Brand Name
Vardenafil
View Brand InformationFDA approval date: October 26, 2018
Classification: Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitor
Form: Tablet
What is Vardenafil?
Vardenafil hydrochloride orally disintegrating tablets are indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Vardenafil hydrochloride orally disintegrating tablets are phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Vardenafil Hydrochloride (Vardenafil Hydrochloride)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets are formulated as orange, round, tablets embossed with "2.5", "5", "10" or "20" on one side corresponding to 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg of vardenafil, respectively.
3WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
The evaluation of erectile dysfunction should include a medical assessment, a determination of potential underlying causes and the identification of appropriate treatment.
Before prescribing vardenafil hydrochloride tablets, it is important to note the following:
3.1Potential for Drug Interactions with Potent or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Concomitant administration with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as ritonavir, indinavir, ketoconazole) or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as erythromycin) increases plasma concentrations of vardenafil. Dosage adjustment is necessary when vardenafil hydrochloride tablets are administered with certain CYP3A4 inhibitors
Long-term safety information is not available on the concomitant administration of vardenafil with HIV protease inhibitors.
3.2Risk of Priapism
There have been rare reports of prolonged erections greater than 4 hours and priapism (painful erections greater than 6 hours in duration) for this class of compounds, including vardenafil. In the event that an erection persists longer than 4 hours, the patient should seek immediate medical assistance. If priapism is not treated immediately, penile tissue damage and permanent loss of potency may result.
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets should be used with caution by patients with anatomical deformation of the penis (such as angulation, cavernosal fibrosis, or Peyronie's disease) or by patients who have conditions that may predispose them to priapism (such as sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia).
3.3Effects on the Eye
Physicians should advise patients to stop use of all phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, including vardenafil hydrochloride tablets, and seek medical attention in the event of sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes. Such an event may be a sign of non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a rare condition and a cause of decreased vision, including permanent loss of vision, that has been reported rarely postmarketing in temporal association with the use of all PDE5 inhibitors. Based on published literature, the annual incidence of NAION is 2.5–11.8 cases per 100,000 in males aged ≥50.
An observational case-crossover study evaluated the risk of NAION when PDE5 inhibitor use, as a class, occurred immediately before NAION onset (within 5 half-lives), compared to PDE5 inhibitor use in a prior time period. The results suggest an approximate 2-fold increase in the risk of NAION, with a risk estimate of 2.15 (95% CI 1.06, 4.34). A similar study reported a consistent result, with a risk estimate of 2.27 (95% CI 0.99, 5.20). Other risk factors for NAION, such as the presence of “crowded” optic disc, may have contributed to the occurrence of NAION in these studies.
Neither the rare postmarketing reports, nor the association of PDE5 inhibitor use and NAION in the observational studies, substantiate a causal relationship between PDE5 inhibitor use and NAION
Physicians should consider whether their patients with underlying NAION risk factors could be adversely affected by use of PDE5 inhibitors. Individuals who have already experienced NAION are at increased risk of NAION recurrence. Therefore, PDE5 inhibitors, including vardenafil hydrochloride tablets, should be used with caution in these patients and only when the anticipated benefits outweigh the risks. Individuals with "crowded" optic disc are also considered at greater risk for NAION compared to the general population, however, evidence is insufficient to support screening of prospective users of PDE5 inhibitors, including vardenafil hydrochloride tablets, for this uncommon condition.
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets have not been evaluated in patients with known hereditary degenerative retinal disorders, including retinitis pigmentosa, therefore its use is not recommended until further information is available in those patients.
3.4Sudden Hearing Loss
Physicians should advise patients to stop taking all PDE5 inhibitors, including vardenafil hydrochloride tablets, and seek prompt medical attention in the event of sudden decrease or loss of hearing. These events, which may be accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness, have been reported in temporal association to the intake of PDE5 inhibitors, including vardenafil. It is not possible to determine whether these events are related directly to the use of PDE5 inhibitors or to other factors
3.5Alpha-Blockers
Caution is advised when PDE5 inhibitors are co-administered with alpha-blockers. PDE5 inhibitors, including vardenafil hydrochloride tablets, and alpha-adrenergic blocking agents are both vasodilators with blood-pressure lowering effects. When vasodilators are used in combination, an additive effect on blood pressure may be anticipated. In some patients, concomitant use of these two drug classes can lower blood pressure significantly leading to symptomatic hypotension (for example, fainting)
- Patients should be stable on alpha-blocker therapy prior to initiating a PDE5 inhibitor. Patients who demonstrate hemodynamic instability on alpha-blocker therapy alone are at increased risk of symptomatic hypotension with concomitant use of PDE5 inhibitors.
- In those patients who are stable on alpha-blocker therapy, PDE5 inhibitors should be initiated at the lowest recommended starting dose
- In those patients already taking an optimized dose of PDE5 inhibitor, alpha-blocker therapy should be initiated at the lowest dose. Stepwise increase in alpha-blocker dose may be associated with further lowering of blood pressure in patients taking a PDE5 inhibitor.
