESCOL XL controlled trials with a frequency ≥ 2% included the following:
In the LESCOL Intervention Prevention Study (LIPS), the effect of LESCOL (fluvastatin capsules) 40 mg, administered twice daily on the risk of recurrent cardiac events was assessed in 1677 patients with coronary heart disease who had undergone a percutaneous coronary intervention. This was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, patients were treated with dietary/lifestyle counseling and either fluvastatin capsules 40 mg (n = 844) or placebo (n = 833) given twice daily for a median of 3.9 years [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].Table 2. Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 2% in Patients Treated with Fluvastatin Capsules/LESCOL XL and at an Incidence Greater Than Placebo in the LIPS Trial
Elevations in Liver Enzyme Tests
Approximately 1.1% of patients treated with fluvastatin capsules in clinical trials developed dose-related, persistent elevations of serum transaminase levels to more than 3 times the ULN. Fourteen of these patients (0.6%) were discontinued from therapy. In all clinical trials, a total of 33/2969 patients (1.1%) had persistent transaminase elevations with an average fluvastatin exposure of approximately 71.2 weeks; 19 of these patients (0.6%) were discontinued. The majority of patients with these abnormal biochemical findings were asymptomatic.
In a pooled analysis of all placebo-controlled studies in which LESCOL capsules were used, persistent transaminase elevations (> 3 times the ULN on two consecutive weekly measurements) occurred in 0.2%, 1.5%, and 2.7% of patients treated with daily doses of 20, 40, and 80 mg (titrated to 40 mg twice daily) fluvastatin capsules, respectively. Ninety-one percent of the cases of persistent ALT/AST increased abnormalities (20 of 22 patients) occurred within 12 weeks of therapy and in all patients with persistent liver function test abnormalities there was an abnormal liver function test present at baseline or by Week 8.
In the pooled analysis of 24-week controlled trials, persistent transaminase elevation occurred in 1.9%, 1.8%, and 4.9% of patients treated with LESCOL XL 80 mg, fluvastatin capsules 40 mg and fluvastatin capsules 40 mg twice daily, respectively. In 13 of 16 patients treated with LESCOL XL the abnormality occurred within 12 weeks of initiation of treatment with LESCOL XL 80 mg.
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of fluvastatin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Musculoskeletal: Muscle cramps, myopathy, rhabdomyolysis, arthralgias, muscle spasms, muscle weakness, myositis. There have been rare reports of IMNM associated with statin use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Neurological: Dysfunction of certain cranial nerves (including alteration of taste, impairment of extra-ocular movement, facial paresis), tremor, vertigo, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, dysesthesia, peripheral neuropathy, peripheral nerve palsy. There have been rare postmarketing reports of cognitive impairment (e.g., memory loss, forgetfulness, amnesia, memory impairment, confusion) associated with the use of all statins. The reports are generally nonserious, and reversible upon statin discontinuation, with variable times to symptom onset (1 day to years) and symptom resolution (median of 3 weeks). There have been rare reports of new-onset or exacerbation of myasthenia gravis, including ocular myasthenia, and reports of recurrence when the same or a different statin was administered.
Psychiatric: Anxiety, depression, psychic disturbances
Respiratory: Interstitial lung disease
Hypersensitivity reactions: An apparent hypersensitivity syndrome has been reported rarely which has included one or more of the following features: anaphylaxis, angioedema, lupus erythematosus-like syndrome, polymyalgia rheumatica, vasculitis, purpura, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, positive ANA, ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) increase, eosinophilia, arthritis, arthralgia, urticaria, asthenia, photosensitivity reaction, fever, chills, flushing, malaise, dyspnea, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis, hepatitis, including chronic active hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, fatty change in liver, cirrhosis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, hepatoma, anorexia, vomiting, fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure.
Skin: Rash, dermatitis, including bullous dermatitis, eczema, alopecia, pruritus, lichen planus, a variety of skin changes (e.g., nodules, discoloration, dryness of skin/mucous membranes, changes to hair/nails).
Reproductive: Gynecomastia, loss of libido, erectile dysfunction.
Eye: Progression of cataracts (lens opacities), ophthalmoplegia.
