Cefaclor
View Brand InformationWhat is Cefaclor?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: Cephalosporin antibiotics are commonly used but can result in allergic reactions and anaphylaxis. There is no clear diagnostic approach for cephalosporin-allergic patients, and guidance for the use of other antibiotics in allergic patients is based on side chain chemical similarity and limited skin testing evidence. This project includes a clinical trial and mechanistic studies to optimize the app...
Summary: Non-inferiority trial to determine whether partial oral treatment is non-inferior to OPAT(Outpatient parenteral therapy) in patients diagnosed with infective endocarditis
Summary: This study is non-inferiority trial design. This study aimed to investigate the effect of prophylactic oral antibiotics on preventing cholangitis in biliary atresia (BA) patients after Kasai portoenterostomy (KP) by comparing the cholangitis rate in BA patients who received prophylactic oral antibiotics and those who did not. The patients were followed up for 2 years after KP.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
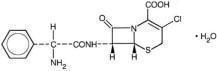
As with other cephalosporins, the bactericidal action of cefaclor results from inhibition of cell-wall synthesis.
Cefaclor has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
Gram-positive Bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin susceptible only)
Coagulase negative staphylococci (methicillin susceptible only)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pyogenes (group A β-hemolytic streptococci)
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae (excluding β-lactamase-negative, ampicillin-resistant strains)
Klebsiella spp.
Proteus mirabilis
Citrobacter diversus
Moraxella catarrhalis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Bacteroides spp.
Peptococcus spp.
Peptostreptococcus spp.
Propionibacterium acnes
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
Yung Shin Pharmaceutical Ind. Co., Ltd.
Tachia, Taichung 43769
TAIWAN
Distributed by:
5922 Farnsworth Court,
Carlsbad, CA 92008, USA