Brevibloc
What is Brevibloc (Esmolol)?
Approved To Treat
Top Global Experts
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: 1. Pain management is a crucial part of general anesthesia surgery. Nociception monitoring can help anesthesiologists better titrate the use of intraoperative analgesic drugs, especially the opioid. 2. Although a variety of nociception monitoring devices have been developed to date, there is not a specific monitoring indicator that serves as the gold standard to objectively guide analgesic managem...
Summary: Chronic mitral regurgitation is the most common valvular abnormality worldwide, it occurs in 10% of the general population and its prevalence increases with age. When left untreated, it can lead to left ventricular dysfunction and cause disabling symptoms (e.g., fatigue and dyspnea), life-threatening complications (e.g., ventricular dilation, congestive heart failure) and death. Surgical correctio...
Summary: Large ischemic stroke is a severe subtype of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), often leading to malignant cerebral edema, elevated intracranial pressure, and poor functional outcomes. Despite early aggressive treatment, malignant cerebral edema remains a major determinant of prognosis, even in cases of successful recanalization. Preclinical studies suggest that a pharmacological cocktail (PPA) may alle...
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
- Severe sinus bradycardia: May precipitate or worsen bradycardia resulting in cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest
- Heart block greater than first degree: Second- or third-degree atrioventricular block may precipitate or worsen bradycardia resulting in cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest
- Sick sinus syndrome: May precipitate or worsen bradycardia resulting in cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest
- Decompensated heart failure: May worsen heart failure.
- Cardiogenic shock: May precipitate further cardiovascular collapse and cause cardiac arrest.
- IV administration of cardiodepressant calcium-channel antagonists (e.g., verapamil) and BREVIBLOC injection in close proximity (i.e., while cardiac effects from the other are still present); fatal cardiac arrests have occurred in patients receiving BREVIBLOC injection and intravenous verapamil.
- Pulmonary hypertension: May precipitate cardiorespiratory compromise.
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, to esmolol or any of the inactive ingredients of the product (cross-sensitivity between beta blockers is possible).
- Digitalis glycosides: Concomitant administration of digoxin and BREVIBLOC injection leads to an approximate 10% to 20% increase of digoxin blood levels at some time points. Digoxin does not affect BREVIBLOC injection pharmacokinetics. Both digoxin and beta blockers slow atrioventricular conduction and decrease heart rate. Concomitant use increases the risk of bradycardia.
- Anticholinesterases: BREVIBLOC injection prolonged the duration of succinylcholine-induced neuromuscular blockade and moderately prolonged clinical duration and recovery index of mivacurium.
- Antihypertensive agents clonidine, guanfacine, or moxonidine: Beta blockers also increase the risk of clonidine-, guanfacine-, or moxonidine-withdrawal rebound hypertension. If, during concomitant use of a beta blocker, antihypertensive therapy needs to be interrupted or discontinued, discontinue the beta blocker first, and the discontinuation should be gradual.
- Calcium channel antagonists: In patients with depressed myocardial function, use of BREVIBLOC injection with cardiodepressant calcium channel antagonists (e.g., verapamil) can lead to fatal cardiac arrests.
- Sympathomimetic drugs: Sympathomimetic drugs having beta-adrenergic agonist activity will counteract effects of BREVIBLOC injection.
- Vasoconstrictive and positive inotropic agents: Because of the risk of reducing cardiac contractility in presence of high systemic vascular resistance, do not use BREVIBLOC injection to control tachycardia in patients receiving drugs that are vasoconstrictive and have positive inotropic effects, such as epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
- (±)-Methyl p-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino) propoxy] hydrocinnamate hydrochloride and has the following structure:
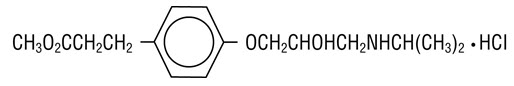
- Esmolol hydrochloride has the empirical formula C
- Esmolol hydrochloride is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is a relatively hydrophilic compound which is very soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. Its partition coefficient (octanol/water) at pH 7.0 is 0.42 compared to 17.0 for propranolol.
- The most common adverse reactions are symptomatic hypotension (hyperhidrosis, dizziness) and asymptomatic hypotension.
- Inform patients or caregivers that there is a risk of hypoglycemia when esmolol is given to patients who are fasting or who are vomiting. Monitor for symptoms of hypoglycemia.

INFORMATION
CONTAINER FIRMLY IF LEAKS ARE FOUND DISCARD AS
STERILITY MAY BE IMPAIRED USE ONLY IF SOLUTION IS
CLEAR COLORLESS TO LIGHT YELLOW

CAUTIONS CHECK FOR LE AKS BY SQUEEZING CONTAINER FIRMLY
IF LEAKS ARE FOUND DISCARD AS STERILITY MAY BE IMPAIRED USE
ONLY IF SOLUTION IS CLEAR COLORLESS TO LIGHT YELLOW DISCARD
UNUSED PORTION
DO NOT INTRODUCE ADDITIVESMUST NOT BE USED IN SERIES CONNECTIONS
STORE AT 25°C (77°F) EXCURSIONS PERMITTED TO 15°-30°C




