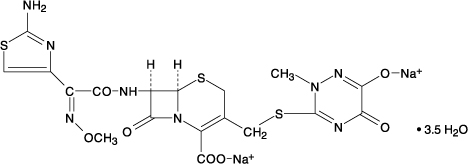
CefTRIAXone
View Brand InformationWhat is CefTRIAXone?
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The goal of this clinical trial is to learn if oral treatment with pivmecillinam is effective to treat febrile urinary tract infections in adult patients. Hospitalized patients who have received 2-4 days of intravenous antibiotic therapy for febrile urinary tract infections, and have responded to treatment, will be randomized to either pivmecillinam or standard treatment (other oral or intravenous...
Summary: Lyme disease is a public health crisis in the US. It is estimated that over 400,000 cases occur every year with 10-20% of those infected going on to develop Post-Treatment Lyme disease Syndrome (PTLDS). The goal of this study is to investigate if giving Ceftriaxone every 5 days for about 6 weeks kills the organism that produces persistent Lyme infection. Enrolled participants will be randomized 1:...
Summary: Whether prophylactic antibiotics should be administered in the endoscopic secondary prevention of GVB or not is unclear. In this non-inferiority trial, we are aimed to evaluate whether prophylactic antibiotics are essential in the endoscopic secondary prevention of cirrhotic patients with gastroesophageal variceal bleeding.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Advise patients that neurological adverse reactions could occur with ceftriaxone for injection use. Instruct patients or their caregivers to inform their healthcare provider at once of any neurological signs and symptoms, including encephalopathy (disturbance of consciousness including somnolence, lethargy, and confusion), seizures, myoclonus, and nonconvulsive status epilepticus, for immediate treatment, or discontinuation of ceftriaxone for injection (see
- Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including ceftriaxone for injection should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., common cold).
- When ceftriaxone for injection is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by ceftriaxone for injection or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.


