Brand Name
Renacidin
Generic Name
Gluconolactone
View Brand Information FDA approval date: February 01, 2016
Classification: Anti-coagulant
Form: Solution
What is Renacidin (Gluconolactone)?
Renacidin is indicated for dissolution of bladder calculi of the struvite or apatite variety by local intermittent irrigation through a urethral catheter or cystostomy tube as an alternative or adjunct to surgical procedures. Renacidin is also indicated for use as an intermittent irrigating solution to prevent encrustations of indwelling urethral catheters and cystostomy tubes.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Tired of the same old research?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
Renacidin (citric acid, gluconolactone and magnesium carbonate)
1DESCRIPTION
Renacidin
Each 30 mL of Renacidin contains:
Active ingredients:
Citric Acid

Glucono delta-lactone

Magnesium Carbonate
(MgCO
Inert ingredients:
2CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Renacidin's action on susceptible apatite calculi results from an exchange of magnesium from the irrigating solution for calcium contained in the stone matrix. The magnesium salts thereby formed are soluble in the gluconocitrate irrigating solution resulting in the dissolution of the calculus. Struvite calculi are composed mainly of magnesium ammonium phosphates which are solubilized by Renacidin due to its acidic pH. Renacidin is not effective for dissolution of calcium oxalate, uric acid or cysteine stones.
3INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Renacidin is indicated for dissolution of bladder calculi of the struvite or apatite variety by local intermittent irrigation through a urethral catheter or cystostomy tube as an alternative or adjunct to surgical procedures.
Renacidin is also indicated for use as an intermittent irrigating solution to prevent encrustations of indwelling urethral catheters and cystostomy tubes.
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
Renacidin is contraindicated in the presence of demonstrable urinary tract extravasation.
5WARNINGS
Renacidin use should be stopped immediately if the patient develops fever, urinary tract infection, signs and symptoms consistent with urinary tract infection, or persistent flank pain. Irrigation should be stopped if elevated serum creatinine develops.
The contents of individual Renacidin containers should not be combined for use as continuous irrigation of the urinary tract because of complications that may arise from inadequate aseptic technique. Terminal sterilization processes that are not adequate may result in sepsis and/or injury to product handlers (e.g., irritation to exposed, unprotected areas of the skin).
Serious adverse reactions, including sepsis and hypermagnesemia, have been reported to occur when Renacidin was used for continuous irrigation of the upper urinary tract. Renacidin is not indicated for continuous irrigation of the upper urinary tract.
6ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions with use of Renacidin for dissolution of bladder calculi or prevention of encrustations of indwelling urethral catheters are “bladder irritability” and chemical cystitis, both reported to occur in approximately 3% of patients. A transient burning sensation in the bladder following Renacidin has been reported to occur in less than 1% of patients receiving Renacidin.
7DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Renacidin for local irrigation within the lower urinary tract is available in single-use 30 mL containers.
Prepare and Administer the Dose:
Step 1: Inspect Renacidin visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. If particulate matter or discoloration are observed, do not administer.
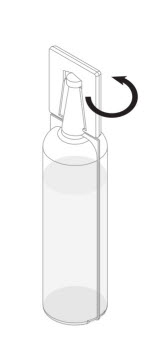
Step 2: Remove the plastic tab connected to the conical tip of the Renacidin container by twisting the plastic tab. See Figure 1.
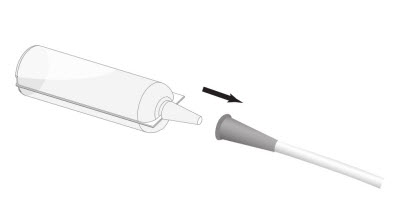
Step 3: Connect the conical tip of the Renacidin container to the end of the urethral catheter or cystostomy tube. See Figure 2.
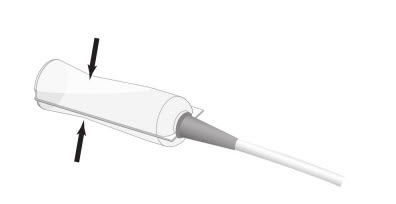
Step 4: Squeeze the Renacidin container to expel the entire contents into the urethral catheter or cystostomy tube. See Figure 3.
For Dissolution of Bladder Calculi: Instill 30 mL (one container) of Renacidin into the bladder via a urethral catheter or cystostomy tube. Clamp the urethral catheter or cystostomy tube for 30 to 60 minutes. Release the clamp and drain the bladder. Repeat the instillation procedure 4 to 6 times a day. Monitor for dissolution of calculi.
For Prevention of Encrustations in Urethral Catheters and Cystostomy Tubes: Instill 30 mL (one container) of Renacidin into the urethral catheter or cystostomy tube. Clamp the urethral catheter or cystostomy tube for 10 minutes. Remove the clamp and drain the bladder. Repeat the instillation procedure 3 times a day.
8HOW SUPPLIED
Renacidin is available as a sterile, non-pyrogenic irrigation solution in 30 mL single-use, low density, polyethylene containers, supplied in boxes of 30 containers each. Exposure of Renacidin to heat or cold should be minimized. Renacidin should be stored at room temperature, 59° to 86°F (15° to 30°C). Avoid excessive heat or cold (keep from freezing). Brief exposure to temperatures of up to 40°C or temperatures down to 5°C does not adversely affect the product.
NDC: 0327-0012-30
PRODUCT CODE: RN030
Revised: December, 2018

Manufactured for

9PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

NDC 0327-0012-30 Rx Only
RENACIDIN
For Urological Irrigation Only
For Urological Irrigation Only
Each 30 ml. contains:
Read accompanying package insert for complete instructions on use.
Box of thirty units – 30 ml. each
Made in U.S.A.
RENACIDIN
For Urological Irrigation Only
For Urological Irrigation Only
Manufactured for
GUARDIAN LABORATORIES
Rev. 3 - Dec 2018