Generic Name
Dabigatran Etexilate
Brand Names
Dabigatran, Pradaxa
FDA approval date: August 08, 2011
Classification: Direct Thrombin Inhibitor
Form: Pellet, Capsule
What is Dabigatran (Dabigatran Etexilate)?
Dabigatran etexilate capsules are direct thrombin inhibitor indicated: To reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
There are no experts for this drug
Save this treatment for later
Not sure about your diagnosis?
Related Clinical Trials
There is no clinical trials being done for this treatment
Related Latest Advances
There is no latest advances for this treatment
Brand Information
DABIGATRAN (DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE)
WARNING: (A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF DABIGATRAN INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS, and (B) SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA
(A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF DABIGATRAN INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS
Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including dabigatran, increases the risk of thrombotic events. If anticoagulation with dabigatran is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant
Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients treated with dabigatran who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis. Consider these risks when scheduling patients for spinal procedures. Factors that can increase the risk of developing epidural or spinal hematomas in these patients include:
1DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
150 mg capsules with a white to light yellow colored blend compressing granular powder, pellets in size “0” capsule having white opaque cap imprinted “MD” and white opaque body imprinted with “150” with black ink.
2CONTRAINDICATIONS
Dabigatran is contraindicated in patients with:
3ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
3.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Drug Discontinuation in RE-LY
The rates of adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation were 21% for dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg and 16% for warfarin. The most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of dabigatran etexilate capsules were bleeding and gastrointestinal events (i.e., dyspepsia, nausea, upper abdominal pain, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and diarrhea).
Bleeding [see
Table 3 shows the number of adjudicated major bleeding events during the treatment period in the RE-LY study, with the bleeding rate per 100 subject-years (%). Major bleeding is defined as bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥2 g/dL, a transfusion of ≥2 units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site or with a fatal outcome. Intracranial hemorrhage included intracerebral (hemorrhagic stroke), subarachnoid, and subdural bleeds.
Table 3 Adjudicated Major Bleeding Events in Treated Patientsa
The rates of adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation were 21% for dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg and 16% for warfarin. The most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of dabigatran etexilate capsules were bleeding and gastrointestinal events (i.e., dyspepsia, nausea, upper abdominal pain, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and diarrhea).
Bleeding [see
Table 3 shows the number of adjudicated major bleeding events during the treatment period in the RE-LY study, with the bleeding rate per 100 subject-years (%). Major bleeding is defined as bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥2 g/dL, a transfusion of ≥2 units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site or with a fatal outcome. Intracranial hemorrhage included intracerebral (hemorrhagic stroke), subarachnoid, and subdural bleeds.
Table 3 Adjudicated Major Bleeding Events in Treated Patientsa
a Patients during treatment or within 2 days of stopping study treatment. Major bleeding events within each subcategory were counted once per patient, but patients may have contributed events to multiple subcategories.
bAnnual event rate per 100 pt-years = 100 * number of subjects with event/subject-years. Subject-years is defined as cumulative number of days from first drug intake to event date, date of last drug intake + 2, death date (whatever occurred first) across all treated subjects divided by 365.25. In case of recurrent events of the same category, the first event was considered.
c Defined as bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥ 2 g/dL, a transfusion of 2 or more units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site or with fatal outcome.
d Intracranial bleed included intracerebral (hemorrhagic stroke), subarachnoid, and subdural bleeds.
e On-treatment analysis based on the safety population, compared to ITT analysis presented in Section 14 Clinical Studies.
f Fatal bleed: Adjudicated major bleed as defined above with investigator reported fatal outcome and adjudicated death with primary cause from bleeding.
g Non-intracranial fatal bleed: Adjudicated major bleed as defined above and adjudicated death with primary cause from bleeding but without symptomatic intracranial bleed based on investigator’s clinical assessment.
There was a higher rate of any gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg than in patients receiving warfarin (6.6% vs 4.2%, respectively).
The risk of major bleeds was similar with dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg and warfarin across major subgroups defined by baseline characteristics (see Figure 1), with the exception of age, where there was a trend toward a higher incidence of major bleeding on dabigatran etexilate capsules (hazard ratio 1.2, 95% CI: 1.0 to 1.5) for patients ≥75 years of age.