Laboratory abnormalities: elevated transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and bilirubin; thyroid function abnormalities.
5OVERDOSAGE
No specific antidotes for LESCOL XL are known. In the event of an overdose of LESCOL XL, consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations.
6DESCRIPTION
Fluvastatin sodium inhibits 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase.
Fluvastatin sodium is [
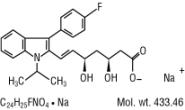
Fluvastatin sodium is a white to pale yellow, hygroscopic powder soluble in water, ethanol and methanol. LESCOL XL is supplied as extended-release tablets containing 84.24 mg of fluvastatin sodium, equivalent to 80 mg of fluvastatin, for oral use. LESCOL XL tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol 8000, potassium bicarbonate, povidone, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide.
7CLINICAL STUDIES
Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
In the LESCOL Intervention Prevention Study (LIPS), the effect of fluvastatin capsules 40 mg administered twice daily on the risk of recurrent cardiac events (time to first occurrence of cardiac death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or revascularization) was assessed in 1677 adult patients with CHD who had undergone a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedure (mean time from PCI to randomization = 3 days). In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, patients were treated with dietary/lifestyle counseling and either fluvastatin 40 mg (n = 844) or placebo (n = 833) given twice daily for a median of 3.9 years. The study population was 84% male, 98% White, with 37% > 65 years of age. Mean baseline lipid concentrations were: total cholesterol 201 mg/dL, LDL-C 132 mg/dL, triglycerides 70 mg/dL, and HDL-C 39 mg/dL.
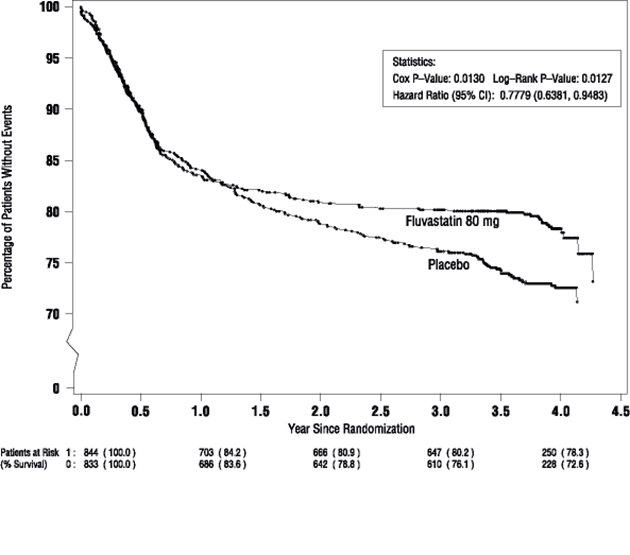
Fluvastatin capsules significantly reduced the risk of recurrent cardiac events (Figure 1) by 22% (p = 0.013, 181 patients in the fluvastatin capsules group versus 222 patients in the placebo group). Revascularization procedures comprised the majority of the initial recurrent cardiac events (143 revascularization procedures in the fluvastatin capsules group and 171 in the placebo group). Consistent trends in risk reduction were observed in patients > 65 years of age.
