Generic Name
Eltrombopag
Brand Names
Promacta, Alvaiz
FDA approval date: April 01, 2016
Classification: Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonist
Form: Tablet, Powder
What is Promacta (Eltrombopag)?
PROMACTA is a thrombopoietin receptor agonist indicated: for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult and pediatric patients 1 year and older with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy. PROMACTA should be used only in patients with ITP whose degree of thrombocytopenia and clinical condition increase the risk for bleeding.
Approved To Treat
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?
Related Clinical Trials
Early Initiation of Oral Therapy With Cyclosporine and Eltrombopag for Treatment Naive Severe Aplastic Anemia (SAA)
Background: Severe aplastic anemia (SAA) is a rare and serious blood disorder. It causes the immune system to turn against bone marrow cells. Standard treatment for SSA is a combination of 3 drugs (Cyclosporine \[CsA\], Eltrombopag \[EPAG\], and horse anti-thymocyte globulin \[h-ATG\]). Researchers want to see if starting people at a lower dose of CsA with EPAG before giving them h-ATG is helpful.
High Dose Ruxolitinib and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Myelofibrosis Patients With Splenomegaly
Summary: To learn if giving ruxolitinib and busulfan before a stem cell transplant can help to reduce spleen size and help the transplant to succeed.
Eltrombopag Induced Liver Dysfunction During Treatment of Immunethrombocytopenic Purpura
Summary: this study amis to assess the incidence and severity of liver dysfunction in ITP patients receiving eltrombopag.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
PROMACTA (eltrombopag olamine)
WARNING: RISK FOR HEPATIC DECOMPENSATION IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS C and RISK OF HEPATOTOXICITY
In patients with chronic hepatitis C, PROMACTA in combination with interferon and ribavirin may increase the risk of hepatic decompensation
PROMACTA may increase the risk of severe and potentially life-threatening hepatotoxicity. Monitor hepatic function and discontinue dosing as recommended
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets
- 12.5 mg tablets —– round, biconvex, white, film-coated tablets debossed with “GS MZ1” and 12.5 on one side. Each tablet, for oral administration, contains eltrombopag olamine, equivalent to 12.5 mg of eltrombopag free acid.
- 25 mg tablets —– round, biconvex, orange, film-coated tablets debossed with “GS NX3” and 25 on one side. Each tablet, for oral administration, contains eltrombopag olamine, equivalent to 25 mg of eltrombopag free acid.
- 50 mg tablets —– round, biconvex, blue, film-coated tablets debossed with “GS UFU” and 50 on one side. Each tablet, for oral administration, contains eltrombopag olamine, equivalent to 50 mg of eltrombopag free acid.
- 75 mg tablets —– round, biconvex, pink, film-coated tablets debossed with “GS FFS” and 75 on one side. Each tablet, for oral administration, contains eltrombopag olamine, equivalent to 75 mg of eltrombopag free acid.
For Oral Suspension
- 12.5 mg packet —– contains a reddish-brown to yellow powder for reconstitution.
- 25 mg packet —– contains a reddish-brown to yellow powder for reconstitution.
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions associated with PROMACTA are described in other sections.
- Hepatic Decompensation in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C
- Hepatotoxicity
- Increased Risk of Death and Progression of Myelodysplastic Syndromes to Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications
- Cataracts
3.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
Adults: In clinical trials, hemorrhage was the most common serious adverse reaction and most hemorrhagic reactions followed discontinuation of PROMACTA. Other serious adverse reactions included thrombotic/thromboembolic complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. The data described below reflect exposure of PROMACTA to patients with persistent or chronic ITP aged 18 to 85 years, of whom 66% were female, in three placebo-controlled trials and one open-label extension trial [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. PROMACTA was administered to 330 patients for at least 6 months and 218 patients for at least 1 year.
Table 8 presents the most common adverse drug reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 3% of patients receiving PROMACTA) from the three placebo-controlled trials, with a higher incidence in PROMACTA versus placebo.
In the three controlled clinical persistent or chronic ITP trials, alopecia, musculoskeletal pain, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, and dry mouth were the adverse reactions reported in 2% of patients treated with PROMACTA and in no patients who received placebo.
Among 302 patients with persistent or chronic ITP who received PROMACTA in the single-arm extension trial, the adverse reactions occurred in a pattern similar to that seen in the placebo-controlled trials. Table 9 presents the most common treatment-related adverse reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 3% of patients receiving PROMACTA) from the extension trial.