Figure 1 Adjudicated Major Bleeding by Baseline Characteristics Including Hemorrhagic Stroke Treated Patients
bAnnual event rate per 100 pt-years = 100 * number of subjects with event/subject-years. Subject-years is defined as cumulative number of days from first drug intake to event date, date of last drug intake + 2, death date (whatever occurred first) across all treated subjects divided by 365.25. In case of recurrent events of the same category, the first event was considered.
c Defined as bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥ 2 g/dL, a transfusion of 2 or more units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site or with fatal outcome.
d Intracranial bleed included intracerebral (hemorrhagic stroke), subarachnoid, and subdural bleeds.
e On-treatment analysis based on the safety population, compared to ITT analysis presented in Section 14 Clinical Studies.
f Fatal bleed: Adjudicated major bleed as defined above with investigator reported fatal outcome and adjudicated death with primary cause from bleeding.
g Non-intracranial fatal bleed: Adjudicated major bleed as defined above and adjudicated death with primary cause from bleeding but without symptomatic intracranial bleed based on investigator’s clinical assessment.
There was a higher rate of any gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg than in patients receiving warfarin (6.6% vs 4.2%, respectively).
The risk of major bleeds was similar with dabigatran etexilate capsules 150 mg and warfarin across major subgroups defined by baseline characteristics (see Figure 1), with the exception of age, where there was a trend toward a higher incidence of major bleeding on dabigatran etexilate capsules (hazard ratio 1.2, 95% CI: 1.0 to 1.5) for patients ≥75 years of age.
Figure 1 Adjudicated Major Bleeding by Baseline Characteristics Including Hemorrhagic Stroke Treated Patients
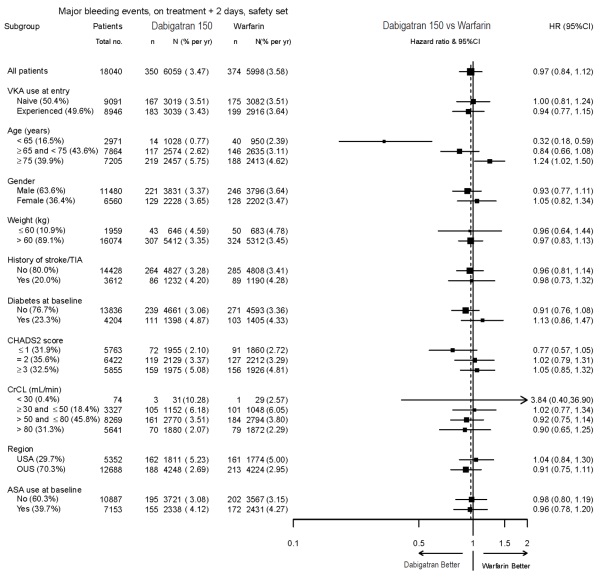
Note: The figure above presents effects in various subgroups all of which are baseline characteristics and all of which were pre-specified. The 95% confidence limits that are shown do not take into account how many comparisons were made, nor do they reflect the effect of a particular factor after adjustment for all other factors. Apparent homogeneity or heterogeneity among groups should not be over-interpreted.
Note: MBE can belong to more than one criterion.
Note: MBE can belong to more than one criterion.
Note: MBE can belong to more than one criterion.
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Following Hip Replacement Surgery Dabigatran etexilate capsules was studied in 5,476 patients, randomized and treated in two double-blind, active-controlled non-inferiority trials (RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II). The demographic characteristics were similar across the two studies and between the treatment groups within these studies. Approximately 45.3% of the treated patients were male, with a mean age of 63.2 years. The majority of the patients were white (96.1%), 3.6% were Asian, and 0.3% were black with a mean CrCl of 92 mL/min.
Bleeding events for the RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II studies were classified as major bleeding events if at least one of the following criteria applied: fatal bleeding, symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ (intraocular, intracranial, intraspinal or retroperitoneal bleeding), bleeding causing a fall in hemoglobin level of 2.0 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more, or leading to transfusion of 2 or more units of whole blood or red cells, requiring treatment cessation or leading to re-operation.
The RE-NOVATE study compared dabigatran etexilate capsules 75 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 150 mg once daily, dabigatran etexilate capsules 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg once daily and subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. The RE-NOVATE II study compared dabigatran etexilate capsules 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg once daily and subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. In the RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II studies, patients received 28-35 days of dabigatran etexilate capsules or enoxaparin with median exposure of 33 days. Tables 7 and 8 show the number of patients experiencing bleeding events in the analysis of RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II.
