Brand Name
Mycamine
Generic Name
Micafungin
View Brand Information FDA approval date: March 16, 2005
Classification: Echinocandin Antifungal
Form: Injection
What is Mycamine (Micafungin)?
Micafungin in Sodium Chloride Injection is indicated for: Treatment of Candidemia, Acute Disseminated Candidiasis, Candida Peritonitis and Abscesses in adult and pediatric patients 4 months of age and older for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved [ see Clinical Studies (1.
Approved To Treat
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Mycamine (Micafungin sodium)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
MYCAMINE
• Treatment of Candidemia, Acute Disseminated Candidiasis, Candida Peritonitis and Abscesses in adult and pediatric patients 4 months of age and older [see Clinical Studies (
• Treatment of Candidemia, Acute Disseminated Candidiasis, Specific Populations (.
• Treatment of Esophageal Candidiasis in adult and pediatric patients 4 months of age and older Studies (.
• Prophylaxis of Clinical Studies (.
• Treatment of Candidemia, Acute Disseminated Candidiasis, Specific Populations (.
• Treatment of Esophageal Candidiasis in adult and pediatric patients 4 months of age and older Studies (.
• Prophylaxis of Clinical Studies (.
Limitations of Use
• The safety and effectiveness of MYCAMINE have Populations (.
• MYCAMINE has not been adequately studied in patients with endocarditis, osteomyelitis and meningoencephalitis due to
• The efficacy of MYCAMINE against infections caused by fungi other than
• MYCAMINE has not been adequately studied in patients with endocarditis, osteomyelitis and meningoencephalitis due to
• The efficacy of MYCAMINE against infections caused by fungi other than
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
MYCAMINE is a sterile, white lyophilized powder for reconstitution for intravenous infusion available as:
- 50 mg single-dose vial
- 100 mg single-dose vial
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
MYCAMINE is contraindicated in persons with known hypersensitivity to micafungin, any component of MYCAMINE, or other echinocandins.
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Hematological Effects
- Hepatic Effects
- Renal Effects
- Infusion and Injection Site Reactions
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of MYCAMINE cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The overall safety of MYCAMINE was assessed in 520 healthy volunteers and 3417 adult and pediatric patients who received single or multiple doses of MYCAMINE across 50 clinical trials, including the invasive candidiasis, esophageal candidiasis and prophylaxis trials. The doses of MYCAMINE administered included doses above and below the recommended doses
Clinical Trials Experience in Adults
In clinical trials with MYCAMINE, 2497/2748 (91%) adult patients experienced at least one adverse reaction.
Candidemia and Other Candida Infections
In a randomized, double-blind trial for the treatment of candidemia and other
In a second, supportive, randomized, double-blind trial for the treatment of candidemia and other
Esophageal Candidiasis
In a randomized, double-blind study for treatment of esophageal candidiasis, a total of 202/260 (78%) patients who received MYCAMINE 150 mg/day and 186/258 (72%) patients who received intravenous fluconazole 200 mg/day experienced an adverse reaction. Adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation were reported in 17 (7%) MYCAMINE-treated patients; and in 12 (5%) fluconazole-treated patients. Selected treatment-emergent adverse reactions occurring in 5% or more of the patients and more frequently in the MYCAMINE group, are shown in
Prophylaxis of Candida Infections in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients
A double-blind trial was conducted in a total of 882 patients scheduled to undergo an autologous or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. The median duration of treatment was 18 days (range 1 to 51 days) in both treatment arms.
All adult patients who received MYCAMINE (382) or fluconazole (409) experienced at least one adverse reaction during the study. Treatment-emergent adverse reactions resulting in MYCAMINE discontinuation were reported in 15 (4%) adult patients; while those resulting in fluconazole discontinuation were reported in 32 (8%). Selected adverse reactions reported in 15% or more of adult patients and more frequently in the MYCAMINE treatment arm, are shown in
Other selected adverse reactions reported at less than 5% in adult clinical trials are listed below:
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders: coagulopathy, pancytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Cardiac disorders: cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, pericardial effusion
- General disorders and administration site conditions: infusion reaction, injection site thrombosis
- Hepatobiliary disorders: hepatocellular damage, hepatomegaly, jaundice, hepatic failure
- Immune disorders: hypersensitivity, anaphylactic reaction
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders: hypernatremia, hypokalemia
- Nervous system disorders: convulsions, encephalopathy, intracranial hemorrhage
- Psychiatric disorders: delirium
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: urticaria
Clinical Trials Experience in Pediatric Patients
The safety of MYCAMINE was assessed in 593 pediatric patients, 425 of whom were 4 months through 16 years of age and 168 of whom were 3 days to less than 4 months of age who received at least one dose of MYCAMINE across 15 clinical trials.