- Safety of combined use of PDE5 inhibitors and alpha-blockers may be affected by other variables, including intravascular volume depletion and other anti-hypertensive drugs.
3.6Congenital or Acquired QT Prolongation
In a study of the effect of vardenafil hydrochloride tablets on QT interval in 59 healthy males
Patients taking Class 1A (for example. quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (for example, amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications or those with congenital QT prolongation, should avoid using vardenafil hydrochloride tablets.
3.7Hepatic Impairment
Dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B). Do not use vardenafil hydrochloride tablets in patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment.
3.8Renal Impairment
Do not use vardenafil hydrochloride tablets in patients on renal dialysis, as vardenafil has not been evaluated in this population
3.9Combination with Other Erectile Dysfunction Therapies
The safety and efficacy of vardenafil hydrochloride tablets used in combination with other treatments for erectile dysfunction have not been studied. Therefore, the use of such combinations is not recommended.
3.10Effects on Bleeding
In humans, vardenafil alone in doses up to 20 mg does not prolong the bleeding time. There is no clinical evidence of any additive prolongation of the bleeding time when vardenafil is administered with aspirin. Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets have not been administered to patients with bleeding disorders or significant active peptic ulceration. Therefore vardenafil hydrochloride tablets should be administered to these patients after careful benefit-risk assessment.
3.11Sexually Transmitted Disease
The use of vardenafil hydrochloride tablets offers no protection against sexually transmitted diseases. Counseling of patients about protective measures necessary to guard against sexually transmitted diseases, including the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), should be considered.
3.12Risks in Patients with Phenylketonuria
Phenylalanine can be harmful to patients with phenylketonuria (PKU). Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets contain phenylalanine, a component of aspartame. Each 2.5 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablet contains 0.7 mg phenylalanine; each 5 mg tablet contains 1.4 mg phenylalanine; each 10 mg tablet contains 2.8 mg phenylalanine; each 20 mg tablet contains 5.6 mg phenylalanine. Before prescribing vardenafil hydrochloride tablets in a patient with PKU, consider the combined daily amount of phenylalanine from all sources, including vardenafil hydrochloride tablets.ardenafil hydrochloride tablets contain aspartame, a source of phenylalanine. Each 2.5 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablet contains 0.7 mg phenylalanine; each 5 mg tablet contains 1.4 mg phenylalanine; each 10 mg tablet contains 2.8 mg phenylalanine; each 20 mg tablet contains 5.6 mg phenylalanine.
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions with the use of vardenafil hydrochloride tablets (vardenafil) are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Effects
- Priapism
- Effects on Eye
- Sudden Hearing Loss
- QT Prolongation
4.1Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets were administered to over 4430 men (mean age 56, range 18-89 years; 81% White, 6% Black, 2% Asian, 2% Hispanic and 9% Other) during controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials worldwide. Over 2200 patients were treated for 6 months or longer and 880 patients were treated for at least 1 year.
In placebo-controlled clinical trials, the discontinuation rate due to adverse events was 3.4% for vardenafil hydrochloride tablets compared to 1.1% for placebo.
When vardenafil hydrochloride tablets were taken as recommended in placebo-controlled clinical trials, the following adverse reactions were reported (see
Back pain was reported in 2.0% of patients treated with vardenafil hydrochloride tablets and 1.7% of patients on placebo.
Placebo-controlled trials suggested a dose effect in the incidence of some adverse reactions (headache, flushing, dyspepsia, nausea, and rhinitis) over the 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg doses of vardenafil hydrochloride tablets.
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of vardenafil hydrochloride tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AvKARE at 1-855-361-3993; email drugsafety@avkare.com; or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
5OVERDOSAGE
The maximum dose of vardenafil hydrochloride tablets for which human data are available is a single 120 mg dose administered to healthy male volunteers. The majority of these subjects experienced reversible back pain/myalgia and/or "abnormal vision." Single doses up to 80 mg vardenafil and multiple doses up to 40 mg vardenafil administered once daily over 4 weeks were tolerated without producing serious adverse side effects.
When 40 mg of vardenafil was administered twice daily, cases of severe back pain were observed. No muscle or neurological toxicity was identified.
In cases of overdose, standard supportive measures should be taken as required. Renal dialysis is not expected to accelerate clearance as vardenafil is highly bound to plasma proteins and not significantly eliminated in the urine.
6DESCRIPTION
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets (vardenafil hydrochloride) are administered orally for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. This monohydrochloride salt of vardenafil is a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5).
Vardenafil HCl is designated chemically as piperazine, 1-[[3-(1,4-dihydro-5-methyl-4-oxo-7-propylimidazo[5,1-
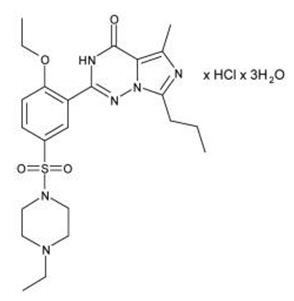
Vardenafil HCl is a nearly colorless, solid substance with a molecular weight of 579.1 g/mol and a solubility of 0.11 mg/mL in water.