Table 7 Bleeding Events in RE-NOVATE Treated Patients
Bleeding events for the RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II studies were classified as major bleeding events if at least one of the following criteria applied: fatal bleeding, symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ (intraocular, intracranial, intraspinal or retroperitoneal bleeding), bleeding causing a fall in hemoglobin level of 2.0 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more, or leading to transfusion of 2 or more units of whole blood or red cells, requiring treatment cessation or leading to re-operation.
The RE-NOVATE study compared dabigatran etexilate capsules 75 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 150 mg once daily, dabigatran etexilate capsules 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg once daily and subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. The RE-NOVATE II study compared dabigatran etexilate capsules 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg once daily and subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. In the RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II studies, patients received 28-35 days of dabigatran etexilate capsules or enoxaparin with median exposure of 33 days. Tables 7 and 8 show the number of patients experiencing bleeding events in the analysis of RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II.
Table 7 Bleeding Events in RE-NOVATE Treated Patients
Table 8 Bleeding Events in RE-NOVATE II Treated Patients
In the two studies, the rate of major gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving dabigatran etexilate capsules and enoxaparin was the same (0.1%) and for any gastrointestinal bleeds was 1.4% for dabigatran etexilate capsules 220 mg and 0.9% for enoxaparin.
Pediatric use information is approved for Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s Pradaxa (dabigatran etexilate) capsules. However, due to Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.
3.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of dabigatran. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Agranulocytosis, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Esophageal ulcer
Immune System Disorders: Angioedema
Renal and Urinary Disorders: Anticoagulant-related nephropathy
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Alopecia
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Esophageal ulcer
Immune System Disorders: Angioedema
Renal and Urinary Disorders: Anticoagulant-related nephropathy
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Alopecia
4OVERDOSAGE
Accidental overdose may lead to hemorrhagic complications. In the event of hemorrhagic complications, initiate appropriate clinical support, discontinue treatment with dabigatran, and investigate the source of bleeding. A specific reversal agent (idarucizumab) is available for adult patients.
5DESCRIPTION
The chemical name for dabigatran etexilate mesylate, a direct thrombin inhibitor, is β-Alanine,N-[[2-[[[4-[[[(hexyloxy)carbonyl]amino]iminomethyl]phenyl]amino]methyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl]carbonyl]-N-2-pyridinyl-,ethyl ester, methanesulfonate. The molecular formula is C
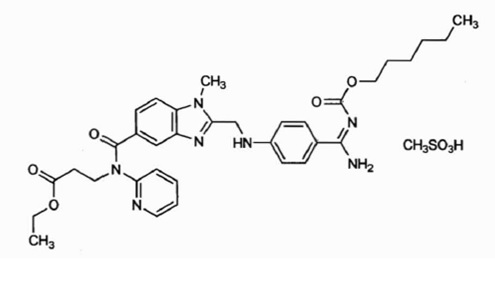
Dabigatran etexilate mesylate is a yellow-white to yellow powder. It is freely soluble in methanol, soluble in ethanol, and practically insoluble in ethyl acetate.
6HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Dabigatran etexilate capsules 75 mg capsules have a white to light yellow colored blend compressing granular powder, pellets in size “2” capsule having white opaque cap imprinted “MD” and white opaque body imprinted with “75” with black ink. The capsules are supplied in the packages listed:
Bottles
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Once opened, the product must be used within 4 months. Keep the bottle tightly closed. Store in the original package to protect from moisture.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Once opened, the product must be used within 4 months. Keep the bottle tightly closed. Store in the original package to protect from moisture.
Keep out of the reach of children.
7PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
- Tell patients to take dabigatran etexilate capsules exactly as prescribed.
- Remind patients not to discontinue dabigatran etexilate capsules without talking to the healthcare provider who prescribed it.
- Keep dabigatran etexilate capsules in the original bottle to protect from moisture. Do not put dabigatran etexilate capsules in pill boxes or pill organizers.
- When more than one bottle is dispensed to the patient, instruct them to open only one bottle at a time.
- Instruct patient to remove only one capsule from the opened bottle at the time of use. The bottle should be immediately and tightly closed.
- Advise patients not to chew or break the capsules before swallowing them and not to open the capsules and take the pellets alone.
- Advise patients that the capsule should be taken with a full glass of water.
