Alprazolam
What is Xanax (Alprazolam)?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The purpose of the study is to assess the success of a single administration of Staccato alprazolam compared with placebo both in rapidly terminating a seizure episode within 90 seconds and with no recurrence of seizure(s) up to 2 hours after investigational medicinal product (IMP) administration.
Summary: The goal of this clinical trial is to find out if taking a pill (oral sedation) works just as well as getting medicine through a vein (IV sedation) to help older adults feel relaxed during cataract surgery. We are also studying how these two methods affect recovery, especially thinking and memory after surgery, and how satisfied people are with their care. Participants in this study will be random...
Summary: The purpose of this study is to estimate the difference in the time to onset of action between Staccato alprazolam and intravenous (iv) midazolam using changes in power in the combined spindle and β1 frequency bands in the qEEG (quantitative electroencephalogram).
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation
- The use of benzodiazepines, including XANAX, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose or death. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes. Before prescribing XANAX and throughout treatment, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction
- The continued use of benzodiazepines, including XANAX, may lead to clinically significant physical dependence. The risks of dependence and withdrawal increase with longer treatment duration and higher daily dose. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of XANAX after continued use may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue XANAX or reduce the dosage
- acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults.
- treatment of panic disorder (PD), with or without agoraphobia in adults.
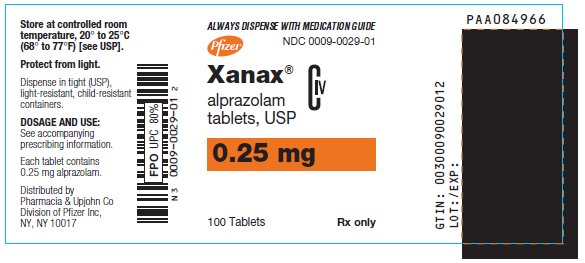
- 0.25 mg: white, oval, scored, imprinted “XANAX 0.25”
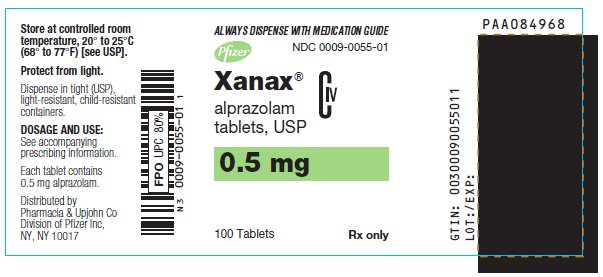
- 0.5 mg: peach, oval, scored, imprinted “XANAX 0.5”
- 1 mg: blue, oval, scored, imprinted “XANAX 1.0”
- 2 mg: white, oblong, multi-scored, imprinted “XANAX ” on one side and “2” on the reverse side
- with known hypersensitivity to alprazolam or other benzodiazepines. Angioedema has been reported
- taking strong cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole), except ritonavir
- Risks from Concomitant Use with Opioids
- Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction
- Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions
- Effects on Driving and Operating Machinery
- Patients with Depression
- Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome
- Risks in Patients with Impaired Respiratory Function
- 4-week placebo-controlled clinical studies with XANAX dosages up to 4 mg per day for the acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (Table 1)
- Short-term (up to 10 weeks) placebo-controlled clinical studies with XANAX dosages up to 10 mg per day for panic disorder, with or without agoraphobia (Table 2).
See accompanying
prescribing information.
See accompanying
prescribing information.
See accompanying
prescribing information.

See accompanying
prescribing information.

