Brand Name
Aubagio
Generic Name
Teriflunomide
View Brand Information FDA approval date: May 01, 2013
Classification: Pyrimidine Synthesis Inhibitor
Form: Tablet
What is Aubagio (Teriflunomide)?
Teriflunomide tablets are indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis , to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults. Teriflunomide is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis , to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Aubagio (teriflunomide)
WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY and EMBRYOFETAL TOXICITY
- Hepatotoxicity
Clinically significant and potentially life-threatening liver injury, including acute liver failure requiring transplant, has been reported in patients treated with AUBAGIO in the postmarketing setting
Obtain transaminase and bilirubin levels within 6 months before initiation of AUBAGIO therapy. Monitor ALT levels at least monthly for six months after starting AUBAGIO
- Embryofetal Toxicity
AUBAGIO is contraindicated for use in pregnant women and in females of reproductive potential who are not using effective contraception because of the potential for fetal harm. Teratogenicity and embryolethality occurred in animals at plasma teriflunomide exposures lower than that in humans. Exclude pregnancy before the start of treatment with AUBAGIO in females of reproductive potential. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during AUBAGIO treatment and during an accelerated drug elimination procedure after AUBAGIO treatment. Stop AUBAGIO and use an accelerated drug elimination procedure if the patient becomes pregnant
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUBAGIO
2DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose of AUBAGIO is 7 mg or 14 mg orally once daily. AUBAGIO can be taken with or without food.
3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
AUBAGIO is available as 7 mg and 14 mg tablets.
The 14 mg tablet is a pale blue to pastel blue, pentagonal film-coated tablet with the dose strength "14" imprinted on one side and engraved with the corporate logo on the other side. Each tablet contains 14 mg of teriflunomide.
The 7 mg tablet is a very light greenish-bluish grey to pale greenish-blue, hexagonal film-coated tablet with the dose strength "7" imprinted on one side and engraved with the corporate logo on the other side. Each tablet contains 7 mg of teriflunomide.
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the prescribing information:
- Hepatotoxicity
- Bone Marrow Effects/Immunosuppression Potential/Infections
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Serious Skin Reactions
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Increased Blood Pressure
- Respiratory Effects
- Pancreatitis in Pediatric Patients
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
A total of 2047 patients receiving AUBAGIO (7 mg or 14 mg once daily) constituted the safety population in the pooled analysis of placebo-controlled studies in patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis; of these, 71% were female. The average age was 37 years.
Table 1 lists adverse reactions in placebo-controlled trials with rates that were at least 2% for AUBAGIO patients and also at least 2% above the rate in placebo patients. The most common were headache, an increase in ALT, diarrhea, alopecia, and nausea. The adverse reaction most commonly associated with discontinuation was an increase in ALT (3.3%, 2.6%, and 2.3% of all patients in the AUBAGIO 7 mg, AUBAGIO 14 mg, and placebo treatment arms, respectively).
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of AUBAGIO. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Thrombocytopenia [see
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Pancreatitis, colitis
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) [see
- Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions, some of which were severe, such as anaphylaxis and angioedema [see
- Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: Interstitial lung disease [see
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Severe skin reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome [see ; drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) [see ; psoriasis or worsening of psoriasis (including pustular psoriasis and nail psoriasis); nail disorders
5OVERDOSAGE
There is no experience regarding teriflunomide overdose or intoxication in humans. Teriflunomide 70 mg daily up to 14 days was well tolerated by healthy subjects.
In the event of clinically significant overdose or toxicity, cholestyramine or activated charcoal is recommended to accelerate elimination
6DESCRIPTION
AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) is an oral de novo pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor of the DHO-DH enzyme, with the chemical name (Z)-2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-but-2-enoic acid-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-amide. Its molecular weight is 270.21, and the empirical formula is C
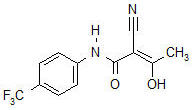
Teriflunomide is a white to almost white powder that is sparingly soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in polyethylene glycol and ethanol, very slightly soluble in isopropanol and practically insoluble in water.
Teriflunomide is formulated as film-coated tablets for oral administration. AUBAGIO tablets contain 7 mg or 14 mg of teriflunomide and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, corn starch, hydroxypropyl cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, and magnesium stearate. The film coating for the 14 mg tablet is made of hypromellose, titanium dioxide, talc, polyethylene glycol and indigo carmine aluminum lake. In addition to these, the 7 mg tablet film coating includes iron oxide yellow.
7CLINICAL STUDIES
Four randomized, controlled, double-blind clinical trials established the efficacy of AUBAGIO in patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis.
Study 1 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that evaluated once daily doses of AUBAGIO 7 mg and AUBAGIO 14 mg for up to 26 months in patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. Patients were required to have a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis exhibiting a relapsing clinical course, with or without progression, and to have experienced at least one relapse over the year preceding the trial or at least two relapses over the two years preceding the trial. Patients were required not to have received interferon-beta for at least four months, or any other multiple sclerosis medication for at least six months before entering the study, nor were these medications permitted during the study. Neurological evaluations were to be performed at screening, every 12 weeks until week 108, and after suspected relapses. MRI was to be performed at screening, and at week 24, 48, 72, and 108. The primary endpoint was the annualized relapse rate (ARR).
