Generic Name
DEXmedetomidine
Brand Names
Precedex, Igalmi
FDA approval date: November 30, 2004
Classification: Central alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist
Form: Injection, Film
What is Precedex (DEXmedetomidine)?
Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride Injection is a central alpha-2 adrenergic agonist indicated for: Sedation of initially intubated and mechanically ventilated patients during treatment in an intensive care setting. Administer Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride Injection by continuous infusion not to exceed 24 hours.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Precedex (DEXMEDETOMIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE)
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
PRECEDEX (dexmedetomidine hydrochloride) in 0.9% sodium chloride injection is a clear and colorless solution, ready to use. It is available as:
PRECEDEX 80 mcg/20 mL (4 mcg/mL) single-dose vial.
PRECEDEX 200 mcg/50 mL (4 mcg/mL) single-dose glass bottle.
PRECEDEX 400 mcg/100 mL (4 mcg/mL) single-dose glass bottle.
PRECEDEX 1,000 mcg dexmedetomidine/250 mL (4 mcg/mL) in a glass bottle. Ready to use.
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypotension, bradycardia and sinus arrest
- Transient hypertension
3.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Most common treatment-emergent adverse reactions, occurring in greater than 2% of adult patients in both Intensive Care Unit and procedural sedation studies include hypotension, bradycardia and dry mouth.
3.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of PRECEDEX. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypotension and bradycardia were the most common adverse reactions associated with the use of PRECEDEX during post-approval use of the drug.
4OVERDOSAGE
The tolerability of PRECEDEX was studied in one study in which healthy adult subjects were administered doses at and above the recommended dose of 0.2 to 0.7 mcg/kg/hr. The maximum blood concentration achieved in this study was approximately 13 times the upper boundary of the therapeutic range. The most notable effects observed in two subjects who achieved the highest doses were first degree atrioventricular block and second-degree heart block. No hemodynamic compromise was noted with the atrioventricular block and the heart block resolved spontaneously within one minute.
Five adult patients received an overdose of PRECEDEX in the intensive care unit sedation studies. Two of these patients had no symptoms reported; one patient received a 2 mcg/kg loading dose over 10 minutes (twice the recommended loading dose) and one patient received a maintenance infusion of 0.8 mcg/kg/hr. Two other patients who received a 2 mcg/kg loading dose over 10 minutes, experienced bradycardia and/or hypotension. One patient who received a loading bolus dose of undiluted PRECEDEX (19.4 mcg/kg), had cardiac arrest from which he was successfully resuscitated.
5DESCRIPTION
PRECEDEX (dexmedetomidine hydrochloride) in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection (4 mcg/mL) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic ready to use solution suitable for intravenous infusion.
PRECEDEX contains dexmedetomidine hydrochloride as the active pharmaceutical ingredient. Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride is a central alpha