In the three controlled persistent or chronic ITP trials, serum liver test abnormalities (predominantly Grade 2 or less in severity) were reported in 11% and 7% of patients for PROMACTA and placebo, respectively. Four patients (1%) treated with PROMACTA and three patients in the placebo group (2%) discontinued treatment due to hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities. Seventeen of the patients treated with PROMACTA in the controlled trials with hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities were re-exposed to PROMACTA in the extension trial. Eight of these patients again experienced liver test abnormalities (less than or equal to Grade 3) resulting in discontinuation of PROMACTA in one patient. In the extension persistent or chronic ITP trial, six additional patients had PROMACTA discontinued due to liver test abnormalities (less than or equal to Grade 3).
In the three controlled persistent or chronic ITP trials, cataracts developed or worsened in 7% of patients treated with PROMACTA and 7% of patients in the placebo group. All patients had documented, preexisting risk factors for cataractogenesis, including corticosteroid use. In the extension trial, cataracts developed or worsened in 11% of patients who underwent ocular examination prior to therapy with PROMACTA. Seventy-two percent of patients had preexisting risk factors, including corticosteroid use.
The safety of PROMACTA was also assessed in all patients treated in 7 adult persistent or chronic ITP clinical trials (N = 763 PROMACTA-treated patients and 179 placebo-treated patients). Thromboembolic events were reported in 6% of PROMACTA-treated patients versus 0% of placebo-treated patients and thrombotic microangiopathy with acute renal failure was reported in < 1% of PROMACTA-treated patients versus 0% of placebo-treated patients.
In a placebo-controlled trial of PROMACTA in patients with chronic liver disease and thrombocytopenia not related to ITP, six patients treated with PROMACTA and one patient in the placebo group developed portal vein thromboses
Pediatric Patients: The data described below reflect median exposure to PROMACTA of 91 days for 107 pediatric patients (aged 1 to 17 years) with persistent or chronic ITP, of whom 53% were female, across the randomized phase of two placebo-controlled trials.
Table 10 presents the most common adverse drug reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 3% of pediatric patients 1 year and older receiving PROMACTA) across the two placebo-controlled trials, with a higher incidence for PROMACTA versus placebo.
In the two controlled clinical persistent or chronic ITP trials, cataracts developed or worsened in 2 (1%) patients treated with PROMACTA. Both patients had received chronic oral corticosteroids, a risk factor for cataractogenesis.
Chronic Hepatitis C-associated Thrombocytopenia: In the two placebo-controlled trials, 955 patients with chronic hepatitis C-associated thrombocytopenia received PROMACTA. Table 11 presents the most common adverse drug reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 10% of patients receiving PROMACTA compared with placebo).
Rash was reported in 9% and 7% of patients receiving PROMACTA and placebo, respectively.
In the two controlled clinical trials in patients with chronic hepatitis C, hyperbilirubinemia was reported in 8% of patients receiving PROMACTA compared with 3% for placebo. Total bilirubin greater than or equal to 1.5 x ULN was reported in 76% and 50% of patients receiving PROMACTA and placebo, respectively. ALT or AST greater than or equal to 3 x ULN was reported in 34% and 38% of patients for PROMACTA and placebo, respectively.
In the two controlled clinical trials in patients with chronic hepatitis C, cataracts developed or worsened in 8% of patients treated with PROMACTA and 5% of patients treated with placebo.
The safety of PROMACTA was also assessed in all patients treated with PROMACTA in the two controlled trials, including patients who initially received PROMACTA in the pre-antiviral treatment phase of the trial and were later randomized to the placebo arm (N = 1520 PROMACTA-treated patients). Hepatic failure was reported in 0.8% of PROMACTA-treated patients and 0.4% of placebo-treated patients.
Severe Aplastic Anemia
First-Line Treatment of Severe Aplastic Anemia
The safety of PROMACTA was established based upon a single-arm trial of 153 patients with severe aplastic anemia who had not received prior definitive immunosuppressive therapy. In this trial, PROMACTA was administered in combination with horse antithymocyte globulin (h-ATG) and cyclosporine
In this cohort, PROMACTA was administered at up to 150 mg once daily on Day 1 to Month 6 (D1-M6) in combination with h-ATG on Days 1 to 4 and cyclosporine for 6 months, followed by low dose of cyclosporine (maintenance dose) for an additional 18 months for patients who achieved a hematologic response at 6 months. The median duration of exposure to PROMACTA in this cohort was 183 days with 70% of patients exposed for > 24 weeks.
Table 12 presents the most common adverse reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 5% of patients) associated with PROMACTA in the D1-M6 cohort.
