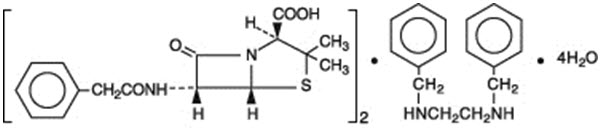
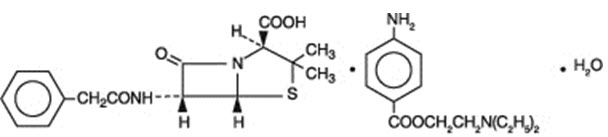
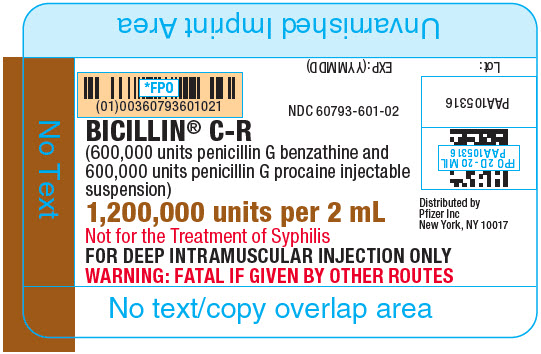
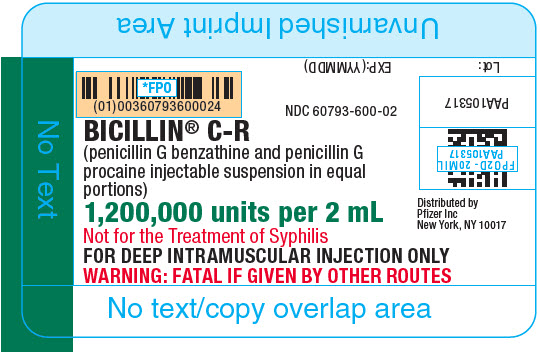
As with other penicillins, untoward reactions of the sensitivity phenomena are likely to occur, particularly in individuals who have previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to penicillins or in those with a history of allergy, asthma, hay fever, or urticaria.
The following adverse reactions have been reported with Bicillin C-R during post-marketing experience:
Skin and Appendages: Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) (See WARNINGS.) The following have been reported with parenteral penicillin G (the active moiety in Bicillin C-R):
General: Hypersensitivity reactions including the following: skin eruptions (maculopapular to exfoliative dermatitis), urticaria, laryngeal edema, fever, eosinophilia; other serum sickness-like reactions (including chills, fever, edema, arthralgia, and prostration); and anaphylaxis including shock and death: severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), such as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) (See WARNINGS.) Note: Urticaria, other skin rashes, and serum sickness-like reactions may be controlled with antihistamines and, if necessary, systemic corticosteroids. Whenever such reactions occur, penicillin G should be discontinued unless, in the opinion of the physician, the condition being treated is life-threatening and amenable only to therapy with penicillin G. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine. Oxygen, intravenous steroids, and airway management, including intubation, should also be administered as indicated. Gastrointestinal: Pseudomembranous colitis. Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibacterial treatment. (See WARNINGS section.) Hematologic: Hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Neurologic: Neuropathy.
Urogenital: Nephropathy.
The following adverse events have been temporally associated with parenteral administrations of penicillin G benzathine (a component of Bicillin C-R):
Body as a Whole: Hypersensitivity reactions including allergic vasculitis, pruritis, fatigue, asthenia, and pain; aggravation of existing disorder; headache, Nicolau syndrome.
Cardiovascular: Cardiac arrest; hypotension; tachycardia; palpitations; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary embolism; vasodilation; vasovagal reaction; cerebrovascular accident; syncope.
Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting; blood in stool; intestinal necrosis.
Hemic and Lymphatic: Lymphadenopathy.
Immune System Disorders: Acute myocardial ischemia with or without myocardial infarction may occur as part of an allergic reaction (Kounis syndrome).
Injection Site: Injection site reactions including pain, inflammation, lump, abscess, necrosis, edema, hemorrhage, cellulitis, hypersensitivity, atrophy, ecchymosis, and skin ulcer. Neurovascular reactions including warmth, vasospasm, pallor, mottling, gangrene, numbness of the extremities, cyanosis of the extremities, and neurovascular damage.
Metabolic: Elevated BUN, creatinine, and SGOT.
Musculoskeletal: Joint disorder, periostitis; exacerbation of arthritis; myoglobinuria; rhabdomyolysis.
Nervous System: Nervousness; tremors; dizziness; somnolence; confusion; anxiety; euphoria; transverse myelitis; seizures; coma. A syndrome manifested by a variety of CNS symptoms such as severe agitation with confusion, visual and auditory hallucinations, and a fear of impending death (Hoigne's syndrome), has been reported after administration of penicillin G procaine and, less commonly, after injection of the combination of penicillin G benzathine and penicillin G procaine. Other symptoms associated with this syndrome, such as psychosis, seizures, dizziness, tinnitus, cyanosis, palpitations, tachycardia, and/or abnormal perception in taste, also may occur.
Respiratory: Hypoxia; apnea; dyspnea.
Skin: Diaphoresis.
Special Senses: Blurred vision; blindness.
Urogenital: Neurogenic bladder; hematuria; proteinuria; renal failure; impotence; priapism.