Savaysa
What is Savaysa (edoxaban tosylate)?
Blood clots are a serious health concern that can lead to life-threatening events like strokes, heart attacks, or pulmonary embolisms. For many people living with conditions that increase clot risk, maintaining healthy blood flow isn’t just about comfort—it’s about survival. Savaysa (edoxaban tosylate) is a medication that helps prevent these dangerous clots from forming, offering patients protection and peace of mind in their daily lives.
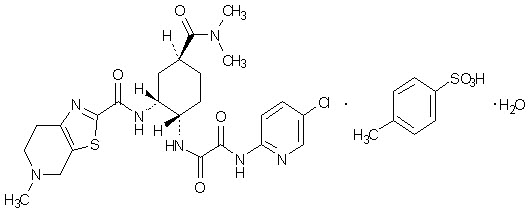
Savaysa is an oral anticoagulant, or “blood thinner,” belonging to a class of drugs known as factor Xa inhibitors. It is used to reduce the risk of stroke and blood clots in people with certain types of irregular heartbeats and to treat or prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2015, Savaysa is part of a newer generation of anticoagulants that offer a simpler, more predictable alternative to traditional therapies like warfarin.
What does Savaysa do?
Savaysa helps prevent the formation of harmful blood clots in the veins and arteries. It is prescribed for adults with:
- Nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib): an irregular heart rhythm that can cause blood to pool and clot in the heart, increasing the risk of stroke.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): a blood clot that forms in deep veins, typically in the legs.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE): a clot that travels to the lungs, which can be life-threatening.
By reducing the blood’s tendency to clot, Savaysa lowers the risk of stroke, recurrent DVT, and PE, helping patients lead safer, more active lives.
In clinical studies, Savaysa was shown to be as effective as warfarin in preventing strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation, with a lower risk of major bleeding in some cases (FDA, 2024). This makes it a strong and reliable option for long-term anticoagulation therapy.
How does Savaysa work?
Savaysa contains edoxaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor. Factor Xa is a key enzyme in the body’s natural clotting process, it helps produce thrombin, which in turn helps form blood clots. By blocking factor Xa, Savaysa slows the formation of thrombin, preventing new clots from forming and stopping existing ones from getting larger.
This mechanism provides a more targeted and consistent anticoagulant effect than older drugs like warfarin, which require frequent blood testing and dietary restrictions.
From a clinical perspective, this is significant because it allows patients to maintain stable anticoagulation without constant monitoring, helping reduce anxiety and improving adherence to treatment. However, doctors still monitor kidney function and other health parameters to ensure the medication remains safe and effective over time.
Savaysa side effects
Like all anticoagulants, Savaysa can increase the risk of bleeding, since it works by reducing the blood’s ability to clot. While most side effects are mild, it’s important for patients and caregivers to recognize the signs of more serious complications.
Common side effects may include:
- Easy bruising or prolonged bleeding from minor cuts
- Nosebleeds
- Mild anemia (fatigue or pale skin)
- Upset stomach or nausea
Serious side effects (seek medical help immediately):
- Unexpected or severe bleeding (such as vomiting blood or passing black, tarry stools)
- Severe headache, dizziness, or weakness (possible internal bleeding)
- Signs of allergic reaction such as rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing
Because Savaysa affects blood clotting, it should not be used in patients with active bleeding, mechanical heart valves, or certain types of severe kidney disease.
Patients should inform their doctor if they have liver problems, a history of bleeding disorders, or if they take other medications that affect clotting such as aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or other anticoagulants.
Reassuringly, for most patients, Savaysa’s side effects are manageable under proper medical supervision. Its predictable dosing and lower dietary impact make it easier to live a normal, active lifestyle while maintaining effective stroke and clot prevention.
Savaysa dosage
Savaysa is an oral tablet taken once daily, with the dose adjusted based on kidney function, body weight, and the condition treated. For atrial fibrillation, excellent kidney function may reduce effectiveness, requiring an alternative. It also treats DVT and PE, often following injectable anticoagulants.
Doctors regularly check kidney and liver function, especially in older adults or those with chronic conditions, to ensure proper medication processing and reduce bleeding risks. Patients should never abruptly stop Savaysa without consulting a healthcare provider, as this can increase the risk of clots or stroke.
Does Savaysa have a generic version?
As of 2025, Savaysa (edoxaban tosylate) does not yet have a generic version approved by the U.S. FDA. It is currently available only as the brand-name product manufactured by Daiichi Sankyo, Inc. However, international versions may exist in other markets.
A generic version of Savaysa must have the same active ingredient, strength, safety, and effectiveness. Patients can inquire about financial aid for brand-name Savaysa. Savaysa, Eliquis (apixaban), and Xarelto (rivaroxaban) are modern anticoagulants, and doctors may consider these options based on patient profiles and budgets.
Conclusion
Savaysa is a modern, effective oral anticoagulant designed to reduce the risk of stroke and blood clots in people with atrial fibrillation and to treat or prevent DVT and PE. By directly inhibiting factor Xa, it provides predictable and steady blood thinning without the dietary limitations or frequent monitoring required by older medications like warfarin.
Savaysa, a convenient and effective blood thinner, manages bleeding risks under professional care. Regular checkups, open communication about side effects, and adherence to dosing ensure successful treatment, offering patients greater confidence and control against clot-related complications.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2024). Savaysa (edoxaban) prescribing information. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Edoxaban (oral route) drug information. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Edoxaban: Uses, side effects, and precautions. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2024). Anticoagulants and blood clot prevention overview. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: Multinational, investigator-initiated study of oral anticoagulation versus no anticoagulation for the prevention of stroke and other adverse cardiovascular events in patients with transient perioperative atrial fibrillation after noncardiac surgery and additional stroke risk factors.
Summary: The present trial is addressing the question if a biologically distinct subgroup of ischemic stroke patients without known atrial fibrillation at admission, selected by a cut-off level of MRproANP concentration, which represents a underlying increased risk of cardiac thrombogenicity, benefits from direct oral anticoagulation (DOAC) within 7 days of symptom onset versus standard of care (antiplatel...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- 60 mg, yellow round shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with DSC L60 on one side
- 30 mg, pink round shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with DSC L30 on one side
- 15 mg, orange round shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with DSC L15 on one side
- Active pathological bleeding
- Increased Risk of Stroke with Discontinuation of SAVAYSA in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
- Risk of Bleeding
- Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia or Puncture