Of the 425 pediatric patients, 4 months through 16 years of age enrolled in 11 clinical trials, 235 (55%) were male, 290 (68%) were white, with the following age distribution: 62 (15%) 4 months to <2 years, 108 (25%) 2 to 5 years, 140 (33%) 6 to 11 years, and 115 (27%) 12 to 16 years of age. The mean treatment duration was 26.1 days. A total of 246 patients received at least one dose of MYCAMINE ranging from 2 to 10 mg/kg. Overall, 388/425 (91%) patients experienced at least one adverse reaction. Adverse reactions occurring in ≥15% or more of micafungin-treated pediatric patients 4 months of age and older are: vomiting (32%), diarrhea (24%), pyrexia (24%), hypokalemia (22%), nausea (21%), mucosal inflammation (19%), thrombocytopenia (19%), abdominal pain (18%), headache (15%), and hypertension (15%).
Two randomized, double-blind active-controlled trials included pediatric patients. In the invasive candidiasis/candidemia trial, the efficacy and safety of MYCAMINE (2 mg/kg/day for patients weighing 40 kg or less and 100 mg/day for patients weighing greater than 40 kg) was compared to amphotericin B liposome (3 mg/kg/day) in 112 pediatric patients. Treatment-emergent adverse reactions occurred in 51/56 (91%) of patients in the MYCAMINE group and 52/56 (93%) of patients in the amphotericin B liposome group. Treatment-emergent adverse reactions resulting in drug discontinuation were reported in 2 (4%) MYCAMINE-treated pediatric patients and in 9 (16%) amphotericin B liposome-treated pediatric patients.
The prophylaxis study in patients undergoing HSCT investigated the efficacy of MYCAMINE (1 mg/kg/day for patients weighing 50 kg or less and 50 mg/day for patients weighing greater than 50 kg) as compared to fluconazole (8 mg/kg/day for patients weighing 50 kg or less and 400 mg/day for patients weighing greater than 50 kg). All 91 pediatric patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse reaction. Three (7%) pediatric patients discontinued MYCAMINE due to adverse reaction, while one (2%) patient discontinued fluconazole.
Selected adverse reactions, occurring in 15% or more of the patients and more frequently in a MYCAMINE group, for the two comparative trials are shown in
Other clinically significant adverse reactions reported at less than 15% in pediatric clinical trials are listed below:
- Hepatobiliary disorders: hyperbilirubinemia
- Investigations: liver tests abnormal
- Renal Disorders: renal failure
Clinical Trials Experience in Pediatric Patients Younger than 4 Months of Age
The safety of MYCAMINE was assessed in 168 pediatric patients younger than 4 months of age who received varying doses of MYCAMINE in 9 clinical trials. The mean treatment duration was 16.6 days. A total of 59 patients received MYCAMINE at doses ≤4 mg/kg/day and 109 patients received MYCAMINE doses >4 mg/kg/day [5 to 15 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.3 to 3.8 times the recommended dosage in pediatric patients less than 4 months old)].
The adverse reaction profile of MYCAMINE in pediatric patients younger than 4 months of age was generally comparable to that of pediatric patients 4 months of age and older and adults. The most frequent adverse reactions (≥15%) in pediatric patients younger than 4 months old receiving a MYCAMINE dose of approximately 4 mg/kg/day included hypokalemia (25%), thrombocytopenia (25%), acidosis (20%), sepsis (20%), anemia (15%), oxygen saturation decreased (15%), and vomiting (15%). No new safety signals were seen in patients who received 5 to 15 mg/kg/day
Additional clinically significant adverse reactions reported in less than 15% of pediatric patients younger than 4 months of age who received approximately 4 mg/kg/day are listed below:
- Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, coagulation disorder neonatal
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: hematochezia, intestinal perforation, ascites, ileus, intestinal infarction, diarrhea, abdominal distension
- General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: peripheral swelling, generalized edema, pyrexia, infusion site extravasation, edema neonatal
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: hyperbilirubinemia
- Investigations: blood lactate dehydrogenase increased, blood urea increased, ECG QRS complex prolonged
- Vascular Disorders: neonatal hypotension, thrombophlebitis
- Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: hypertonia neonatal
- Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: pleural effusion, respiratory failure, neonatal aspiration, respiratory distress
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders: hyperglycemia, dehydration, hypocalcemia, hypermagnesemia
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of micafungin for injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders: disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Hepatobiliary disorders: hepatic disorder
- Renal and urinary disorders: renal impairment
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Vascular disorders: shock
5DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
There has been no evidence of either psychological or physical dependence or withdrawal or rebound effects with MYCAMINE.
