Generic Name
Ritonavir
Brand Names
Lopinavir-Ritonavir, Norvir, Lopinavir, Kaletra, Paxlovid
FDA approval date: June 18, 2010
Classification: Protease Inhibitor
Form: Tablet, Kit, Powder, Solution
What is Lopinavir-Ritonavir (Ritonavir)?
Ritonavir tablets are indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Ritonavir tablets are HIV protease inhibitor indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. .
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Lopinavir-Ritonavir (Lopinavir-Ritonavir)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Lopinavir and ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients 14 days and older.
Limitations of Use:
Genotypic or phenotypic testing and/or treatment history should guide the use of lopinavir and ritonavir. The number of baseline lopinavir resistance-associated substitutions affects the virologic response to lopinavir and ritonavir
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Lopinavir and Ritonavir Oral Solution USP: Colorless to yellow colored liquid containing 400 mg lopinavir and 100 mg ritonavir per 5 mL (80 mg lopinavir and 20 mg ritonavir per mL).
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
Lopinavir and ritonavir is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated clinically significant hypersensitivity (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, urticaria, angioedema) to any of its ingredients, including ritonavir.
Lopinavir and ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening reactions
- Alpha 1- Adrenoreceptor Antagonist: alfuzosin
- Antianginal: ranolazine
- Antiarrhythmic: dronedarone
- Anti-gout: colchicine
- Antipsychotics: lurasidone, pimozide
- Ergot Derivatives: dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine
- GI Motility Agent: cisapride
- Hepatitis C direct acting antiviral: elbasvir/grazoprevir
- HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: lovastatin, simvastatin
- Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) Inhibitor: lomitapide
- PDE5 Inhibitor: sildenafil (Revatio
- Sedative/Hypnotics: triazolam, orally administered midazolam
- Lopinavir and ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are potent CYP3A inducers where significantly reduced lopinavir plasma concentrations may be associated with the potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance and cross-resistance
- Anticancer Agents: apalutamide
- Antimycobacterial: rifampin
- Herbal Products: St. John's Wort (hypericum perforatum)
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling.
- QT Interval Prolongation, PR Interval Prolongation
- Drug Interactions
- Pancreatitis
- Hepatotoxicity
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Reactions in Adults
The safety of lopinavir and ritonavir has been investigated in about 2,600 patients in Phase II-IV clinical trials, of which about 700 have received a dose of 800/200 mg (6 capsules or 4 tablets) once daily. Along with nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), in some studies, lopinavir and ritonavir was used in combination with efavirenz or nevirapine.
In clinical studies the incidence of diarrhea in patients treated with either lopinavir and ritonavir capsules or tablets was greater in those patients treated once daily than in those patients treated twice daily. Any grade of diarrhea was reported by at least half of patients taking once daily lopinavir and ritonavir capsules or tablets. At the time of treatment discontinuation, 4.2-6.3% of patients taking once daily lopinavir and ritonavir and 1.8-3.7% of those taking twice daily lopinavir and ritonavir reported ongoing diarrhea.
Commonly reported adverse reactions to lopinavir and ritonavir included diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia. Diarrhea, nausea and vomiting may occur at the beginning of the treatment while hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia may occur later. The following have been identified as adverse reactions of moderate or severe intensity (Table 8):
Laboratory Abnormalities in Adults
The percentages of adult patients treated with combination therapy with Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities are presented in Table 9 (treatment-naïve patients) and Table 10 (treatment-experienced patients).
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients
Lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution dosed up to 300/75 mg/m
Dysgeusia (22%), vomiting (21%), and diarrhea (12%) were the most common adverse reactions of any severity reported in pediatric patients treated with combination therapy for up to 48 weeks in Study 940. A total of 8 patients experienced adverse reactions of moderate to severe intensity. The adverse reactions meeting these criteria and reported for the 8 subjects include: hypersensitivity (characterized by fever, rash and jaundice), pyrexia, viral infection, constipation, hepatomegaly, pancreatitis, vomiting, alanine aminotransferase increased, dry skin, rash, and dysgeusia. Rash was the only event of those listed that occurred in 2 or more subjects (N=3).
Lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution dosed at 300/75 mg/m
Lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution and soft gelatin capsules dosed at higher than recommended doses including 400/100 mg/m
Laboratory Abnormalities in Pediatric Patients
The percentages of pediatric patients treated with combination therapy including lopinavir and ritonavir with Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities are presented in Table 11.
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during postmarketing use of lopinavir and ritonavir. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to lopinavir and ritonavir exposure.