PRECEDEX in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection is ready to be used. It is supplied as a clear, colorless, isotonic solution with a pH between 4.5 to 8.0. Each mL contains 4.72 mcg of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride (equivalent to 4 mcg or 0.004 mg of dexmedetomidine) and 9 mg sodium chloride in water for injection. The solution is preservative-free and contains no additives or chemical stabilizers.
6CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of PRECEDEX has been evaluated in four randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trials in 1,185 adult patients.
6.1Intensive Care Unit Sedation
Two randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trials included 754 adult patients being treated in a surgical intensive care unit. All patients were initially intubated and received mechanical ventilation. These trials evaluated the sedative properties of PRECEDEX by comparing the amount of rescue medication (midazolam in one trial and propofol in the second) required to achieve a specified level of sedation (using the standardized Ramsay Sedation Scale) between PRECEDEX and placebo from onset of treatment to extubation or to a total treatment duration of 24 hours. The Ramsay Level of Sedation Scale is displayed in
In the first study, 175 adult patients were randomized to receive placebo and 178 to receive PRECEDEX by intravenous infusion at a dose of 0.4 mcg/kg/hr (with allowed adjustment between 0.2 and 0.7 mcg/kg/hr) following an initial loading infusion of one mcg/kg intravenous over 10 minutes. The study drug infusion rate was adjusted to maintain a Ramsay sedation score of ≥3. Patients were allowed to receive "rescue" midazolam as needed to augment the study drug infusion. In addition, morphine sulfate was administered for pain as needed. The primary outcome measure for this study was the total amount of rescue medication (midazolam) needed to maintain sedation as specified while intubated. Patients randomized to placebo received significantly more midazolam than patients randomized to PRECEDEX (see
A second prospective primary analysis assessed the sedative effects of PRECEDEX by comparing the percentage of adult patients who achieved a Ramsay sedation score of ≥3 during intubation without the use of additional rescue medication. A significantly greater percentage of adult patients in the PRECEDEX group maintained a Ramsay sedation score of ≥3 without receiving any midazolam rescue compared to the placebo group (see
A prospective secondary analysis assessed the dose of morphine sulfate administered to adult patients in the PRECEDEX and placebo groups. On average, PRECEDEX -treated patients received less morphine sulfate for pain than placebo-treated patients (0.47 versus 0.83 mg/h). In addition, 44% (79 of 178 patients) of PRECEDEX patients received no morphine sulfate for pain versus 19% (33 of 175 patients) in the placebo group.
In a second study, 198 adult patients were randomized to receive placebo and 203 to receive PRECEDEX by intravenous infusion at a dose of 0.4 mcg/kg/hr (with allowed adjustment between 0.2 and 0.7 mcg/kg/hr) following an initial loading infusion of one mcg/kg intravenous over 10 minutes. The study drug infusion was adjusted to maintain a Ramsay sedation score of ≥3. Patients were allowed to receive "rescue" propofol as needed to augment the study drug infusion. In addition, morphine sulfate was administered as needed for pain. The primary outcome measure for this study was the total amount of rescue medication (propofol) needed to maintain sedation as specified while intubated.
Adult patients randomized to placebo received significantly more propofol than adult patients randomized to PRECEDEX (see
A significantly greater percentage of adult patients in the PRECEDEX group compared to the placebo group maintained a Ramsay sedation score of ≥3 without receiving any propofol rescue (see
A prospective secondary analysis assessed the dose of morphine sulfate administered to adult patients in the PRECEDEX and placebo groups. On average, PRECEDEX -treated patients received less morphine sulfate for pain than placebo-treated patients (0.43 versus 0.89 mg/h). In addition, 41% (83 of 203 patients) of PRECEDEX patients received no morphine sulfate for pain versus 15% (30 of 198 patients) in the placebo group.
In a controlled clinical trial, PRECEDEX was compared to midazolam for ICU sedation exceeding 24 hours duration. PRECEDEX was not shown to be superior to midazolam for the primary efficacy endpoint, the percent of time patients were adequately sedated (81% versus 81%). In addition, administration of PRECEDEX for longer than 24 hours was associated with tolerance, tachyphylaxis, and a dose-related increase in adverse events
6.2Procedural Sedation
Adult Patients
The safety and efficacy of PRECEDEX for sedation of non-intubated adult patients prior to and/or during surgical and other procedures was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trials. Study 1 evaluated the sedative properties of PRECEDEX in adult patients having a variety of elective surgeries/procedures performed under monitored anesthesia care. Study 2 evaluated Precedex in adult patients undergoing awake fiberoptic intubation prior to a surgical or diagnostic procedure.
In Study 1, the sedative properties of PRECEDEX were evaluated by comparing the percent of adult patients not requiring rescue midazolam to achieve a specified level of sedation using the standardized Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale (see
Adult patients were randomized to receive a loading infusion of either PRECEDEX 1 mcg/kg, PRECEDEX 0.5 mcg/kg, or placebo (normal saline) given over 10 minutes and followed by a maintenance infusion started at 0.6 mcg/kg/hr. The maintenance infusion of study drug could be titrated from 0.2 mcg/kg/hr to 1 mcg/kg/hr to achieve the targeted sedation score (Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale ≤4). Adult patients were allowed to receive rescue midazolam as needed to achieve and/or maintain an Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale ≤4. After achieving the desired level of sedation, a local or regional anesthetic block was performed. Demographic characteristics were similar between the PRECEDEX and comparator groups. Efficacy results showed that Precedex was more effective than the comparator group when used to sedate non-intubated patients requiring monitored anesthesia care during surgical and other procedures (see
In Study 2, the sedative properties of PRECEDEX were evaluated by comparing the percent of adult patients requiring rescue midazolam to achieve or maintain a specified level of sedation using the Ramsay Sedation Scale score ≥2 (see
Pediatric Patients
The safety and efficacy of PRECEDEX for sedation of non-intubated pediatric patients aged 1 month to less than 17 years undergoing MRI scans was evaluated in one randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging, dose‑controlled multicenter clinical trial utilizing 3 different PRECEDEX dosages. The sedative properties of PRECEDEX were evaluated by age group and by the percent of pediatric patients at the high dose level versus the low dose level who did not require concomitant propofol to complete the MRI scan.
A total of 122 pediatric patients were randomized to the PRECEDEX low dose group (42 of 122), the middle dose group (42 of 122) or the high dose treatment group (38 of 122). All patients received a PRECEDEX loading dose infusion over 10 minutes followed by a maintenance infusion for the duration of the MRI scan (
The primary efficacy results from this pediatric procedural sedation study are summarized in
Secondarily, the sedative properties were also evaluated by examining the percent of time at a target sedation score using the Pediatric Sedation State Scale (PSSS). The PSSS is a validated 6-point scale specifically designed for evaluating pediatric patients undergoing sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. The PSSS measures the effectiveness and quality of procedural sedation in children. The target sedation level was indicated by a PSSS score of 2 (i.e., patient is quiet [asleep or awake], not moving during procedure, has no frown [or brow furrow] indicating pain or anxiety and no verbalization of any complaint).
In the PRECEDEX high dose group, pediatric patients in both the combined and individual age group were at the target sedation rating scale score (PSSS of 2) for a mean >87% of the time during the PRECEDEX maintenance infusion. In both the combined and individual age group, an increase in the percentage of time at the target sedation rating scale score (PSSS of 2) was observed with increasing PRECEDEX dosage.
7PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
PRECEDEX is indicated for short-term intravenous sedation. Dosage must be individualized and titrated to the desired clinical effect. Blood pressure, heart rate and oxygen levels will be monitored both continuously during the infusion of PRECEDEX and as clinically appropriate after discontinuation.
- When PRECEDEX is infused for more than 6 hours, patients should be informed to report nervousness, agitation, and headaches that may occur for up to 48 hours.
- Additionally, patients should be informed to report symptoms that may occur within 48 hours after the administration of PRECEDEX.
- such as: weakness, confusion, excessive sweating, weight loss, abdominal pain, salt cravings, diarrhea, constipation, dizziness or light-headedness.
- Advise breastfeeding mothers who were exposed to PRECEDEX to monitor breastfed neonates for irritability
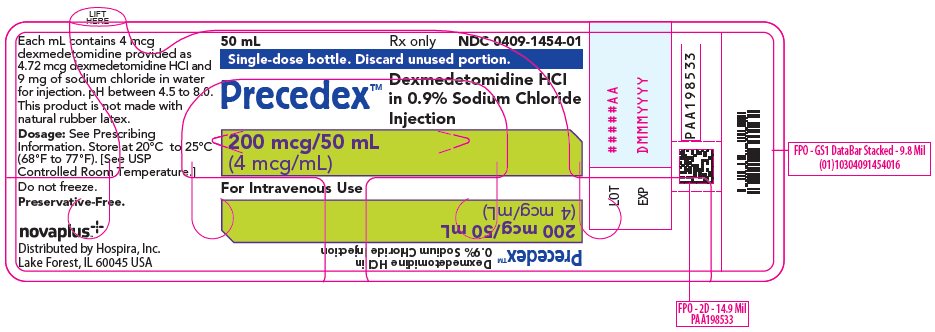
8PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mL Bottle Label
50 mL
Single-dose bottle. Discard unused portion.
Precedex™
200 mcg/50 mL
For Intravenous Use
9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mL Bottle Tray
20 Units X 50 mL
Single-dose bottle. Discard unused portion.
Precedex™
200 mcg/50 mL
For Intravenous Use
novaplus

