Generic Name
Topiramate
Brand Names
Qsymia, Qudexy, Eprontia, Phentermine, Trokendi, Topamax
FDA approval date: January 01, 1997
Classification: Sympathomimetic Amine Anorectic
Form: Tablet, Capsule, Solution
What is Qsymia (Topiramate)?
QUDEXY XR is indicated for: Epilepsy: initial monotherapy for the treatment of partial-onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in patients 2 years of age and older.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Qsymia (phentermine and topiramate)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
QSYMIA is indicated in combination with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in:
- Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity
- Adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition
2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
QSYMIA extended-release capsules are available in four strengths (phentermine mg/topiramate mg):
- 3.75 mg/23 mg - purple cap imprinted with VIVUS and purple body imprinted with 3.75/23
- 7.5 mg/46 mg - purple cap imprinted with VIVUS and yellow body imprinted with 7.5/46
- 11.25 mg/69 mg - yellow cap imprinted with VIVUS and yellow body imprinted with 11.25/69
- 15 mg/92 mg - yellow cap imprinted with VIVUS and white body imprinted with 15/92
3CONTRAINDICATIONS
QSYMIA is contraindicated in patients:
- Who are pregnant
- With glaucoma
- With hyperthyroidism
- Taking or within 14 days of stopping a monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- With known hypersensitivity to phentermine, topiramate or any of the excipients in QSYMIA, or idiosyncrasy to the sympathomimetic amines
4ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
- Risk of Ophthalmologic Adverse Reactions
- Mood and Sleep Disorders
- Cognitive Impairment
- Slowing of Linear Growth
- Metabolic Acidosis
- Decrease in Renal Function
- Risk of Seizures with Abrupt Withdrawal of QSYMIA
- Kidney Stones
- Oligohydrosis and Hyperthermia
- Hypokalemia
- Serious Skin Reactions
4.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described herein reflect exposure to QSYMIA in two 1-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trials and two supportive trials in 2,318 adult patients with overweight or obesity [936 (40%) patients with hypertension, 309 (13%) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, 808 (35%) patients with BMI greater than 40 kg/m
4.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post approval use of QSYMIA, phentermine, and topiramate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
5DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 5 displays clinically significant drug interactions with QSYMIA.
6OVERDOSAGE
In the event of a significant overdose with QSYMIA, if the ingestion is recent, the stomach should be emptied immediately by gastric lavage or by induction of emesis. Appropriate supportive treatment should be provided according to the patient's clinical signs and symptoms. In the event of an overdose of QSYMIA, consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations.
Acute overdose of phentermine may be associated with restlessness, tremor, hyperreflexia, rapid respiration, confusion, aggressiveness, hallucinations, and panic states. Fatigue and depression usually follow the central stimulation. Cardiovascular effects include arrhythmia, hypertension or hypotension, and circulatory collapse. Gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Fatal poisoning usually terminates in convulsions and coma. Manifestations of chronic intoxication with anorectic drugs include severe dermatoses, marked insomnia, irritability, hyperactivity, and personality changes. A severe manifestation of chronic intoxication is psychosis, often clinically indistinguishable from schizophrenia.
Management of acute phentermine intoxication is largely symptomatic and includes lavage and sedation with a barbiturate. Acidification of the urine increases phentermine excretion. Intravenous phentolamine has been suggested for possible acute, severe hypertension, if this complicates phentermine overdosage.
Topiramate overdose has resulted in severe metabolic acidosis. Other signs and symptoms include convulsions, drowsiness, speech disturbance, blurred vision, diplopia, impaired mentation, lethargy, abnormal coordination, stupor, hypotension, abdominal pain, agitation, dizziness, and depression. The clinical consequences were not severe in most cases, but deaths have been reported after overdoses involving topiramate. A patient who ingested a dose between 96 and 110 gm topiramate was admitted to hospital with coma lasting 20 to 24 hours followed by full recovery after 3 to 4 days.
Hemodialysis is an effective means of removing topiramate from the body.
7DESCRIPTION
QSYMIA extended-release capsules are comprised of immediate-release phentermine hydrochloride (expressed as the weight of the free base) and extended-release topiramate. QSYMIA contains phentermine hydrochloride, a sympathomimetic amine anorectic, and topiramate, a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide.
8HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
QSYMIA (phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules) are available as follows (see
9PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
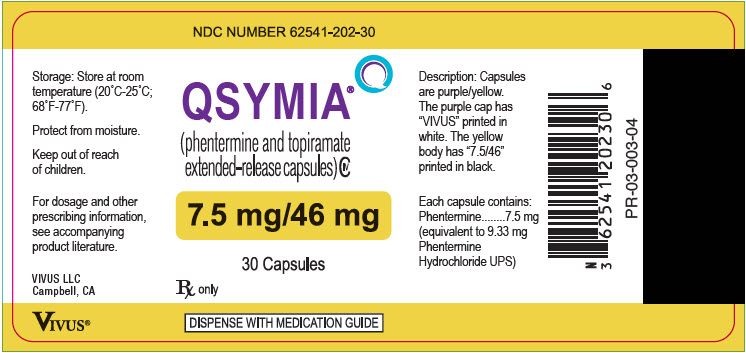
10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 7.5 mg/46 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC NUMBER 62541-202-30
QSYMIA
7.5 mg/46 mg
30 Capsules
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 3.75 mg/23 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC NUMBER 62541-201-30
QSYMIA
3.75 mg/23 mg
30 Capsules
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE

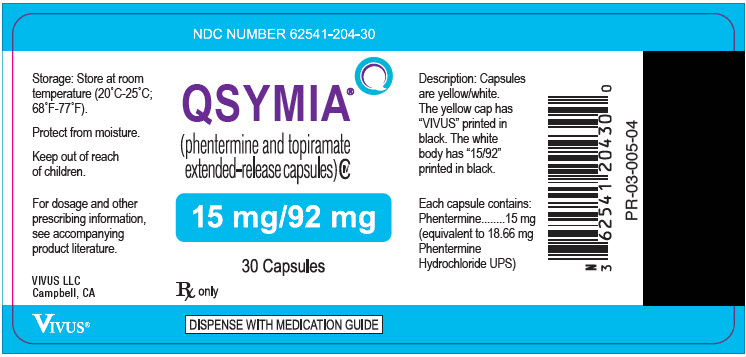
12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 mg/92 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC NUMBER 62541-204-30
QSYMIA
15 mg/92 mg
30 Capsules
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
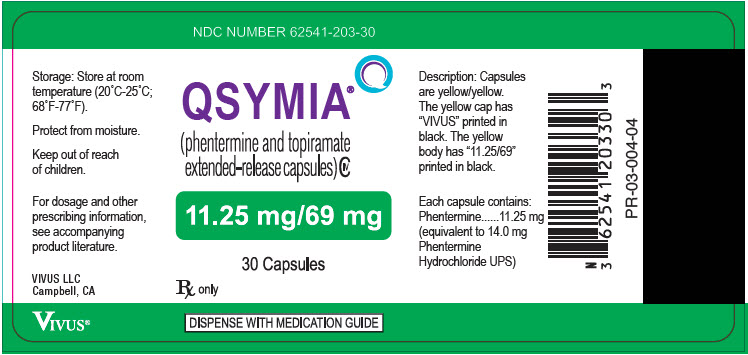
13PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 11.25 mg/69 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC NUMBER 62541-203-30
QSYMIA
11.25 mg/69 mg
30 Capsules
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE