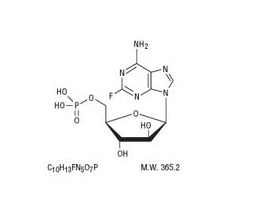
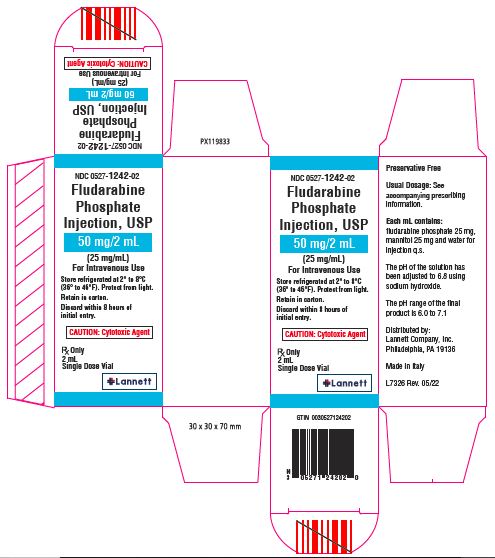
Fludarabine
View Brand InformationWhat is Fludarabine?
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: The purpose of this study is to determine the safety, tolerability, optimal dose, and preliminary efficacy of BMS-986515, a healthy donor (HD) allogeneic CD19-targeted CART cell product, in participants with severe, refractory autoimmune diseases.
Background: Blood cancers (such as leukemias) can be hard to treat, especially if they have mutations in the TP53 or RAS genes. These mutations can cause the cancer cells to create substances called neoepitopes. Researchers want to test a method of treating blood cancers by altering a person s T cells (a type of immune cell) to target neoepitopes.
Background: High-risk blood cancers (leukemias and lymphomas) often come back after treatment, and many cannot be cured with chemotherapy alone. These cancers may be treated and potentially cured in 2 ways: (1) Bone marrow transplant (allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, or alloHCT) gives immune and blood stem cells from a donor. These new cells can attack the cancer and also grow into healthy blood...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information