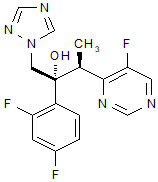
Vfend
What is Vfend (Voriconazole)?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: This screening and multi-sub-study Phase 1b/2 trial will establish a method for genomic screening followed by assigning and accruing simultaneously to a multi-study Master Protocol (BAML-16-001-M1). The specific subtype of acute myeloid leukemia will determine which sub-study, within this protocol, a participant will be assigned to evaluate investigational therapies or combinations with the ultima...
Summary: The purpose of this study is to determine if EL219 is safe and effective compared to the standard of care for early treatment of suspected invasive mould infection.
Summary: This project aims to address invasive fungal infections in patients with blood cancer, by precision dosing of voriconazole based on CYP2C19 genotype testing with Bayesian dose-forecasting dosing software to develop patient-centric and maximally effective dosing regimens. This study investigates if voriconazole increases the proportion of patients achieving therapeutic exposure at day 8 of dosing c...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- VFEND is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to voriconazole or its excipients. There is no information regarding cross-sensitivity between VFEND (voriconazole) and other azole antifungal agents. Caution should be used when prescribing VFEND to patients with hypersensitivity to other azoles.
- Coadministration of pimozide, quinidine or ivabradine with VFEND is contraindicated because increased plasma concentrations of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and rare occurrences of
- Coadministration of VFEND with sirolimus is contraindicated because VFEND significantly increases sirolimus concentrations
- Coadministration of VFEND with rifampin, carbamazepine, long-acting barbiturates or St. John's Wort is contraindicated because these drugs are likely to decrease plasma voriconazole concentrations significantly
- Coadministration of standard doses of voriconazole with efavirenz doses of 400 mg every 24 hours or higher is contraindicated, because efavirenz significantly decreases plasma voriconazole concentrations in healthy subjects at these doses. Voriconazole also significantly increases efavirenz plasma concentrations
- Coadministration of VFEND with high-dose ritonavir (400 mg every 12 hours) is contraindicated because ritonavir (400 mg every 12 hours) significantly decreases plasma voriconazole concentrations. Coadministration of voriconazole and low-dose ritonavir (100 mg every 12 hours) should be avoided, unless an assessment of the benefit/risk to the patient justifies the use of voriconazole
- Coadministration of VFEND with rifabutin is contraindicated since VFEND significantly increases rifabutin plasma concentrations and rifabutin also significantly decreases voriconazole plasma concentrations
- Coadministration of VFEND with ergot alkaloids (ergotamine and dihydroergotamine) is contraindicated because VFEND may increase the plasma concentration of ergot alkaloids, which may lead to ergotism
- Coadministration of VFEND with naloxegol is contraindicated because VFEND may increase plasma concentrations of naloxegol which may precipitate opioid withdrawal symptoms
- Coadministration of VFEND with tolvaptan is contraindicated because VFEND may increase tolvaptan plasma concentrations and increase risk of adverse reactions
- Coadministration of VFEND with venetoclax at initiation and during the ramp-up phase is contraindicated in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) due to the potential for increased risk of tumor lysis syndrome
- Coadministration of VFEND with lurasidone is contraindicated since it may result in significant increases in lurasidone exposure and the potential for serious adverse reactions
- Coadministration of VFEND with finerenone is contraindicated since it may result in significant increases in finerenone exposure and the potential for serious adverse reactions
- Advise patients of the risk of photosensitivity (with or without concomitant methotrexate), accelerated photoaging, and skin cancer.
- Advise patients that VFEND can cause serious photosensitivity and to immediately contact their healthcare provider for new or worsening skin rash.
- Advise patients to avoid exposure to direct sun light and to use measures such as protective clothing and sunscreen with high sun protection factor (SPF).
- Advise female patients of the potential risks to a fetus.
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with VFEND.
(voriconazole) for injection
200 mg* of voriconazole
No Preservatives

200 mg* of voriconazole
rubber latex
No Preservatives