In Study 1, 1088 patients were randomized to receive AUBAGIO 7 mg (n=366), AUBAGIO 14 mg (n=359), or placebo (n=363). At entry, patients had an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score ≤5.5. Patients had a mean age of 38 years, mean disease duration of 5 years, and mean EDSS at baseline of 2.7. A total of 91% of patients had relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, and 9% had a progressive form of multiple sclerosis with relapses. The mean duration of treatment was 635, 627, and 631 days for AUBAGIO 7 mg, AUBAGIO 14 mg, and placebo, respectively. The percentage of patients who completed the study treatment period was 75%, 73%, and 71% for AUBAGIO 7 mg, AUBAGIO 14 mg, and placebo, respectively.
There was a statistically significant reduction in ARR for patients who received AUBAGIO 7 mg or AUBAGIO 14 mg, compared to patients who received placebo (see
There was a statistically significant reduction in the relative risk of disability progression at week 108 sustained for 12 weeks (as measured by at least a 1-point increase from baseline EDSS ≤5.5 or a 0.5 point increase for those with a baseline EDSS >5.5) in the AUBAGIO 14 mg group compared to placebo (see
The effect of AUBAGIO on several magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) variables, including the total lesion volume of T2 and hypointense T1 lesions, was assessed in Study 1. The change in total lesion volume from baseline was significantly lower in the AUBAGIO 7 mg and AUBAGIO 14 mg groups than in the placebo group. Patients in both AUBAGIO groups had significantly fewer gadolinium-enhancing lesions per T1-weighted scan than those in the placebo group (see
Study 2 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that evaluated once daily doses of AUBAGIO 7 mg and AUBAGIO 14 mg for up to 40 months in patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. Patients were required to have a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis exhibiting a relapsing clinical course and to have experienced at least one relapse over the year preceding the trial, or at least two relapses over the two years preceding the trial. Patients were required not to have received any multiple sclerosis medication for at least three months before entering the trial, nor were these medications permitted during the trial. Neurological evaluations were to be performed at screening, every 12 weeks until completion, and after every suspected relapse. The primary end point was the ARR.
A total of 1165 patients received AUBAGIO 7 mg (n=407), AUBAGIO 14 mg (n=370), or placebo (n=388). Patients had a mean age of 38 years, a mean disease duration of 5 years, and a mean EDSS at baseline of 2.7. A total of 98% of patients had relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, and 2% had a progressive form of multiple sclerosis with relapses. The mean duration of treatment was 552, 567, and 571 days for AUBAGIO 7 mg, AUBAGIO 14 mg, and placebo, respectively. The percentage of patients who completed the study treatment period was 67%, 66%, and 68% for AUBAGIO 7 mg, AUBAGIO 14 mg, and placebo, respectively.
There was a statistically significant reduction in the ARR for patients who received AUBAGIO 7 mg or AUBAGIO 14 mg compared to patients who received placebo (see
There was a statistically significant reduction in the relative risk of disability progression at week 108 sustained for 12 weeks (as measured by at least a 1-point increase from baseline EDSS ≤5.5 or a 0.5 point increase for those with a baseline EDSS >5.5) in the AUBAGIO 14 mg group compared to placebo (see
Study 3 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that evaluated once daily doses of AUBAGIO 7 mg and AUBAGIO 14 mg for up to 108 weeks in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. Patients were required to have had a first clinical event consistent with acute demyelination occurring within 90 days of randomization with 2 or more T2 lesions at least 3 mm in diameter that were characteristic of multiple sclerosis. A total of 614 patients received AUBAGIO 7 mg (n=203), AUBAGIO 14 mg (n=214), or placebo (n=197). Patients had a mean age of 32 years, EDSS at baseline of 1.7, and mean disease duration of two months. The proportion of patients free of relapse was greater in the AUBAGIO 7 mg (70.5%, p<0.05) and AUBAGIO 14 mg (72.2%, p<0.05) groups than in the placebo group (61.7%).
The effect of AUBAGIO on MRI activity was also demonstrated in Study 4, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of multiple sclerosis patients with relapse. In Study 4, MRI was to be performed at baseline, 6 weeks, 12 weeks, 18 weeks, 24 weeks, 30 weeks, and 36 weeks after treatment initiation. A total of 179 patients were randomized to AUBAGIO 7 mg (n=61), AUBAGIO 14 mg (n=57), or placebo (n=61). Baseline demographics were consistent across treatment groups. The primary endpoint was the average number of unique active lesions/MRI scan during treatment. The mean number of unique active lesions per brain MRI scan during the 36-week treatment period was lower in patients treated with AUBAGIO 7 mg (1.06) and AUBAGIO 14 mg (0.98) as compared to placebo (2.69), the difference being statistically significant for both (p=0.0234 and p=0.0052, respectively).
8HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
AUBAGIO is available as 7 mg and 14 mg tablets.
The 14 mg tablet is pale blue to pastel blue, pentagonal film-coated tablet with dose strength "14" imprinted on one side and engraved with corporate logo on the other side. Each tablet contains 14 mg of teriflunomide.
The 7 mg tablet is very light greenish-bluish grey to pale greenish-blue, hexagonal film-coated tablet with dose strength "7" imprinted on one side and engraved with corporate logo on the other side. Each tablet contains 7 mg of teriflunomide.
AUBAGIO 14 mg tablets are supplied as:
AUBAGIO 7 mg tablets are supplied as:
9PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
A Medication Guide is required for distribution with AUBAGIO.
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 7 mg Tablet Bottle Carton
NDC 58468-0211-4
Aubagio
7 mg
Rx only
Dispense with Medication Guide
30 Tablets
sanofi

11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 14 mg Tablet Bottle Carton
NDC 58468-0210-4
Aubagio
14 mg
Rx only
Dispense with Medication Guide
30 Tablets
sanofi
