Brand Name
Tikosyn
Generic Name
Dofetilide
View Brand Information FDA approval date: October 01, 1999
Classification: Antiarrhythmic
Form: Capsule
What is Tikosyn (Dofetilide)?
Maintenance of Normal Sinus Rhythm Dofetilide Capsules are indicated for the maintenance of normal sinus rhythm (delay in time to recurrence of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter ) in patients with atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter of greater than one week duration who have been converted to normal sinus rhythm. Because Dofetilide Capsules can cause life threatening ventricular arrhythmias, it should be reserved for patients in whom atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter is highly symptomatic. In general, antiarrhythmic therapy for atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter aims to prolong the time in normal sinus rhythm. Recurrence is expected in some patients. Conversion of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter Dofetilide Capsules are indicated for the conversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter to normal sinus rhythm. Dofetilide Capsules have not been shown to be effective in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
Tikosyn (dofetilide)
1DESCRIPTION
TIKOSYN
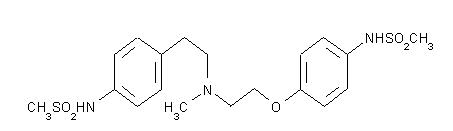
The chemical name for dofetilide is:
Dofetilide is a white to off-white powder. It is very slightly soluble in water and propan-2-ol and is soluble in 0.1M aqueous sodium hydroxide, acetone, and aqueous 0.1M hydrochloric acid.
TIKOSYN capsules contain the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch, colloidal silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate. TIKOSYN is supplied for oral administration in three dosage strengths: 125 mcg (0.125 mg) orange and white capsules, 250 mcg (0.25 mg) peach capsules, and 500 mcg (0.5 mg) peach and white capsules.
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
TIKOSYN is contraindicated in patients with congenital or acquired long QT syndromes. TIKOSYN should not be used in patients with a baseline QT interval or QTc >440 msec (500 msec in patients with ventricular conduction abnormalities). TIKOSYN is also contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (calculated creatinine clearance <20 mL/min).
The concomitant use of verapamil or the cation transport system inhibitors cimetidine, trimethoprim (alone or in combination with sulfamethoxazole), or ketoconazole with TIKOSYN is contraindicated (see
The concomitant use of hydrochlorothiazide (alone or in combinations such as with triamterene) with TIKOSYN is contraindicated (see
TIKOSYN is also contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug.
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The TIKOSYN clinical program involved approximately 8,600 patients in 130 clinical studies of normal volunteers and patients with supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias. TIKOSYN was administered to 5,194 patients, including two large, placebo-controlled mortality trials (DIAMOND CHF and DIAMOND MI) in which 1,511 patients received TIKOSYN for up to three years.
In the following section, adverse reaction data for cardiac arrhythmias and non-cardiac adverse reactions are presented separately for patients included in the supraventricular arrhythmia development program and for patients included in the DIAMOND CHF and MI mortality trials (see
In studies of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias, a total of 1,346 and 677 patients were exposed to TIKOSYN and placebo for 551 and 207 patient years, respectively. A total of 8.7% of patients in the dofetilide groups were discontinued from clinical trials due to adverse events compared to 8.0% in the placebo groups. The most frequent reason for discontinuation (>1%) was ventricular tachycardia (2.0% on dofetilide vs. 1.3% on placebo). The most frequent adverse events were headache, chest pain, and dizziness.
3.1Serious Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances:
Torsade de Pointes is the only arrhythmia that showed a dose-response relationship to TIKOSYN treatment. It did not occur in placebo treated patients. The incidence of Torsade de Pointes in patients with supraventricular arrhythmias was 0.8% (11/1346) (see
In the DIAMOND trials, a total of 1,511 patients were exposed to TIKOSYN for 1757 patient years. The incidence of Torsade de Pointes was 3.3% in CHF patients and 0.9% in patients with a recent MI.
Table 7 shows the incidence of serious arrhythmias and conduction disturbances reported as adverse events in the DIAMOND subpopulation that had AF at entry to these trials.
3.2Other Adverse Reactions:
Table 8 presents other adverse events reported with a frequency of >2% on TIKOSYN and reported numerically more frequently on TIKOSYN than on placebo in the studies of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias.
Adverse events reported at a rate >2% but no more frequently on TIKOSYN than on placebo were: angina pectoris, anxiety, arthralgia, asthenia, atrial fibrillation, complications (application, injection, incision, insertion, or device), hypertension, pain, palpitation, peripheral edema, supraventricular tachycardia, sweating, urinary tract infection, ventricular tachycardia.
The following adverse events have been reported with a frequency of ≤2% and numerically more frequently with TIKOSYN than placebo in patients with supraventricular arrhythmias: angioedema, bradycardia, cerebral ischemia, cerebrovascular accident, edema, facial paralysis, flaccid paralysis, heart arrest, increased cough, liver damage, migraine, myocardial infarct, paralysis, paresthesia, sudden death, and syncope.