In the PROMACTA D1-M6 cohort, ALT increased (29%), AST increased (17%), and blood bilirubin increased (17%) were reported more frequently than in patients with refractory severe aplastic anemia (see Table 13).
New or worsening liver function laboratory abnormalities (CTCAE Grade 3 and Grade 4) in the PROMACTA D1-M6 cohort were 15% and 2% for AST, 26% and 4% for ALT, and 12% and 1% for bilirubin, respectively.
In this single-arm open-label clinical trial, ALT or AST > 3 x ULN with total bilirubin > 1.5 x ULN and ALT or AST > 3 x ULN with total bilirubin > 2 x ULN were reported in 44% and 32% of patients, respectively, in the PROMACTA D1-M6 cohort.
Pediatric Patients
A total of 34 pediatric patients (2 patients 2 to 5 years of age, 12 patients 6 to 11 years of age, and 20 patients 12 to 16 years of age) were enrolled in this single-arm trial of which 26 pediatric patients were enrolled in the PROMACTA D1-M6 cohort. In this cohort, the most frequent serious adverse reactions (experienced by ≥ 10% of patients) were upper respiratory tract infection (12% in patients age 2 to 16 years compared to 5% in patients 17 years of age and older, respectively) and rash (12% compared to 2%). The most common adverse reactions (experienced by ≥ 10% of patients) associated with PROMACTA were ALT increased (23% in patients age 2 to 16 years compared to 32% in patients 17 years of age and older, respectively), blood bilirubin increased (12% compared to 20%), AST increased (12% compared to 20%), and rash (12% compared to 6%).
Cytogenetic Abnormalities
In this trial, patients had bone marrow aspirates evaluated for cytogenetic abnormalities. Seven patients in the PROMACTA D1-M6 cohort had a new cytogenetic abnormality reported of which 4 had the loss of chromosome 7; these 4 occurred within 6.1 months. Across all cohorts, clonal cytogenetic evolution occurred in 15 out of 153 (10%) patients. Of the 15 patients who experienced a cytogenetic abnormality: 7 patients had the loss of chromosome 7, 6 of which occurred within 6.1 months; 4 patients had chromosomal aberrations which were of unclear significance; 3 patients had a deletion of chromosome 13; and 1 patient had a follow-up bone marrow assessment at 5 years with features of dysplasia with hypercellularity concerning for potential development of MDS. It is unclear whether these findings occurred due to the underlying disease, the immunosuppressive therapy, and/or treatment with PROMACTA.
Refractory Severe Aplastic Anemia
In the single-arm, open-label trial, 43 patients with refractory severe aplastic anemia received PROMACTA. Eleven patients (26%) were treated for greater than 6 months and 7 patients (16%) were treated for greater than 1 year. The most common adverse reactions (greater than or equal to 20%) were nausea, fatigue, cough, diarrhea, and headache.
Rash and hyperbilirubinemia were reported in 7% of patients; cataract was reported in 2% of patients.
In this trial, concurrent ALT or AST greater than 3 x ULN with total bilirubin greater than 1.5 x ULN were reported in 5% of patients. Total bilirubin greater than 1.5 x ULN occurred in 14% of patients.
In this trial, patients had bone marrow aspirates evaluated for cytogenetic abnormalities. Eight patients had a new cytogenetic abnormality reported on therapy, including 5 patients who had complex changes in chromosome 7.
3.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of PROMACTA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Skin discoloration, including hyperpigmentation and skin yellowing.
4OVERDOSAGE
In the event of overdose, platelet counts may increase excessively and result in thrombotic/thromboembolic complications.
In one report, a subject who ingested 5000 mg of PROMACTA had a platelet count increase to a maximum of 929 x 10
In case of an overdose, consider oral administration of a metal cation-containing preparation, such as calcium, aluminum, or magnesium preparations to chelate eltrombopag and thus limit absorption. Closely monitor platelet counts. Reinitiate treatment with PROMACTA in accordance with dosing and administration recommendations
5DESCRIPTION
PROMACTA (eltrombopag) tablets contain eltrombopag olamine, a small molecule thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist for oral administration.
Eltrombopag olamine is a biphenyl hydrazone. The chemical name for eltrombopag olamine is 3'-{(2Z)-2-[1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene]hydrazino}-2'-hydroxy-3-biphenylcarboxylic acid - 2-aminoethanol (1:2). It has the molecular formula C
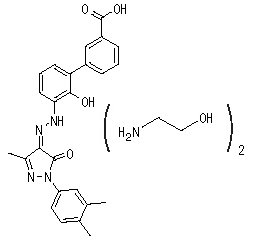
Eltrombopag olamine is practically insoluble in aqueous buffer across a pH range of 1 to 7.4, and is sparingly soluble in water.
PROMACTA (eltrombopag) tablets contain eltrombopag olamine in the amount equivalent to 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, or 75 mg of eltrombopag free acid. The inactive ingredients of PROMACTA tablets are:
Tablet Core: magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate.
Coating: FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake (50-mg tablet), FD&C Yellow No. 6 aluminum lake (25-mg tablet), hypromellose, Iron Oxide Black and Iron Oxide Red (75-mg tablet), polyethylene glycol 400, polysorbate 80 (12.5-mg tablet), or titanium dioxide.
Coating: FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake (50-mg tablet), FD&C Yellow No. 6 aluminum lake (25-mg tablet), hypromellose, Iron Oxide Black and Iron Oxide Red (75-mg tablet), polyethylene glycol 400, polysorbate 80 (12.5-mg tablet), or titanium dioxide.
PROMACTA (eltrombopag) for oral suspension packets contain a reddish-brown to yellow powder which produces a reddish-brown suspension when reconstituted with water. Each packet delivers eltrombopag olamine equivalent to 12.5 mg or 25 mg of eltrombopag free acid. The inactive ingredients of PROMACTA for oral suspension are mannitol, sucralose, and xanthan gum.
6PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Prior to treatment, patients should fully understand and be informed of the following risks and considerations for PROMACTA:
Risks
Hepatotoxicity
- Therapy with PROMACTA may be associated with hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities
- Advise patients with chronic hepatitis C and cirrhosis that they may be at risk for hepatic decompensation when receiving PROMACTA with alfa interferon therapy
- Advise patients that they should report any of the following signs and symptoms of liver problems to their healthcare provider right away
Risk of Bleeding Upon PROMACTA Discontinuation
- Advise patients that thrombocytopenia and risk of bleeding may reoccur upon discontinuing PROMACTA, particularly if PROMACTA is discontinued while the patient is on anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents. Advise patients that during therapy with PROMACTA, they should continue to avoid situations or medications that may increase the risk for bleeding.
Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications
- Advise patients that too much PROMACTA may result in excessive platelet counts and a risk for thrombotic/thromboembolic complications
Cataracts
- Advise patients to have a baseline ocular examination prior to administration of PROMACTA and be monitored for signs and symptoms of cataracts during therapy
Drug Interactions
- Advise patients to take PROMACTA at least 2 hours before or 4 hours after calcium-rich foods, mineral supplements, and antacids which contain polyvalent cations, such as iron, calcium, aluminum, magnesium, selenium, and zinc
Lactation
- Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with PROMACTA
Administration of PROMACTA
- For patients with persistent or chronic ITP, therapy with PROMACTA is administered to achieve and maintain a platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 10
- For patients with chronic hepatitis C, therapy with PROMACTA is administered to achieve and maintain a platelet count necessary to initiate and maintain antiviral therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin
- Advise patients to take PROMACTA without a meal or with a meal low in calcium (≤ 50 mg) and at least 2 hours before or 4 hours after other medications (e.g., antacids) and calcium-rich foods
- Prior to use of the oral suspension, ensure patients or caregivers receive training on proper dosing, preparation, and administration
- Inform patients or caregivers how many packets to administer to get the full dose
- Inform patients or caregivers to use a new oral dosing syringe to prepare each dose of PROMACTA for oral suspension
The following are registered trademarks of their respective owners: PEGASYS/Hoffmann-La Roche Inc.; PEGINTRON/Schering Corporation.
Distributed by:
© Novartis
T2025-27
7PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0684-15
Rx only
Promacta
Swallow tablets whole. Do not
Dispense with Medication Guide
NOVARTIS
30 Tablets

8PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0685-15
Rx only
Promacta
Swallow tablets whole. Do not
Dispense with Medication Guide
NOVARTIS
30 Tablets

9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0686-15
Rx only
Promacta
Swallow tablets whole. Do not
Dispense with Medication Guide
NOVARTIS
30 Tablets

10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0687-15
Rx only
Promacta
Swallow tablets whole. Do not
Dispense with Medication Guide
NOVARTIS
30 Tablets

11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0972-61
Rx only
Promacta
12.5 mg
Dispense with Medication Guide enclosed or provided separately.
30 Packets
NOVARTIS

12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-0697-61
Rx only
Promacta
25 mg
Dispense with Medication Guide enclosed or provided separately.
30 Packets
NOVARTIS