Figure 1. Primary Endpoint – Recurrent Cardiac Events (Cardiac Death, Nonfatal MI or Revascularization Procedure) (ITT Population)
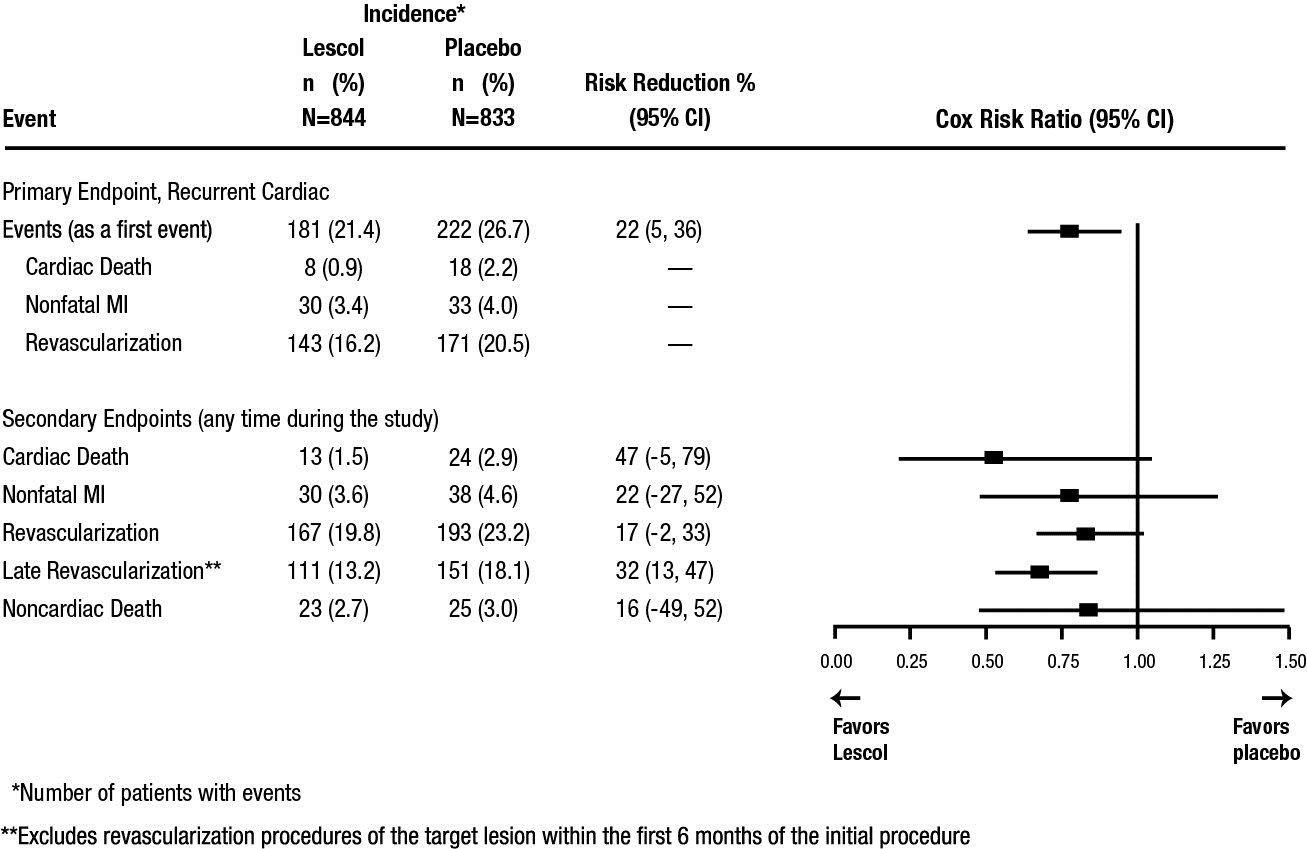
Outcome data for the LESCOL Intervention Prevention Study are shown in Figure 2. After exclusion of revascularization procedures (CABG and repeat PCI) occurring within the first 6 months of the initial procedure involving the originally instrumental site, treatment with fluvastatin capsules was associated with a 32% (p = 0.002) reduction in risk of late revascularization procedures (CABG or PCI occurring at the original site > 6 months after the initial procedure, or at another site).
Figure 2. LESCOL Intervention Prevention Study–- Primary and Secondary Endpoints
In the Lipoprotein and Coronary Atherosclerosis Study (LCAS), the effect of fluvastatin capsule therapy on coronary atherosclerosis was assessed by quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) in patients with CAD and mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia (baseline LDL-C range 115 to 190 mg/dL). In this randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 429 patients were treated with conventional measures (Step 1, AHA Diet) and either fluvastatin 40 mg/day or placebo. In order to provide treatment to patients receiving placebo with LDL-C levels ≥160 mg/dL at baseline, adjunctive therapy with cholestyramine was added after Week 12 to all patients in the study with baseline LDL-C values of ≥ 160 mg/dL, which were present in 25% of the study population. Quantitative coronary angiograms were evaluated at baseline and 2.5 years in 340 (79%) angiographic evaluable patients.
