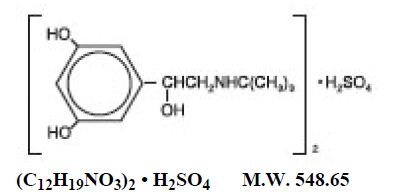
Terbutaline
View Brand InformationWhat is Terbutaline?
For people living with asthma or chronic lung diseases, few things are more frightening than struggling to catch a breath. Coughing, wheezing, or chest tightness can make daily life unpredictable and exhausting. Terbutaline is a medication designed to bring relief and restore control. It helps open the airways, making breathing easier and more comfortable for those affected by asthma, bronchitis, or other breathing disorders.
Terbutaline belongs to a group of drugs called beta₂-adrenergic agonists. These medications work by relaxing the muscles in the airways, allowing more air to move in and out of the lungs. It can be used as a bronchodilator to manage or prevent bronchospasm (narrowing of the airways) in conditions such as asthma, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis. While newer inhalers have become more common, terbutaline remains an important treatment option, especially for patients who need short-term or oral bronchodilator therapy.
What does Terbutaline do?
Terbutaline helps relieve and prevent bronchospasm, the tightening of airway muscles that makes it hard to breathe. It is prescribed for people with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or other lung disorders where airways become constricted.
When taken as directed, terbutaline helps:
- Reduce coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath
- Improve airflow and oxygen delivery
- Make it easier to perform daily activities without feeling breathless
Terbutaline works as a rescue or maintenance medication, depending on how it is prescribed. For some patients, it’s used as a short-term treatment to stop sudden breathing problems. For others, especially those who cannot use inhalers effectively, it may be taken regularly in oral form to maintain airway openness.
Studies and clinical experience have shown that terbutaline effectively increases lung function within minutes of use and continues to provide relief for several hours (NIH, 2024). Its quick onset makes it a reliable choice for managing acute symptoms when used under medical supervision.
How does Terbutaline work?
Terbutaline works by stimulating beta₂ receptors located in the smooth muscles of the airways. These receptors respond by relaxing the muscles, causing the airways to widen, a process known as bronchodilation.
In asthma or COPD, inflammation and muscle tightening reduce the diameter of the airways, trapping air in the lungs and making it difficult to exhale. By activating these receptors, terbutaline helps reverse this narrowing, allowing air to flow freely.
This mechanism provides rapid relief from shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest tightness. Clinically, it’s valuable because it restores airflow quickly and helps prevent severe asthma attacks or COPD flare-ups that might otherwise require emergency care.
Additionally, terbutaline has mild effects on other parts of the body, such as relaxing uterine muscles, which is why it was once used in hospitals to delay premature labor. However, this use is now limited and generally avoided outside specific, short-term medical settings due to potential side effects.
Terbutaline side effects
Like all medications, terbutaline can cause side effects, though many are mild and temporary. Because it stimulates beta receptors throughout the body, some effects are related to increased heart rate and nervous system activity.
Common side effects include:
- Shakiness or tremors (especially in the hands)
- Nervousness or restlessness
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
Less common but serious side effects may include:
- Chest pain or irregular heartbeat
- Severe dizziness or fainting
- Muscle cramps or weakness
- Allergic reactions such as rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing
If any of these serious effects occur, patients should seek medical attention immediately.
Terbutaline should be used with caution in people who have:
- Heart disease or arrhythmias
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes (since it may raise blood sugar levels)
- Seizure disorders or overactive thyroid
Your healthcare provider will assess your medical history to determine whether terbutaline is safe and appropriate for you. Most people tolerate the medication well, and any side effects often decrease as the body adjusts to treatment.
Terbutaline dosage
Terbutaline comes as tablets, injections, or inhalation solutions, chosen based on patient need. Tablets are for maintenance, inhalers for quick relief, and injections for emergencies. Dosage is physician-adjusted; do not self-increase to avoid side effects like irregular heartbeat.
Doctors monitor heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar in older adults or those with chronic illnesses during terbutaline treatment to ensure effectiveness and prevent complications. Adherence to dosage and follow-up appointments is crucial for safe and effective treatment adjustments.
Does Terbutaline have a generic version?
Yes. Terbutaline is available as a generic medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Generic terbutaline contains the same active ingredient, strength, and quality as brand-name versions such as Brethine and Bricanyl (available in some countries).
Generic drugs are safe, effective, and often cheaper, increasing treatment accessibility. Patients can confidently use prescribed generic versions. In the U.S., terbutaline is mainly available as tablets and injections; inhalants are less common now due to newer options.
Conclusion
Terbutaline remains a valuable and reliable bronchodilator for managing asthma, COPD, and other breathing disorders. By relaxing the airway muscles, it provides quick relief from symptoms like wheezing and breathlessness, helping patients breathe more freely and comfortably.
Terbutaline remains important for acute symptom control and when inhalers aren’t suitable. Used correctly under medical supervision, it is safe and effective. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key. Report side effects, follow dosing, and ask questions. With proper use, terbutaline can significantly improve breathing and confidence.
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Terbutaline (oral route, injection route) drug information. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Terbutaline: Uses, side effects, and precautions. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2023). Terbutaline sulfate drug label information. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2024). Beta-agonist bronchodilators in asthma and COPD treatment. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information

Fresenius Kabi