6OVERDOSAGE
MYCAMINE is highly protein bound and, therefore, is not dialyzable. No cases of MYCAMINE overdosage have been reported. Repeated daily doses up to 8 mg/kg (maximum total dose of 896 mg) in adult patients, up to 6 mg/kg in pediatric patients 4 months of age and older, and up to 15 mg/kg in pediatric patients younger than 4 months of age have been administered in clinical trials with no reported dose-limiting toxicity
7DESCRIPTION
MYCAMINE is a sterile, lyophilized product for intravenous (IV) infusion that contains micafungin sodium. Micafungin sodium is a semisynthetic lipopeptide (echinocandin) synthesized by a chemical modification of a fermentation product of
Each single-dose vial contains 50 mg micafungin (equivalent to 50.86 mg micafungin sodium) or 100 mg micafungin (equivalent to 101.73 mg micafungin sodium), 200 mg lactose monohydrate, with citric acid and/or sodium hydroxide (used for pH adjustment). MYCAMINE must be diluted with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
Micafungin sodium is chemically designated as:
Pneumocandin A0,1-[(4
The chemical structure of micafungin sodium is:
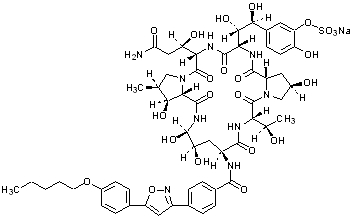
The empirical/molecular formula is C
Micafungin sodium is a light-sensitive, hygroscopic white powder that is freely soluble in water, isotonic sodium chloride solution, N,N-dimethylformamide and dimethylsulfoxide, slightly soluble in methyl alcohol, and practically insoluble in acetonitrile, ethyl alcohol (95%), acetone, diethyl ether and n-hexane.
8HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
MYCAMINE is supplied as a sterile, white lyophilized powder for reconstitution for intravenous infusion, and is available in the following packaging configurations:
- cartons of 10 individually packaged 50 mg single-dose vials, coated with a light protective film and sealed with a blue flip-off cap. (NDC 0469-3250-10)
- cartons of 10 individually packaged 100 mg single-dose vials, coated with a light protective film and sealed with a red flip-off cap. (NDC 0469-3211-10)
Storage
Unopened vials of lyophilized material must be stored at room temperature, 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]
Store the reconstituted product at 25°C (77°F)
Store the diluted solution at 25°C (77°F)
Protect from light.
9PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Hypersensitivity
Inform patients about the serious adverse effects of MYCAMINE including hypersensitivity reactions
Hepatic
Inform patients about the serious adverse effects of MYCAMINE including hepatic effects e.g., abnormal liver tests, hepatic impairment, hepatitis or worsening hepatic failure.
Hematologic
Inform patients about the serious adverse effects of MYCAMINE including hematological effects e.g., acute intravascular hemolysis, hemolytic anemia and hemoglobinuria.
Renal
Inform patients about the serious adverse effects of MYCAMINE including renal effects e.g., elevations in BUN and creatinine, renal impairment or acute renal failure.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk of MYCAMINE to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy.
Concomitant Medications
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider of any other medications they are currently taking with MYCAMINE, including over-the-counter medications.
Manufactured by:
Marketed by:
MYCAMINE
286316-MYC
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 50 mg/vial
NDC 0469-3250-10
Mycamine
(micafungin) for injection
(micafungin) for injection
50 mg/vial
For Intravenous Infusion Only
Single-Dose Vial
Discard unused portion
Single-Dose Vial
Discard unused portion
astellas 325010
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 100 mg/vial

NDC 0469-3211-10
Mycamine
(micafungin) for injection
(micafungin) for injection
100 mg/vial
For Intravenous Infusion Only
Single-Dose Vial
Discard unused portion
Single-Dose Vial
Discard unused portion
astellas 321110