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets are formulated as orange, round, tablets embossed with "2.5", "5", "10" or "20" on one side corresponding to 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg of vardenafil, respectively. In addition to the active ingredient, vardenafil HCl, each tablet contains microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, aspartame, titanium dioxide, ferric oxide red, and ferric oxide yellow.
7CLINICAL STUDIES
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets were evaluated in four major double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose, parallel design, multicenter trials in 2431 men aged 20-83 (mean age 57 years; 78% White, 7% Black, 2% Asian, 3% Hispanic and 10% Other/Unknown). The doses of vardenafil hydrochloride tablets in these studies were 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg. Two of these trials were conducted in the general erectile dysfunction (ED) population and two in special ED populations (one in patients with diabetes mellitus and one in post-prostatectomy patients). Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets were dosed without regard to meals on an as needed basis in men with ED, many of whom had multiple other medical conditions. The primary endpoints were assessed at 3 months.
Primary efficacy assessment in all four major trials was by means of the Erectile Function (EF) Domain score of the validated International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) Questionnaire and two questions from the Sexual Encounter Profile (SEP) dealing with the ability to achieve vaginal penetration (SEP2), and the ability to maintain an erection long enough for successful intercourse (SEP3).
In all four fixed-dose efficacy trials, vardenafil hydrochloride tablets showed clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvement in the EF Domain, SEP2, and SEP3 scores compared to placebo. The mean baseline EF Domain score in these trials was 11.8 (scores range from 0-30 where lower scores represent more severe disease). Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets (5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg) were effective in all age categories (<45, 45 to <65, and ≥65 years) and was also effective regardless of race (White, Black, Other).
7.1Trials in a General Erectile Dysfunction Population
In the major North American fixed-dose trial, 762 patients (mean age 57, range 20-83 years; 79% White, 13% Black, 4% Hispanic, 2% Asian and 2% Other) were evaluated. The mean baseline EF Domain scores were 13, 13, 13, 14 for the vardenafil hydrochloride tablets 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg and placebo groups, respectively. There was significant improvement (p <0.0001) at 3 months with vardenafil hydrochloride tablets (EF Domain scores of 18, 21, 21, for the 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg dose groups, respectively) compared to the placebo group (EF Domain score of 15). The European trial (total N=803) confirmed these results. The improvement in mean score was maintained at all doses at 6 months in the North American trial.
In the North American trial, vardenafil hydrochloride tablets significantly improved the rates of achieving an erection sufficient for penetration (SEP2) at doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg compared to placebo (65%, 75%, and 80%, respectively, compared to a 52% response in the placebo group at 3 months; p <0.0001). The European trial confirmed these results.
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets demonstrated a clinically meaningful and statistically significant increase in the overall per-patient rate of maintenance of erection to successful intercourse (SEP3) (51% on 5 mg, 64% on 10 mg, and 65% on 20 mg, respectively, compared to 32% on placebo; p <0.0001) at 3 months in the North American trial. The European trial showed comparable efficacy. This improvement in mean score was maintained at all doses at 6 months in the North American trial.
7.2Trial in Patients with ED and Diabetes Mellitus
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets demonstrated clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvement in erectile function in a prospective, fixed-dose (10 and 20 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of patients with diabetes mellitus (n=439; mean age 57 years, range 33-81; 80% White, 9% Black, 8% Hispanic, and 3% Other).
Significant improvements in the EF Domain were shown in this study (EF Domain scores of 17 on 10 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets and 19 on 20 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets compared to 13 on placebo; p <0.0001).
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets significantly improved the overall per-patient rate of achieving an erection sufficient for penetration (SEP2) (61% on 10 mg and 64% on 20 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets compared to 36% on placebo; p <0.0001).
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets demonstrated a clinically meaningful and statistically significant increase in the overall per-patient rate of maintenance of erection to successful intercourse (SEP3) (49% on 10 mg, 54% on 20 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets compared to 23% on placebo; p <0.0001).
7.3Trial in Patients with ED after Radical Prostatectomy
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets demonstrated clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvement in erectile function in a prospective, fixed-dose (10 and 20 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in post-prostatectomy patients (n=427, mean age 60, range 44-77 years; 93% White, 5% Black, 2% Other).
Significant improvements in the EF Domain were shown in this study (EF Domain scores of 15 on 10 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets and 15 on 20 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets compared to 9 on placebo; p <0.0001).
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets significantly improved the overall per-patient rate of achieving an erection sufficient for penetration (SEP2) (47% on 10 mg and 48% on 20 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets compared to 22% on placebo; p <0.0001).
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets demonstrated a clinically meaningful and statistically significant increase in the overall per-patient rate of maintenance of erection to successful intercourse (SEP3) (37% on 10 mg, 34% on 20 mg vardenafil hydrochloride tablets compared to 10% on placebo; p <0.0001).
8HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Vardenafil hydrochloride tablets are formulated as orange, round, tablets embossed with "2.5", "5", "10" or "20" on one side equivalent to 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg of vardenafil, respectively
9PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
"See
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablet Bottle Label

11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg Tablet Bottle Label