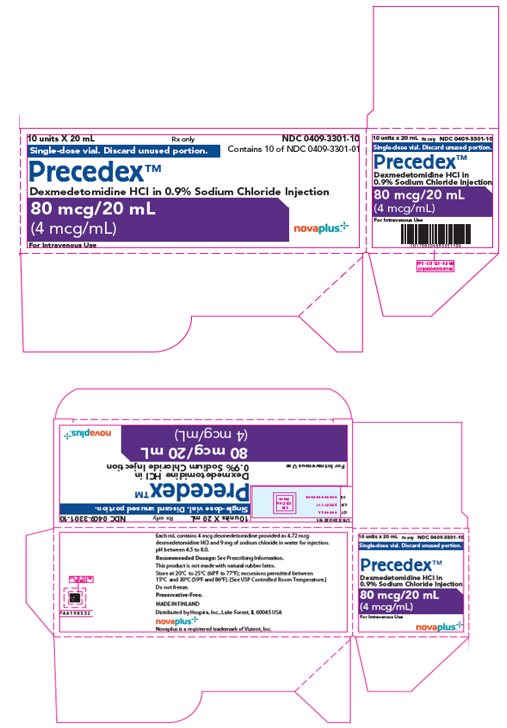
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Vial Label
20 mL
Single-dose vial.
Precedex™
80 mcg/20 mL

11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Vial Carton
10 units X 20 mL
Single-dose vial. Discard unused portion.
80 mcg/20 mL
For Intravenous Use
novaplus
12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mL Bottle Label
100 mL
Single-dose bottle. Discard unused portion.
Precedex™
400 mcg/100 mL
For Intravenous Use

13PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mL Bottle Tray
10 Units X 100 mL
Single-dose bottle. Discard unused portion.
Precedex™
400 mcg/100 mL
For Intravenous Use
novaplus

14PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 250 mL Bottle Label
250 mL
Single-dose bottle. Discard unused portion.
Precedex™
1000 mcg/250 mL
For Intravenous Use

15PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 250 mL Bottle Carton
1 Unit X 250 mL
Single-dose bottle.
Precedex™
1000 mcg/250 mL
For Intravenous Use
novaplus