Body as a Whole
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat has been reported
Cardiovascular
Bradyarrhythmias. First-degree AV block, second-degree AV block, third-degree AV block, QTc interval prolongation, torsades (torsade) de pointes
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Nephrolithiasis
Skin and Appendages
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme.
5OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses with lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution have been reported. One of these reports described fatal cardiogenic shock in a 2.1 kg infant who received a single dose of 6.5 mL of lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution (520 mg lopinavir, approximately 10-fold above the recommended lopinavir dose) nine days prior. The following events have been reported in association with unintended overdoses in preterm neonates: complete AV block, cardiomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and acute renal failure
Lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution contains approximately 42% (v/v) ethanol and approximately 15% (w/v) propylene glycol. Ingestion of the product over the recommended dose by an infant or a young child could result in significant toxicity and could potentially be lethal.
Human experience of acute overdosage with lopinavir and ritonavir is limited. Treatment of overdose with lopinavir and ritonavir should consist of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient. There is no specific antidote for overdose with lopinavir and ritonavir. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed drug should be achieved by gastric lavage. Administration of activated charcoal may also be used to aid in removal of unabsorbed drug. Since lopinavir is highly protein bound, dialysis is unlikely to be beneficial in significant removal of the drug. However, dialysis can remove both ethanol and propylene glycol in the case of overdose with lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution.
6DESCRIPTION
Lopinavir and Ritonavir Oral Solution USP is a co-formulation of lopinavir and ritonavir. Lopinavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease. As co-formulated in lopinavir and ritonavir, ritonavir inhibits the CYP3A-mediated metabolism of lopinavir, thereby providing increased plasma levels of lopinavir.
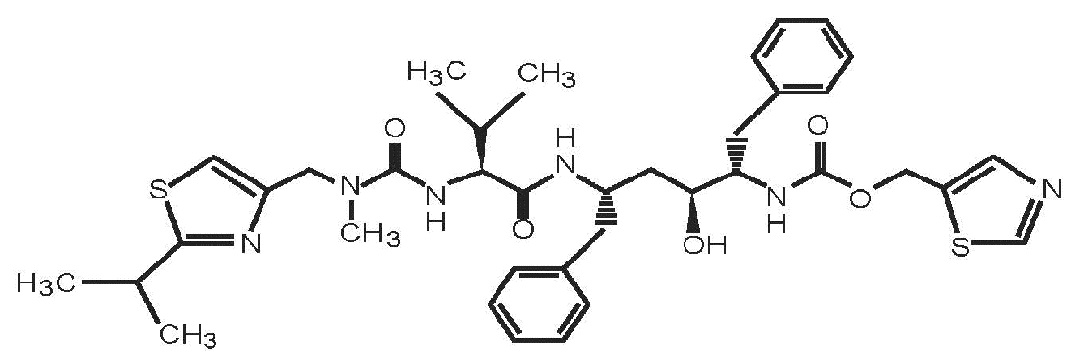
Lopinavir is chemically designated as [1

Ritonavir is chemically designated as 10-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-1-[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]-3,6-dioxo-8,11-bis(phenylmethyl)-2,4,7,12-tetraazatridecan-13-oic acid, 5-thiazolylmethyl ester, [5
Lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution is available for oral administration as 80 mg lopinavir and 20 mg ritonavir per milliliter with the following inactive ingredients: bubble gum flavor, ethanol, glycerin, high fructose corn syrup, malic acid, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, povidone, propylene glycol, sodium hydroxide, sucralose, and water.
Lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution contains approximately 42% (v/v) ethanol and approximately 15% (w/v) propylene glycol.
7HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Lopinavir and Ritonavir Oral Solution USP is a colorless to yellow colored liquid supplied in amber-colored multiple-dose bottles containing 400 mg lopinavir and 100 mg ritonavir per 5 mL (80 mg lopinavir and 20 mg ritonavir per mL) packaged with a marked syringe and bottle adapter in the following size:
160 mL bottle …………………………………(NDC 0527-1947-48)
Recommended Storage:
Store lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution at 2°-8°C (36°-46°F) until dispensed. Avoid exposure to excessive heat. For patient use: refrigerated lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution remains stable until the expiration date printed on the label. If stored at room temperature up to 25°C (77°F), oral solution should be used within 2 months.
8PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (
- Advise patients to pay special attention to accurate administration of their dose to minimize the risk of accidental overdose or underdose of lopinavir and ritonavir.
- Advise patients and caregivers that the oral solution should be administered using the calibrated dosing cup (supplied) or oral dosing syringe.
- Advise caregivers to inform their healthcare provider if the child’s weight changes in order to make sure that the child’s lopinavir and ritonavir dose is adjusted as needed.
- Inform patients and caregivers that lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution should be taken with food to enhance absorption.