The incidences of clinically significant laboratory test abnormalities in patients with supraventricular arrhythmias were similar for patients on TIKOSYN and those on placebo. No clinically relevant effects were noted in serum alkaline phosphatase, serum GGT, LDH, AST, ALT, total bilirubin, total protein, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, serum electrolytes (calcium, chloride, glucose, magnesium, potassium, sodium), or creatine kinase. Similarly, no clinically relevant effects were observed in hematologic parameters.
In the DIAMOND population, adverse events other than those related to the post-infarction and heart failure patient population were generally similar to those seen in the supraventricular arrhythmia groups.
4OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote to TIKOSYN; treatment of overdose should therefore be symptomatic and supportive. The most prominent manifestation of overdosage is likely to be excessive prolongation of the QT interval.
In cases of overdose, cardiac monitoring should be initiated. Charcoal slurry may be given soon after overdosing but has been useful only when given within 15 minutes of TIKOSYN administration. Treatment of Torsade de Pointes or overdose may include administration of isoproterenol infusion, with or without cardiac pacing. Administration of intravenous magnesium sulfate may be effective in the management of Torsade de Pointes. Close medical monitoring and supervision should continue until the QT interval returns to normal levels.
Isoproterenol infusion into anesthetized dogs with cardiac pacing rapidly attenuates the dofetilide-induced prolongation of atrial and ventricular effective refractory periods in a dose-dependent manner. Magnesium sulfate, administered prophylactically either intravenously or orally in a dog model, was effective in the prevention of dofetilide-induced Torsade de Pointes ventricular tachycardia. Similarly, in man, intravenous magnesium sulfate may terminate Torsade de Pointes, irrespective of cause.
TIKOSYN overdose was rare in clinical studies; there were two reported cases of TIKOSYN overdose in the oral clinical program. One patient received very high multiples of the recommended dose (28 capsules), was treated with gastric aspiration 30 minutes later, and experienced no events. One patient inadvertently received two 500 mcg doses one hour apart and experienced ventricular fibrillation and cardiac arrest 2 hours after the second dose.
In the supraventricular arrhythmia population, only 38 patients received doses greater than 500 mcg BID, all of whom received 750 mcg BID irrespective of creatinine clearance. In this very small patient population, the incidence of Torsade de Pointes was 10.5% (4/38 patients), and the incidence of new ventricular fibrillation was 2.6% (1/38 patients).
5DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Therapy with TIKOSYN must be initiated (and, if necessary, re-initiated) in a setting that provides continuous electrocardiographic (ECG) monitoring and in the presence of personnel trained in the management of serious ventricular arrhythmias. Patients should continue to be monitored in this way for a minimum of three days. Additionally, patients should not be discharged within 12 hours of electrical or pharmacological conversion to normal sinus rhythm.
- The dose of TIKOSYN must be individualized according to calculated creatinine clearance and QTc. (QT interval should be used if the heart rate is <60 beats per minute. There are no data on use of TIKOSYN when the heart rate is <50 beats per minute.) The usual recommended dose of TIKOSYN is 500 mcg BID, as modified by the dosing algorithm described below. For consideration of a lower dose, see Special Considerations below.
- Serum potassium should be maintained within the normal range before TIKOSYN treatment is initiated and should be maintained within the normal range while the patient remains on TIKOSYN therapy. (See
- Patients with atrial fibrillation should be anticoagulated according to usual medical practice prior to electrical or pharmacological cardioversion. Anticoagulant therapy may be continued after cardioversion according to usual medical practice for the treatment of people with AF. Hypokalemia should be corrected before initiation of TIKOSYN therapy (see
- Patients to be discharged on TIKOSYN therapy from an inpatient setting as described above must have an adequate supply of TIKOSYN, at the patient's individualized dose, to allow uninterrupted dosing until the patient can fill a TIKOSYN prescription.
5.1Switch to TIKOSYN from Class I or other Class III Antiarrhythmic Therapy
Before initiating TIKOSYN therapy, previous antiarrhythmic therapy should be withdrawn under careful monitoring for a minimum of three (3) plasma half-lives. Because of the unpredictable pharmacokinetics of amiodarone, TIKOSYN should not be initiated following amiodarone therapy until amiodarone plasma levels are below 0.3 mcg/mL or until amiodarone has been withdrawn for at least three months.
5.2Stopping TIKOSYN Prior to Administration of Potentially Interacting Drugs
If TIKOSYN needs to be discontinued to allow dosing of other potentially interacting drug(s), a washout period of at least two days should be followed before starting the other drug(s).
6HOW SUPPLIED
TIKOSYN
TIKOSYN
TIKOSYN
7MEDICATION GUIDE
TIKOSYN
(dofetilide) Capsules
(dofetilide) Capsules
Read the Medication Guide before you start taking TIKOSYN and each time you get a refill. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your condition or treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about TIKOSYN?
TIKOSYN can cause serious side effects, including a type of abnormal heartbeat called Torsade de Pointes, which can lead to death.
To establish the right dose of TIKOSYN, treatment with TIKOSYN must be started in a hospital where your heart rate and kidney function will be checked for the first 3 days of treatment. It is important that when you go home, you take the exact dose of TIKOSYN that your doctor prescribed for you.
While you take TIKOSYN, always watch for signs of abnormal heartbeat.
