Generic Name
DOXOrubicin
Brand Names
Adriamycin, Doxil
FDA approval date: December 23, 1987
Classification: Anthracycline Topoisomerase Inhibitor
Form: Injection, Injectable
What is Adriamycin (DOXOrubicin)?
Doxorubicin is an anthracycline topoisomerase II inhibitor indicated: as a component of multiagent adjuvant chemotherapy for treatment of women with axillary lymph node involvement following resection of primary breast cancer.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Adriamycin (Doxorubicin Hydrochloride)
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Adriamycin (DOXOrubicin HCl) for Injection, USP: Vials contain 10 mg and 50 mg doxorubicin hydrochloride as a red-orange lyophilized powder.
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
Doxorubicin is contraindicated in patients with:
- Severe myocardial insufficiency
- Recent (occurring within the past 4 to 6 weeks) myocardial infarction
- Severe persistent drug-induced myelosuppression
- Severe hypersensitivity reaction to doxorubicin including anaphylaxis
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling.
- Cardiomyopathy and Arrhythmias
- Secondary Malignancies
- Extravasation and Tissue Necrosis
- Severe Myelosuppression
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome
- Radiation Sensitization and Radiation Recall
3.1Clinical Trial Experience in Breast Cancer
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety data below were collected from 1492 women who received doxorubicin at a dose of 60 mg/m
* Includes pooled data from patients who received either AC alone for 4 cycles, or who were treated with AC for 4 cycles followed by 3 cycles of CMF
3.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of doxorubicin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac – cardiogenic shock
Cutaneous – Skin and nail hyperpigmentation, oncolysis, rash, itching, photosensitivity, urticaria, acral erythema, palmar plantar erythrodysesthesia
Gastrointestinal – Nausea, mucositis, stomatitis, necrotizing colitis, typhlitis, gastric erosions, gastrointestinal tract bleeding, hematochezia, esophagitis, anorexia, abdominal pain, dehydration, diarrhea, hyperpigmentation of the oral mucosa
Hypersensitivity – Anaphylaxis
Laboratory Abnormalities –Increased alanine aminotransferase, increased aspartate aminotransferase
Neurological – Peripheral sensory and motor neuropathy, seizures, coma
Ocular – Conjunctivitis, keratitis, lacrimation
Vascular – Phlebosclerosis, phlebitis/thrombophlebitis, hot flashes, thromboembolism
Other – Malaise/asthenia, fever, chills, weight gain
4OVERDOSAGE
Few cases of overdose have been described. A 58-year-old man with acute lymphoblastic leukemia received 10-fold overdose of doxorubicin (300 mg/m
5DESCRIPTION
Doxorubicin is a cytotoxic anthracycline antibiotic isolated from cultures of
6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-5,12-naphthacenedione hydrochloride. The structural formula is as follows:
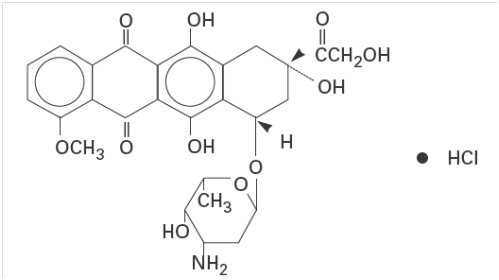
Doxorubicin binds to nucleic acids, presumably by specific intercalation of the planar anthracycline nucleus with the DNA double helix. The anthracycline ring is lipophilic, but the saturated end of the ring system contains abundant hydroxyl groups adjacent to the amino sugar, producing a hydrophilic center. The molecule is amphoteric, containing acidic functions in the ring phenolic groups and a basic function in the sugar amino group. It binds to cell membranes as well as plasma proteins.
It is supplied in the hydrochloride form as a sterile red-orange lyophilized powder containing lactose and as a sterile parenteral, isotonic solution with sodium chloride for intravenous use only.
Adriamycin (DOXOrubicin HCl) for Injection, USP:
Each 10 mg lyophilized vial contains 10 mg of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride, USP and 50 mg of Lactose Monohydrate, NF.
Each 50 mg lyophilized vial contains 50 mg of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride, USP and 250 mg of Lactose Monohydrate, NF.