- Advise patients to remain under the care of a healthcare provider while using lopinavir and ritonavir and to take lopinavir and ritonavir in combination with other antiretroviral drugs as prescribed.
- Advise patients not to alter the dose or discontinue therapy without consulting with their healthcare provider. If a dose of lopinavir and ritonavir is missed patients should take the dose as soon as possible and then return to their normal schedule. However, if a dose is skipped the patient should not double the next dose.
- Inform patients that it is important to take lopinavir and ritonavir on a regular dosing schedule as directed and to avoid missing doses as that can result in development of resistance.
- Inform patients that there may be a greater chance of developing diarrhea with the once daily regimen as compared with the twice daily regimen.
- Inform patients that lopinavir and ritonavir is not a cure for HIV-1 infection and that they may continue to experience illnesses associated with HIV-1 infection, including opportunistic infections.
Drug Interactions
Inform patients that lopinavir and ritonavir may interact with some drugs; therefore, patients should be advised to report to their healthcare provider the use of any prescription, non-prescription medication or herbal products such as St. John’s Wort
Pancreatitis
Advise patients that pancreatitis has been observed in patients receiving lopinavir and ritonavir and to alert their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain
Skin Rash
Inform patients that skin rash ranging in severity from mild to toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, urticaria, and angioedema have been reported in patients receiving lopinavir and ritonavir or its components lopinavir and/or ritonavir. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they develop a rash while taking lopinavir and ritonavir
Hepatotoxicity
Pre-existing liver disease including Hepatitis B or C can worsen with use of lopinavir and ritonavir. This can be seen as worsening of transaminase elevations or hepatic decompensation. Advise patients that their liver function tests will need to be monitored closely especially during the first several months of lopinavir and ritonavir treatment and that they should notify their healthcare provider if they develop the signs and symptoms of worsening liver disease including loss of appetite, abdominal pain, jaundice, and itchy skin
QT and PR Interval Prolongation
Advise patients that lopinavir and ritonavir may produce changes in the electrocardiogram (e.g., PR and/or QT prolongation) and to consult their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, abnormal heart rhythm or loss of consciousness
Diabetes Mellitus/Hyperglycemia
Advise patients that new onset of diabetes or exacerbation of pre-existing diabetes mellitus, and hyperglycemia have been reported during lopinavir and ritonavir use. Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they develop the signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus including frequent urination, excessive thirst, extreme hunger or unusual weight loss and/or an increased blood sugar while on lopinavir and ritonavir as they may require a change in their diabetes treatment or new treatment
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Advise patients that immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in HIV-infected patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including lopinavir and ritonavir
Lipid Disorders
Advise patients that treatment with lopinavir and ritonavir therapy can result in substantial increases in the concentration of total cholesterol and triglycerides
Fat Redistribution
Advise patients that redistribution or accumulation of body fat may occur in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy and that the cause and long term health effects of these conditions are not known at this time
Patients with Hemophilia
Advise patients with hemophilia that they may experience increased bleeding when treated with protease inhibitors such as lopinavir and ritonavir
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
Inform patients that there is an antiretroviral pregnancy registry that monitors fetal outcomes of pregnant women exposed to lopinavir and ritonavir
Lactation
Instruct women with HIV-1 infection not to breastfeed because HIV-1 can be passed to the baby in breast milk
Distributed by:
Philadelphia, PA 19136
10-1133
Rev. 11/2020
MG #38379
9MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
10-1146
Rev. 11/2020
MG #38380
10INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Lopinavir and Ritonavir (loe pin' a vir) (ri ton' na vir)
Read this Instructions for Use before you start taking lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or treatment.
Important information about measuring lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution:
Always use the oral syringe that comes with your lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution to measure your prescribed dose. Ask your doctor or pharmacist to show you how to measure your prescribed dose.
Each lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution carton contains:
1 Lopinavir and Ritonavir Oral Solution bottle 1 Bottle adapter 1 Oral syringe 1 Prescribing Information 1 Medication Guide and Instructions for Use
How should I store lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution?
Store lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution in a refrigerator, between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution that is kept refrigerated may be used until the expiration date printed on the label. Lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution that is stored at room temperature (less than 77°F or 25°C) should be used within 2 months. Keep lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution away from high heat. Throw away any medicine that is out of date or that you no longer need. Keep lopinavir and ritonavir oral solution and all medicines out of the reach of children. This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Lannett Company, Inc.
Philadelphia, PA 19136
10-1154
Rev. 11/2020
MG #38380
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0527-
Lopinavir and
80 mg/20 mg per mL
Rx Only
160 ml (5.4 fl. oz)
Lannett