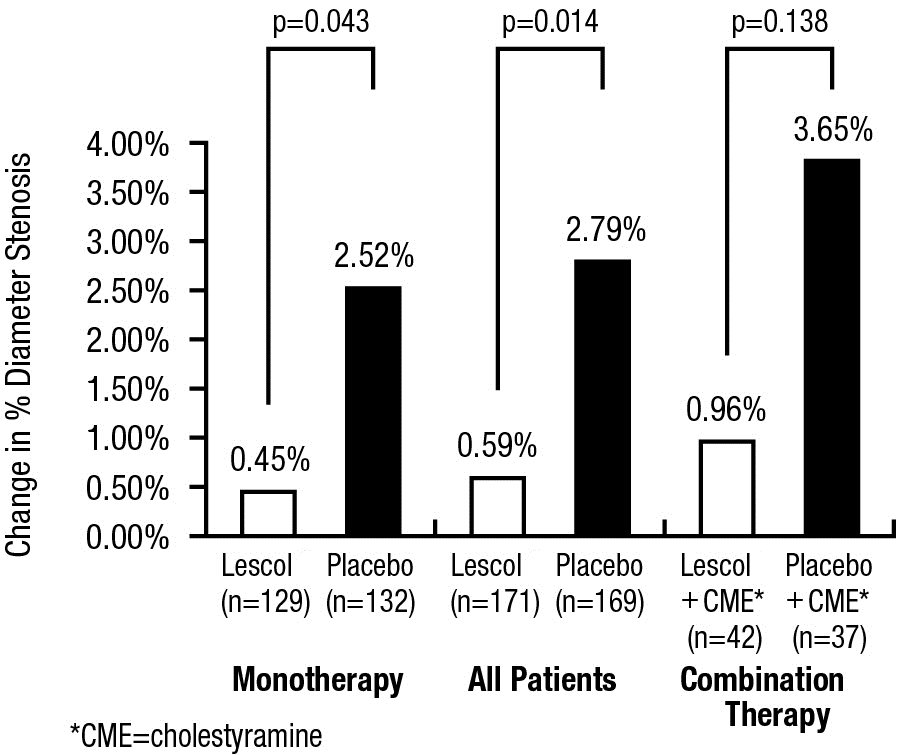
Compared to placebo, fluvastatin capsules significantly slowed the progression of coronary atherosclerosis as measured by within-patient per-lesion change in minimum lumen diameter (MLD), the primary endpoint (Figure 3 below), percent diameter stenosis (Figure 4), and the formation of new lesions (13% of all fluvastatin patients versus 22% of all placebo patients). A significant difference in favor of fluvastatin capsules was found between all fluvastatin and all placebo patients in the distribution among the three categories of definite progression, definite regression, and mixed or no change. Beneficial angiographic results (change in MLD) were independent of patients’ gender and consistent across a range of baseline LDL-C levels.
Figure 3. Change in Minimum Lumen Diameter (mm)
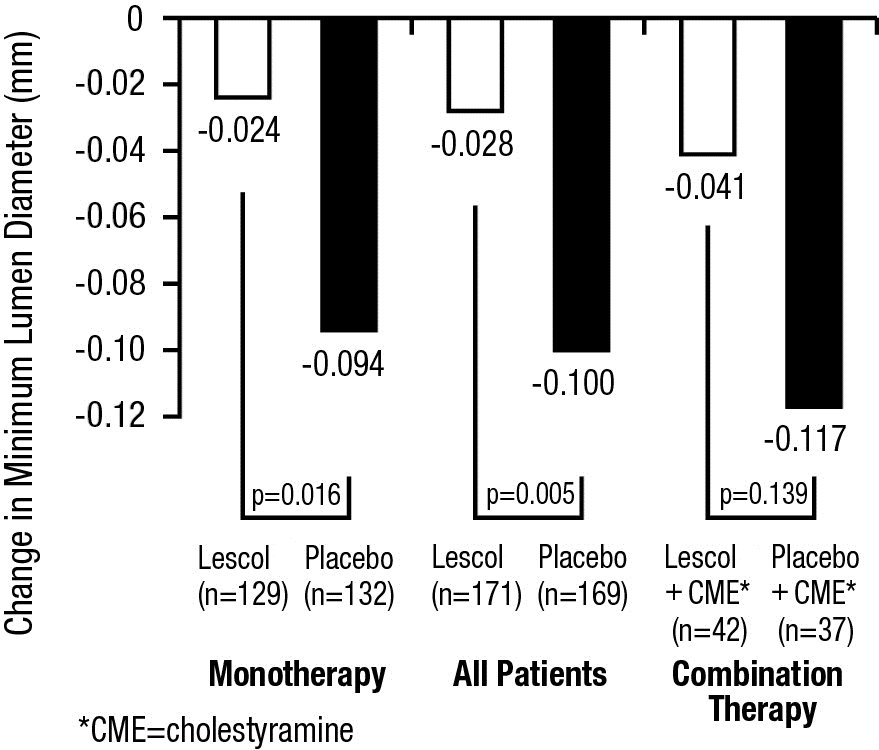
Figure 4. Change in % Diameter Stenosis
Primary Hyperlipidemia in Adults
LESCOL XL has been studied in five controlled trials of adult patients with primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia. LESCOL XL was administered to over 900 patients in trials from 4 to 26 weeks in duration. In the three largest of these trials, LESCOL XL given as a single daily dose of 80 mg significantly reduced Total-C, LDL-C, TG, and Apo B (Table 5).
In patients with primary mixed dyslipidemia as defined by baseline plasma TG levels ≥ 200 mg/dL and < 400 mg/dL, treatment with LESCOL XL produced significant decreases in Total-C, LDL-C, TG, and Apo B (see Table 7).
Table 7. Median Percent Change in Lipid Levels in Adult Patients with Primary Hyperlipidemia and Mixed Dyslipidemia From Baseline to Week 24 Endpoint All Active Controlled Trials (LESCOL XL)
HeFH in Pediatric Patients Aged 10 Years and Older
Fluvastatin capsules were studied in two open-label, uncontrolled, dose-titration trials. The first trial enrolled 29 pre-pubertal males, 9 to12 years of age, who had an LDL-C level > 90