6CLINICAL STUDIES
The clinical efficacy of doxorubicin HCl-containing regimens for the post-operative, adjuvant treatment of surgically resected breast cancer was evaluated in a meta-analysis conducted by the Early Breast Cancer Trialists Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). The EBCTCG meta-analyses compared cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil (CMF) to no chemotherapy (19 trials including 7523 patients) and doxorubicin HCl-containing regimens with CMF as an active control (6 trials including 3510 patients). Data from the meta-analysis of trials comparing CMF to no therapy were used to establish the historical treatment effect size for CMF regimens. The major efficacy outcome measures were disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
Of the 3510 women (2157 received doxorubicin HCl-containing regimens and 1353 received CMF treatment) with early breast cancer involving axillary lymph nodes included in the six trials from the meta-analyses, approximately 70% were premenopausal and 30% were postmenopausal. At the time of the meta-analysis, 1745 first recurrences and 1348 deaths had occurred. The analyses demonstrated that doxorubicin HCl-containing regimens retained at least 75% of the historical CMF adjuvant effect on DFS with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.91 (95% CI, 0.8 to 1.01 ) and on OS with a HR of 0.91 (95% CI, 0.8 to 1.03 ). Results of these analyses for both DFS and OS are provided in Table 2 and Figures 1 and 2.
Table 2. Summary of Randomized Trials Comparing Doxorubicin Containing Regimens Versus CMF in Meta-Analysis
Abbreviations: DFS = disease free survival; OS = overall survival; AC = doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide; AVbCMF = doxorubicin, vinblastine, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil; CMF = cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil; CMFVA = cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil, vincristine, doxorubicin; FAC = 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide; FACV = 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine; HR = hazard ratio; CI = confidence interval
* Includes pooled data from patients who received either AC alone for 4 cycles, or who were treated with AC for 4
† Patients received alternating cycles of AVb and CMF.

7REFERENCES
1. “Hazardous Drugs”.
8HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Adriamycin (DOXOrubicin HCI) for Injection, USP is supplied as a sterile red-orange lyophilized powder in single dose flip-top vials in the following package strengths:
NDC 0143-9275-01: 10 mg vial; individually boxed.
NDC 0143-9277-01: 50 mg vial; individually boxed.
Store all vials at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Reconstituted Solution Stability
After adding the diluent, the vial should be shaken and the contents allowed to dissolve. The reconstituted solution is stable for 7 days at room temperature and under normal room light (100 foot-candles) and 15 days under refrigeration (2° to 8°C). It should be protected from exposure to sunlight. Discard any unused solution from the 10 mg and 50 mg single dose vials.
Handling and Disposal
Handle and dispose of Adriamycin (DOXOrubicin HCl) for Injection, USP consistent with recommendations for the handling and disposal of hazardous drugs.
9PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information). Inform patients of the following:
- Doxorubicin can cause irreversible myocardial damage. Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider for symptoms of heart failure during or after treatment with doxorubicin HCl
- There is an increased risk of treatment-related leukemia from doxorubicin HCl
- Doxorubicin can reduce the absolute neutrophil count resulting in an increased risk of infection. Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider for new onset fever or symptoms of infection
- Doxorubicin can cause fetal harm when administered during pregnancy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with doxorubicin HCl and for 6 months after treatment, and to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, during treatment with doxorubicin HCl
- Doxorubicin may induce chromosomal damage in sperm, which may lead to loss of fertility and offspring with birth defects. Advise patients to use effective contraception during and for 6 months after treatment
- Doxorubicin can cause premature menopause in females and loss of fertility in males
- Discontinue nursing while receiving doxorubicin HCl
- Doxorubicin can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mouth/oral pain and sores. Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider should they develop any severe symptoms that prevent them from eating and drinking
- Doxorubicin causes alopecia
- Doxorubicin can cause their urine to appear red for 1 to 2 days after administration.
Manufactured by
THYMOORGAN PHARMAZIE GmbH,
Schiffgraben 23, 38690 Goslar, Germany
Distributed by
West-Ward Pharmaceuticals
Eatontown, NJ 07724 USA
Revised January 2018
127.207.029/01
10PATIENT INFORMATION
Patient Information
DOXORUBICIN (dok-suh-roo-buh-sin) HYDROCHLORIDE for Injection, for intravenous use
What is the most important information I should know about Doxorubicin?
