Generic Name
Moxifloxacin
Brand Names
Vigamox, Strenza
FDA approval date: May 07, 2003
Classification: Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial
Form: Injection, Tablet, Kit, Solution
What is Vigamox (Moxifloxacin)?
Moxifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial indicated for treating infections in adults 18 years of age and older caused by designated susceptible bacteria, in the conditions listed below: Community Acquired Pneumonia.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
VIGAMOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride)
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
VIGAMOX
Corynebacteriumspecies*
Micrococcus luteus*
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus haemolyticus
Staphylococcus hominis
Staphylococcus warneri*
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus viridansgroup
Acinetobacter lwoffii*
Haemophilus influenza
Haemophilus parainfluenzae*
Chlamydia trachomatis
Micrococcus luteus*
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus haemolyticus
Staphylococcus hominis
Staphylococcus warneri*
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus viridansgroup
Acinetobacter lwoffii*
Haemophilus influenza
Haemophilus parainfluenzae*
Chlamydia trachomatis
*Efficacy for this organism was studied in fewer than 10 infections.
2DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Instill one drop in the affected eye 3 times a day for 7 days. VIGAMOX is for topical ophthalmic use.
3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ophthalmic solution containing moxifloxacin 0.5%.
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
VIGAMOX is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to moxifloxacin, to other quinolones, or to any of the components in this medication.
5ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most frequently reported ocular adverse events were conjunctivitis, decreased visual acuity, dry eye, keratitis, ocular discomfort, ocular hyperemia, ocular pain, ocular pruritus, subconjunctival hemorrhage, and tearing. These events occurred in approximately 1%-6% of patients.
Nonocular adverse events reported at a rate of 1%-4% were fever, increased cough, infection, otitis media, pharyngitis, rash, and rhinitis.
6DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drug-drug interaction studies have not been conducted with VIGAMOX
7DESCRIPTION
VIGAMOX (moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is a sterile solution for topical ophthalmic use. Moxifloxacin hydrochloride is an 8-methoxy fluoroquinolone anti-infective, with a diazabicyclononyl ring at the C7 position. The chemical name for moxifloxacin hydrochloride is 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-[(4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-pyrrolol[3,4b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid, monohydrochloride. The molecular formula for moxifloxacin hydrochloride is C
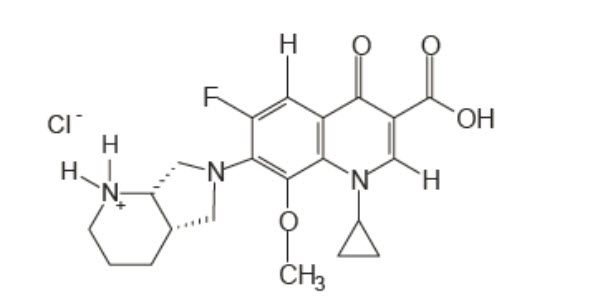
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride is a slightly yellow to yellow crystalline powder.
Each mL of VIGAMOX solution contains 5.45 mg moxifloxacin hydrochloride, equivalent to 5 mg moxifloxacin base. VIGAMOX contains
VIGAMOX
8CLINICAL STUDIES
In two randomized, double-masked, multicenter, controlled clinical trials in which patients were dosed 3 times a day for 4 days, VIGAMOX
In a randomized, double-masked, multicenter, parallel-group clinical trial of pediatric patients with bacterial conjunctivitis between birth and 31 days of age, patients were dosed with VIGAMOX or another anti-infective agent. Clinical outcomes for the trial demonstrated a clinical cure rate of 80% at Day 9 and a microbiological eradication success rate of 92% at Day 9.
Please note that microbiologic eradication does not always correlate with clinical outcome in anti-infective trials.
9HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
VIGAMOX
3 mL in a 4 mL bottle NDC 82667-700-03
Storage: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F).
10PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Avoid Contamination of the Product
Advise patients not to touch the dropper tip to any surface to avoid contaminating the contents.
Avoid Contact Lens Wear
Advise patients not to wear contact lenses if they have signs and symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Systemically administered quinolones including moxifloxacin have been associated with hypersensitivity reactions, even following a single dose. Instruct patients to discontinue use immediately and contact their physician at the first sign of a rash or allergic reaction
11PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 82667-700-03
STERILE
VIGAMOX
(moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution)
3 mL
HARROW