The second trial enrolled 85 male and female patients, 10 to 16 years of age, who had an LDL-C > 190 mg/dL or LDL-C > 160 mg/dL and one or more risk factors for coronary heart disease, or LDL-C > 160 mg/dL and a proven LDL-receptor defect. The mean baseline LDL-C was 225 mg/dL (range, 148 to 343 mg/dL). All patients were started on fluvastatin capsules 20 mg daily with dose adjustments every 6 weeks to 40 mg daily then 80 mg daily (LESCOL XL tablet) to achieve an LDL-C goal of < 130 mg/dL. Endpoint analyses were performed at Week 114. Fluvastatin decreased plasma levels of Total-C and LDL-C by 22% and 28%, respectively. The mean achieved LDL-C was 159 mg/dL (range, 90 to 295 mg/dL).
The majority of patients in both trials (83% in the first trial and 89% in the second trial) were titrated to the maximum daily dose of 80 mg.
8HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
LESCOL XL extended-release tablets supplied as:
Store and Dispense
Store at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF); excursions permitted between 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight container. Protect from light.
9PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Myopathy and Rhabdomyolysis
Advise patients that LESCOL XL may cause myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. Instruct patients to promptly report any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever
Hepatic Dysfunction
Inform patients that LESCOL XL may cause liver enzyme elevations and possibly liver failure. Advise patients to promptly report fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine, or jaundice
Increases in HbA1c and Fasting Serum Glucose Levels
Inform patients that increases in HbA1c and fasting serum glucose levels may occur with LESCOL XL. Encourage patients to optimize lifestyle measures, including regular exercise, maintaining a healthy body weight, and making healthy food choices
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant patients and patients who can become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy to discuss if LESCOL XL should be discontinued
Lactation
Advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with LESCOL XL
Manufactured by
Pfizer Ireland Pharmaceuticals
Newbridge, Ireland for
Sandoz Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540
10PATIENT INFORMATION
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 12/2023
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NOVARTIS
NDC 66758-211-31
Lescol
Extended-Release Tablets
equivalent to
30 tablets
Rx only