[see Boxed Warning,
Bleeding
Inform patients that they may bleed more easily, may bleed longer, and should call their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms of bleeding
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Instruct patients to seek emergency care right away if they have any of the following, which may be a sign or symptom of serious bleeding:
• Unusual bruising (bruises that appear without known cause or that get bigger)
• Pink or brown urine
• Red or black, tarry stools
• Coughing up blood
• Vomiting blood, or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
Instruct patients to call their healthcare provider or to get prompt medical attention if they experience any signs or symptoms of bleeding:
• Pain, swelling or discomfort in a joint
• Headaches, dizziness, or weakness
• Reoccurring nose bleeds
• Unusual bleeding from gums
• Bleeding from a cut that takes a long time to stop
• Menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
If patients have had neuraxial anesthesia or spinal puncture, and particularly, if they are taking concomitant NSAIDs or platelet inhibitors, advise patients to watch for signs and symptoms of spinal or epidural hematoma, such as back pain, tingling, numbness (especially in the lower limbs), muscle weakness, and stool or urine incontinence. If any of these symptoms occur, advise the patient to contact his or her physician immediately [see
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Instruct patients to call their healthcare provider if they experience any signs or symptoms of dyspepsia or gastritis:
Bleeding
Inform patients that they may bleed more easily, may bleed longer, and should call their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms of bleeding
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Instruct patients to seek emergency care right away if they have any of the following, which may be a sign or symptom of serious bleeding:
• Unusual bruising (bruises that appear without known cause or that get bigger)
• Pink or brown urine
• Red or black, tarry stools
• Coughing up blood
• Vomiting blood, or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
Instruct patients to call their healthcare provider or to get prompt medical attention if they experience any signs or symptoms of bleeding:
• Pain, swelling or discomfort in a joint
• Headaches, dizziness, or weakness
• Reoccurring nose bleeds
• Unusual bleeding from gums
• Bleeding from a cut that takes a long time to stop
• Menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
If patients have had neuraxial anesthesia or spinal puncture, and particularly, if they are taking concomitant NSAIDs or platelet inhibitors, advise patients to watch for signs and symptoms of spinal or epidural hematoma, such as back pain, tingling, numbness (especially in the lower limbs), muscle weakness, and stool or urine incontinence. If any of these symptoms occur, advise the patient to contact his or her physician immediately [see
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Instruct patients to call their healthcare provider if they experience any signs or symptoms of dyspepsia or gastritis:
- Dyspepsia (upset stomach), burning, or nausea
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Epigastric discomfort, GERD (gastric indigestion)
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
Invasive or Surgical Procedures
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider that they are taking dabigatran before any invasive procedure (including dental procedures) is scheduled [see
Concomitant Medications
Ask patients to list all prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, or dietary supplements they are taking or plan to take so their healthcare provider knows about other treatments that may affect bleeding risk (e.g., aspirin or NSAIDs) or dabigatran exposure (e.g., dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole) [
Prosthetic Heart Valves
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they will have or have had surgery to place a prosthetic heart valve [
Invasive or Surgical Procedures
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider that they are taking dabigatran before any invasive procedure (including dental procedures) is scheduled [see
Concomitant Medications
Ask patients to list all prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, or dietary supplements they are taking or plan to take so their healthcare provider knows about other treatments that may affect bleeding risk (e.g., aspirin or NSAIDs) or dabigatran exposure (e.g., dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole) [
Prosthetic Heart Valves
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they will have or have had surgery to place a prosthetic heart valve [
Allergic Reactions
Advise adult patients and caregivers that some adults taking dabigatran have developed symptoms of an allergic reaction. Advise adult patients or caregivers to inform their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as hives, rash, or itching. Advise adult patients or caregivers to seek emergency medical attention if they develop chest pain or tightness, swelling of the face or tongue, trouble breathing or wheezing, or feeling dizzy or faint.
Pregnancy
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with dabigatran [
Lactation
Advise patients not to breastfeed if they are taking dabigatran etexilate capsules [
Pediatric use information is approved for Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s Pradaxa (dabigatran etexilate) capsules. However, due to Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.
Advise adult patients and caregivers that some adults taking dabigatran have developed symptoms of an allergic reaction. Advise adult patients or caregivers to inform their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as hives, rash, or itching. Advise adult patients or caregivers to seek emergency medical attention if they develop chest pain or tightness, swelling of the face or tongue, trouble breathing or wheezing, or feeling dizzy or faint.
Pregnancy
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with dabigatran [
Lactation
Advise patients not to breastfeed if they are taking dabigatran etexilate capsules [
Pediatric use information is approved for Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s Pradaxa (dabigatran etexilate) capsules. However, due to Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.
Manufactured by:
8PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