Call your doctor and go to the hospital right away if you:
- feel faint
- become dizzy, or
- have a fast heartbeat
What is TIKOSYN?
TIKOSYN is a prescription medicine that is used to treat an irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter).
It is not known if TIKOSYN is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age.
Who should not take TIKOSYN?
Do not take TIKOSYN if you:
- have an irregular heartbeat called long QT syndrome
- have kidney problems or are on kidney dialysis
- take any of these medicines:
- Ask your doctor if you are not sure if any of your medicines are the kind listed above.
- are allergic to dofetilide in TIKOSYN. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in TIKOSYN.
What should I tell my doctor before taking TIKOSYN?
Before taking TIKOSYN, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions including if you:
- have heart problems
- have kidney or liver problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if TIKOSYN will harm your unborn baby.
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if TIKOSYN passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take TIKOSYN or breast-feed. You should not do both.
Especially tell your doctor if you take medicines to treat:
- heart problems
- high blood pressure
- depression or other mental problems
- asthma
- allergies, or hay fever
- skin problems
- infections
Ask your doctor if you are not sure about the medicines you take. Tell your doctor about all prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, dietary supplements, and any natural or herbal remedies. TIKOSYN and other medicines may affect each other, causing serious side effects. If you take TIKOSYN with certain medicines, you will be more likely to have a different type of abnormal heartbeat. See "Who should not take TIKOSYN?"
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take TIKOSYN?
- Take TIKOSYN exactly as your doctor tells you.
- Do not change your TIKOSYN dose unless your doctor tells you to.
- Your doctor will do tests before you start and while you take TIKOSYN.
- Do not stop taking TIKOSYN until your doctor tells you to stop. If you miss a dose, just take the next dose at your regular time.
- TIKOSYN can be taken with or without food.
- If you take too much TIKOSYN, call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. Take your TIKOSYN capsules with you to show to the doctor.
What are the possible side effects of TIKOSYN?
TIKOSYN can cause serious side effects, including a type of abnormal heartbeat called Torsade de Pointes, which can lead to death. See "What is the most important information I should know about TIKOSYN?"
The most common side effects of TIKOSYN include:
- headache
- chest pain
- dizziness
Call your doctor right away if you have signs of electrolyte imbalance:
- severe diarrhea
- unusual sweating
- vomiting
- not hungry (loss of appetite)
- increased thirst (drinking more than normal)
Tell your doctor if you have any side effects that bother you or do not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of TIKOSYN. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store TIKOSYN?
- Store TIKOSYN between 59° to 86°F (15° to 30°C).
- Keep TIKOSYN away from moisture and humidity.
- Keep TIKOSYN in a tightly closed container.
- Keep TIKOSYN and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about TIKOSYN
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use TIKOSYN for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TIKOSYN to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about TIKOSYN. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about TIKOSYN that is written for health professionals.
For more about TIKOSYN, go to
What are the ingredients in TIKOSYN?
Active ingredient: dofetilide
Inactive ingredients:
- Capsule fill: microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate
- Capsule shell: gelatin, titanium dioxide, and FD&C Yellow 6
- Imprinting ink: iron oxide black, shellac, n-butyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and ammonium hydroxide
8PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.125 mg Capsule Bottle Label
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) Capsules
125 mcg (0.125 mg)
60 Capsules

9PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.125 mg Capsule Blister Pack
FOR INSTITUTION USE
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) Capsule
125mcg (0.125mg)
PFIZER LABS
LOT: XXXXXXX

10PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.125 mg Capsule Blister Pack Carton
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) capsules
125 mcg (0.125 mg)
For in-institution use only
40 Capsules
Rx only

11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.25 mg Capsule Bottle Label
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) Capsules
250 mcg (0.25 mg)
60 Capsules

12PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.25 mg Capsule Blister Pack
FOR INSTITUTION USE
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) Capsule
250mcg (0.25mg)
PFIZER LABS
LOT: XXXXXXX

13PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.25 mg Capsule Blister Pack Carton
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) capsules
250 mcg (0.25 mg)
For in-institution use only
40 Capsules
Rx only

14PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.5 mg Capsule Bottle Label
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) Capsules
500 mcg (0.5 mg)
60 Capsules

15PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.5 mg Capsule Blister Pack
FOR INSTITUTION USE
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) Capsule
500mcg (0.5mg)
PFIZER LABS
LOT: XXXXXXX

16PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.5 mg Capsule Blister Pack Carton
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
Tikosyn
(dofetilide) capsules
500 mcg (0.5 mg)
For in-institution use only
40 Capsules
Rx only