Doxorubicin may cause serious side effects including:
- Heart failure. Doxorubicin may cause heart muscle damage that may lead to heart failure, which is a condition in which the heart does not pump well. Heart failure is irreversible in some cases and can lead to death. Heart failure can happen during your treatment with Doxorubicin or months to years after stopping treatment. Your risk of heart muscle damage increases with higher total amounts of doxorubicin hydrochloride that you receive in your lifetime. Your risk of heart failure is higher if you:
- already have other heart problems
- have had or are currently receiving radiation therapy to your chest
- have had treatment with certain other anti-cancer medicines
- take other medicines that can have severe side effects on your heart
- Tell your doctor if you get any of these symptoms of heart failure during or after treatment with Doxorubicin:
- extreme tiredness or
- fast heartbeat weakness
- swelling of your feet and ankles
- shortness of breath
- Your doctor will do tests to check the strength of your heart muscle before,
- during, and after your treatment with Doxorubicin.
- Risk of new cancers. You may have an increased risk of developing certain blood cancers called acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) after treatment with doxorubicin. Talk with your doctor about your risk of developing new cancers if you take Doxorubicin.
- Skin damage near the vein where Doxorubicin is given (Injection site reaction). Doxorubicin can damage the skin if it leaks out of the vein. Symptoms of infusion reaction include blisters and skin sores at injection site which may require skin grafts.
- Decreased blood cell counts. Doxorubicin can cause a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cells important in fighting bacterial infections) and platelets (important for clotting and to control bleeding). This may lead to a serious infection, the need for blood transfusions, treatment in a hospital and death. Your doctor will check your blood cell count during your treatment with Doxorubicin and after you have stopped your treatment. Call your doctor right away if you get a fever (temperature of 100.4°F or greater) or chills with shivering.
What is Doxorubicin?
Doxorubicin is a prescription medicine used to treat certain types of cancers. Doxorubicin may be used alone or along with other anti-cancer medicines.
Who should not receive Doxorubicin?
Do not receive Doxorubicin if:
- you have had a recent heart attack or have severe heart problems
- your blood cell counts (platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells) are
- very low because of prior chemotherapy
- you have a severe liver problem
- you have had a serious allergic reaction to doxorubicin hydrochloride
What should I tell my doctor before receiving Doxorubicin?
Before you receive Doxorubicin, tell your doctor if you:
- have heart problems including heart failure
- are currently receiving radiation therapy or plan to receive radiation to the chest
- have severe liver problems
- have had an allergic reaction to doxorubicin
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Doxorubicin can harm your unborn baby. Women who are able to become pregnant and men who take Doxorubicin should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 6 months after treatment. Talk to your doctor about birth control methods. If you or your partner becomes pregnant, tell your doctor right away.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breast feed. Doxorubicin can pass into your breast milk and harm your baby. You and your doctor should decide if you will receive Doxorubicin or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Doxorubicin can interact with other medicines. Do not start any new medicine before you talk with the doctor that prescribed Doxorubicin.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How will I receive Doxorubicin?
- Doxorubicin will be given to you into your vein.
What are the possible side effects of Doxorubicin?
Doxorubicin may cause serious side effects, including:
- See
Doxorubicin may cause lower sperm counts and sperm problems in men.
This could affect your ability to father a child and cause birth defects. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you. Talk to your healthcare provider about family planning options that might be right for you.
Irreversible amenorrhea or early menopause. Your periods (menstrual cycle) may completely stop when you receive Doxorubicin. Your periods may or may not return following treatment. Talk to your healthcare provider about family planning options that might be right for you.
The most common side effects of Doxorubicin include:
- Total hair loss (alopecia). Your hair may re-grow after your treatment
- nausea
- vomiting
Other side effects:
- Red colored urine. You may have red colored urine for 1 to 2 days after your infusion of Doxorubicin. This is normal. Tell your doctor if it does not stop in a few days, or if you see what looks like blood or blood clots in your urine.
- Darkening of your nails or separation of your nails from your nail bed.
- Easy bruising or bleeding.
- Call your doctor if you have severe symptoms that prevent you from eating or drinking, such as:
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- mouth sores
Tell your doctor or nurse if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of Doxorubicin.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Doxorubicin.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet.
You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Doxorubicin that is written for health professionals.
For more information, call 1-877-845-0689.
What are the ingredients of Doxorubicin?
Active ingredient: doxorubicin hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients for Doxorubicin Hydrochloride for Injection: Lactose Monohydrate
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by
THYMOORGAN PHARMAZIE GmbH,
Schiffgraben 23, 38690 Goslar, Germany
Distributed by
West-Ward Pharmaceuticals
Eatontown, NJ 07724 USA
Revised January 2018
127.207.029/01
11MG PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

NDC 0143-9275-01 Rx only
10 mg/vial
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
LYOPHILIZED
12MG PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

NDC 0143-9277-01 Rx only
50 mg/vial
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
LYOPHILIZED